
How to Choose Pad Mounted Transformer?
Table of Contents Selecting the right pad-mounted transformer requires careful consideration of several critical
ELECTRIC, WITH AN EDGE
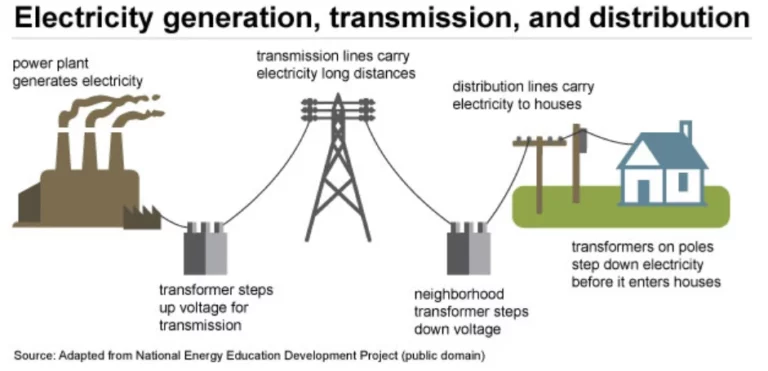
If you are a practitioner in the power industry, whether you are a builder or a transformer wholesaler, you will want to know what the distribution of the different voltage levels in the United States is like. What are the main areas where each voltage level is located? This article explains specifically the high voltage transmission lines, medium voltage transmission lines, and low voltage transmission lines throughout the United States. You can view the content outline and select the responding cities to see the distribution of their transmission lines and learn more about the electric power transmission.
The three main types of transmission lines in the United States include: high-voltage transmission lines, medium transmission line voltage, and low-voltage transmission lines.
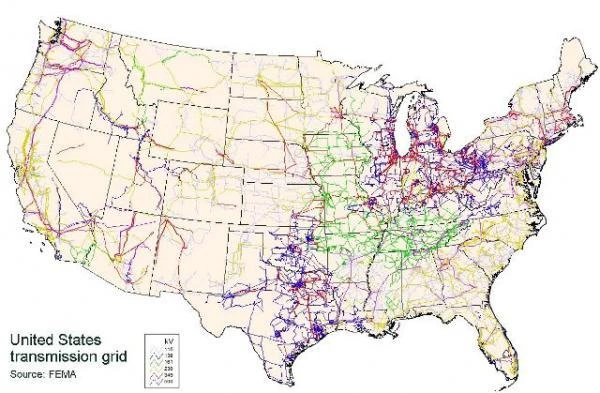
Renewable energy integration and high-voltage transmission lines are essential to support the United States’ transition to a more sustainable and low-carbon energy future. These lines play a vital role in connecting large-scale renewable energy projects, such as wind farms and solar installations, to the electric grid:
An essential north-south transmission corridor in California, Path 15 connects power generation resources in the Pacific Northwest and in-state renewable energy resources with high-demand areas like San Francisco and Los Angeles. The line operates at 500 kV and is subject to regulations by the California Independent System Operator (CAISO), the CPUC, and FERC.
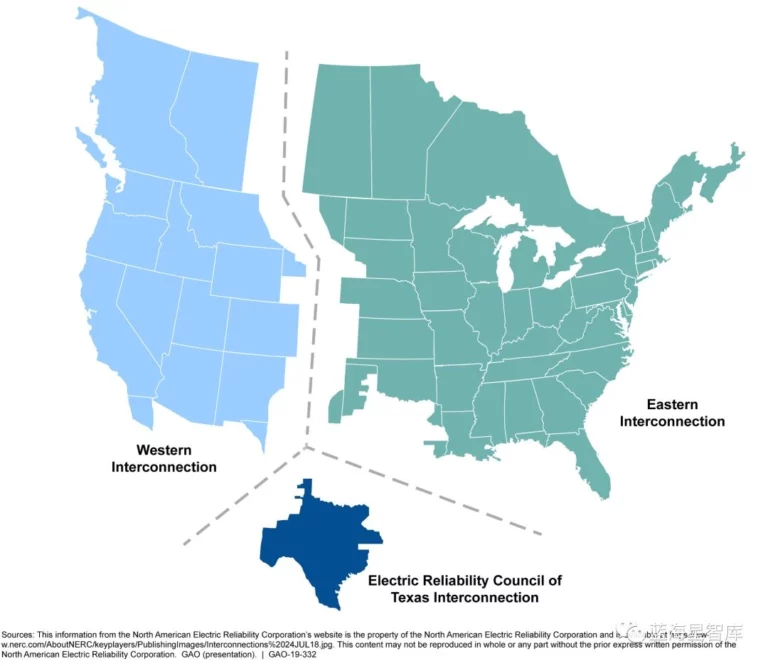
The Eastern Interconnection is a massive high-voltage transmission Lines network that spans from the east coast to the Rocky Mountains. It connects major population centers like New York City, Chicago, Atlanta, and Washington, D.C., with power generation resources across the region. The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) and regional transmission organizations (RTOs) such as PJM Interconnection and the New York Independent System Operator (NYISO) oversee the operations and reliability of this interconnected system.
The SPP is a regional transmission organization that manages the high-voltage transmission lines network across 14 states in the central United States, including Kansas, Oklahoma, and Nebraska. This network connects major power generation resources, such as wind farms in Oklahoma and Kansas, with high-demand areas like Kansas City, Wichita, and Tulsa. The SPP works closely with FERC, NERC, and state PUCs to ensure the reliability, efficiency, and affordability of electricity for consumers in the region.
WAPA is a federal agency responsible for marketing and transmitting electricity from federally owned hydroelectric dams across 15 western states. The high-voltage transmission lines under WAPA’s jurisdiction connect power generation resources in the Rocky Mountain region and the Columbia River Basin with high-demand areas like Denver, Phoenix, and Las Vegas. WAPA operates in coordination with regional entities like the Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC) and state PUCs to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Also known as the Tres Amigas project, Path 66 is a proposed high-voltage transmission line that would connect the Eastern, Western, and Texas Interconnections. This ambitious project aims to enhance the transfer of renewable energy resources, such as wind power from the Great Plains and solar power from the Southwest, to high-demand areas across the country. The project would require collaboration between multiple state and federal regulatory agencies, including FERC, NERC, and regional transmission organizations like SPP, CAISO, and ERCOT.
The AWC is a proposed offshore high-voltage transmission line that would connect offshore wind farms along the East Coast from New Jersey to Virginia. This project would help states in the region achieve their renewable energy goals and reduce their reliance on fossil fuels. The AWC would require coordination between FERC, the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management (BOEM), and state regulatory agencies like the New Jersey Board of Public Utilities and the Virginia State Corporation Commission.
The TransWest Express is a proposed high-voltage transmission line that would connect wind power resources in Wyoming to high-demand areas in California, Nevada, and Arizona. This project is designed to help states meet their renewable energy goals and support the growing demand for electricity from the increasing adoption of EVs. The project will require collaboration between multiple state and federal regulatory agencies, including FERC, the Bureau of Land Management (BLM), and regional transmission organizations like CAISO and WECC.
The Plains & Eastern Clean Line is another proposed high-voltage transmission line that would transport wind power from the Oklahoma Panhandle region to markets in the Southeastern United States. This project aims to support the growing demand for clean energy and help states in the region achieve their renewable energy and carbon reduction goals. The project will require coordination between FERC, DOE, state regulatory agencies, and regional transmission organizations like SPP and SERC Reliability Corporation.
The SunZia project is a proposed high-voltage transmission line that would connect renewable energy resources in New Mexico and Arizona to markets in the Desert Southwest. This project aims to enhance the electric grid’s capacity and reliability while supporting the growth of renewable energy in the region. The project will require collaboration between multiple state and federal regulatory agencies, including FERC, BLM, and regional transmission organizations like WECC and CAISO.
The SOO Green HVDC Link is a proposed high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission line that would transport wind energy from the Upper Midwest to markets in the East. This project aims to increase grid reliability and help states in the Eastern United States achieve their renewable energy goals. The project will require coordination between FERC, state regulatory agencies, and regional transmission organizations like MISO and PJM Interconnection.
The Pacific DC Intertie is an existing high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission line connecting the Pacific Northwest with Southern California. This line plays a critical role in balancing the electric grid by enabling the transfer of surplus hydroelectric power from the north to high-demand areas in the south. The integration of energy storage solutions along the line could enhance grid reliability and flexibility further. Regulatory agencies like FERC, BPA, and regional transmission organizations like CAISO and WECC, must collaborate to support such initiatives.
The Eastern HVDC Link is a proposed high-voltage transmission line that would connect offshore wind farms along the Eastern Seaboard of the United States. This project would not only help states achieve their renewable energy goals but also support the integration of grid-scale energy storage solutions to manage the intermittent nature of wind power. Regulatory agencies like FERC, BOEM, and regional transmission organizations like PJM Interconnection and ISO New England, will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The Tres Amigas SuperStation is a proposed high-voltage transmission hub that aims to interconnect the Eastern, Western, and Texas Interconnections in the United States, creating a more flexible and resilient national grid. By enabling the transfer of power between these three separate grid systems, Tres Amigas could help integrate renewable energy resources and support the deployment of advanced grid technologies like microgrids and energy storage solutions. The project will require collaboration among FERC, state regulatory agencies, and regional transmission organizations like WECC, SPP, and ERCOT.
The Atlantic Wind Connection is a proposed offshore transmission system that would connect multiple offshore wind farms along the Eastern Seaboard to the onshore electric grid. This project could not only support the growth of renewable energy but also help integrate microgrids and smart grid technologies to improve grid reliability and resilience. Regulatory agencies like FERC, BOEM, and regional transmission organizations like PJM Interconnection and ISO New England, will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The Plains & Eastern Clean Line is a proposed high-voltage transmission line that would transport wind energy from the Oklahoma Panhandle to load centers in the Southeastern United States. This project could help states meet their renewable portfolio standards (RPS) and contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Regulatory agencies like FERC and regional transmission organizations like SPP and SERC will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The SunZia Southwest Transmission Project is a proposed High Voltage Electrical Lines that would connect renewable energy resources, primarily wind and solar, in New Mexico and Arizona to population centers in the Desert Southwest. This project could help states meet their RPS goals and promote regional grid reliability. Regulatory agencies like FERC, BLM, and regional transmission organizations like WECC, will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The TransWest Express Transmission Project is a proposed high-voltage lines designed to transport wind energy from Wyoming to the Desert Southwest. This project can help meet the increasing demand for renewable energy and contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Regulatory agencies like FERC and regional transmission organizations like WECC will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The Western Spirit Clean Line is a proposed High Voltage Line that would transport wind energy from New Mexico to western markets. This project could help states meet their renewable energy goals and promote regional grid reliability. Regulatory agencies like FERC, BLM, and regional transmission organizations like WECC will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
A high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission line running from the Pacific Northwest (Oregon and Washington) to Southern California. This transmission line allows for the transfer of electricity generated by hydroelectric dams in the Pacific Northwest to high-demand areas like Los Angeles.
A network of High voltage power lines in Texas that connect remote wind farms in the western part of the state to major population centers like Dallas, Austin, and San Antonio.
The Grain Belt Express Clean Line is a proposed high-voltage transmission line designed to transport wind energy from Kansas to the eastern United States. This project can help meet the increasing demand for renewable energy and contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Regulatory agencies like FERC and regional transmission organizations like SPP and MISO will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The Boardman to Hemingway Transmission Line is a proposed High Voltage Transmission Lines designed to connect renewable energy resources, primarily wind and solar, in eastern Oregon to load centers in Idaho. This project can help meet the increasing demand for renewable energy and contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Regulatory agencies like FERC, BLM, and regional transmission organizations like WECC and BPA will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The Mountain West Transmission Group (MWTG) is a collaboration of electricity service providers in the western United States working to improve and expand high-voltage lines infrastructure. The MWTG aims to increase renewable energy integration, enhance grid reliability, and support the western energy market. Regulatory agencies like FERC and regional transmission organizations like WECC will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The Atlantic Wind Connection is a proposed high-voltage transmission line that would connect offshore wind energy resources along the mid-Atlantic coast to onshore grid infrastructure. This project could help states meet their renewable energy goals and promote regional grid reliability. Regulatory agencies like FERC, BOEM, and regional transmission organizations like PJM Interconnection will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The Northern Pass Transmission is a proposed High Voltage Line that would transport hydropower from Quebec, Canada, to New Hampshire, providing clean energy to New England. This project could help states meet their renewable energy goals and promote regional grid reliability. Regulatory agencies like FERC, NEB, and regional transmission organizations like ISO-NE will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The New England Clean Energy Connect is a proposed high-voltage transmission line that would transport hydropower from Quebec, Canada, to Maine, providing clean energy to New England. This project could help states meet their renewable energy goals and promote regional grid reliability. Regulatory agencies like FERC, NEB, and regional transmission organizations like ISO-NE will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The SunZia Southwest Transmission Project is a proposed High voltage power lines designed to connect renewable energy resources, primarily wind and solar, in New Mexico and Arizona to load centers in the Desert Southwest. This project can help meet the increasing demand for renewable energy and contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Regulatory agencies like FERC, BLM, and regional transmission organizations like WECC will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The Plains & Eastern Clean Line is a proposed high-voltage transmission line that would transport wind energy from Oklahoma to load centers in the southeastern United States. This project could help states meet their renewable energy goals and promote regional grid reliability. Regulatory agencies like FERC and regional transmission organizations like SPP and SERC will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The SOO Green HVDC Link is a proposed high-voltage transmission line that would connect wind energy resources in the Upper Midwest to load centers in the eastern United States. This project could enhance grid reliability and help states meet their renewable energy goals. Regulatory agencies like FERC and regional transmission organizations like MISO and PJM Interconnection will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The Champlain Hudson Power Express is a proposed high-voltage transmission line that would transport hydropower from Quebec, Canada, to New York City, providing clean energy to the northeastern United States. This project could help states meet their renewable energy goals and promote regional grid reliability. Regulatory agencies like FERC, NEB, and regional transmission organizations like NYISO and ISO-NE will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The TransWest Express Transmission Project is a proposed high-voltage transmission line designed to connect renewable energy resources, primarily wind and solar, in Wyoming to load centers in the Desert Southwest. This project can help meet the increasing demand for renewable energy and contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Regulatory agencies like FERC, BLM, and regional transmission organizations like WECC will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The Centennial West Clean Line is a proposed high voltage power lines that would transport wind energy from New Mexico and Arizona to load centers in California. This project could help states meet their renewable energy goals and promote regional grid reliability. Regulatory agencies like FERC and regional transmission organizations like WECC and CAISO will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The Seams Elimination Cost Allocation Policy (SECAP) is a proposal by regional transmission organizations like MISO and PJM Interconnection to upgrade high voltage power lines, which would facilitate the integration of renewable energy resources across their combined service territories. This project could improve grid reliability and help states meet their renewable energy goals. Regulatory agencies like FERC will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The Icebreaker Wind Project is a proposed offshore wind energy project in Lake Erie, Ohio. A high-voltage transmission line would connect the offshore wind farm to the onshore grid, providing clean energy to the Great Lakes region. This project could help states meet their renewable energy goals and promote regional grid reliability. Regulatory agencies like FERC, BOEM, and regional transmission organizations like PJM Interconnection will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The Hampton-Rochester-La Crosse Transmission Line is a high-voltage transmission line that connects wind energy resources in Minnesota and Wisconsin to load centers in the Midwestern United States. This project helps states meet their renewable energy goals and promotes regional grid reliability. Regulatory agencies like FERC and regional transmission organizations like MISO will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
The Energia Sierra Juarez Transmission Line is a high-voltage transmission line that connects wind energy resources in Baja California, Mexico, to load centers in California. This project helps states meet their renewable energy goals and promotes regional grid reliability. Regulatory agencies like FERC and regional transmission organizations like CAISO and CENACE will play a crucial role in enabling such projects.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit。Ut elit tellus、luctus nec ullamcorper mattis、pulvinar dapibus leo。
medium transmission line voltage also play an important role in connecting smaller-scale renewable energy projects to the grid and ensuring that clean energy can be reliably delivered to local communities:
In Michigan, medium voltage sub-transmission lines serve the automotive industry and other manufacturing sectors in cities like Detroit, Grand Rapids, and Flint.
In Ohio, medium voltage sub-transmission lines support the state’s manufacturing, chemical, and automotive industries in cities like Cleveland, Cincinnati, and Toledo.
The expansion and modernization of medium-voltage subtransmission lines across the United States are not limited to specific cities or states. Numerous other regions are also working on similar projects to enhance their grid capabilities and accommodate the growing demand for renewable energy resources. Some additional examples include:
The city of Chicago relies on medium voltage sub-transmission lines to deliver electricity to commercial and industrial sectors, including the financial district and manufacturing plants. The Illinois Commerce Commission (ICC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, while the PJM Interconnection manages the regional grid and wholesale electricity market.
Ann Arbor’s medium-voltage subtransmission network must support the city’s growing focus on clean energy and climate resilience. The integration of small-scale renewable energy resources like community solar projects and small hydroelectric plants can enhance the reliability and sustainability of the local grid. The Michigan Public Service Commission (MPSC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, and the Midcontinent Independent System Operator (MISO) manages the regional grid and wholesale electricity market.
Austin requires a medium-voltage subtransmission infrastructure capable of supporting the integration of renewable energy resources and local clean energy initiatives. These resources can help improve grid reliability and resilience, as well as support the growing demand for clean electricity from the city’s residents and businesses. The Public Utility Commission of Texas (PUCT) regulates the state’s electric utilities, and the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) ensures the reliability of the regional grid.
As a hub for the oil and gas industry and home to the Texas Medical Center, Houston requires a reliable medium voltage sub-transmission network. The PUCT and ERCOT oversee the reliability and operations of the state’s electric grid and enforce regulations related to power generation and transmission.
As a major metropolitan area with a strong concentration of universities, research institutions, and technology companies, Boston requires a reliable medium voltage sub-transmission network. The Massachusetts Department of Public Utilities (DPU) oversees the state’s electric utilities, while the ISO New England manages the regional grid and wholesale electricity market.
As the second-largest city in the United States, Los Angeles relies on medium voltage sub-transmission lines to serve a diverse range of end-users, from residential customers to the entertainment industry. The CPUC regulates the state’s electric utilities, and CAISO manages the regional grid and wholesale electricity market.
Salt Lake City has a growing tech industry and a strong focus on renewable energy. The city’s medium voltage sub-transmission network must be able to handle the increasing demand from these sectors while also integrating renewable energy resources like solar and wind power. The Utah Public Service Commission regulates the state’s electric utilities, and the WECC ensures the reliability of the regional grid.
Portland is known for its commitment to sustainability and renewable energy. The city’s medium voltage sub-transmission infrastructure must support its growing population and the integration of renewable resources, such as wind and solar power. The Oregon Public Utility Commission regulates the state’s electric utilities, while the BPA manages the transmission of electricity from hydroelectric dams in the Pacific Northwest.
Raleigh is a fast-growing city with a strong focus on clean energy and innovation. The city’s medium voltage sub-transmission network needs to support the growing demand for electricity from the expanding tech sector, while also integrating distributed energy resources like rooftop solar panels and energy storage systems. The North Carolina Utilities Commission (NCUC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, and the SERC Reliability Corporation ensures the reliability of the regional grid.
Indianapolis is home to a diverse range of industries, including pharmaceuticals, automotive, and logistics. The city’s medium voltage sub-transmission infrastructure must support these sectors’ electricity needs and accommodate the integration of renewable energy resources and the increasing adoption of EVs. The Indiana Utility Regulatory Commission (IURC) oversees the state’s electric utilities, while MISO manages the regional grid and wholesale electricity market.
San Francisco is a global hub for innovation and technology, with a strong focus on sustainability and clean energy. The city’s medium voltage sub-transmission network must support the growing demand for electricity from the expanding tech sector, while also integrating DERs like rooftop solar panels, energy storage systems, and microgrids. The CPUC regulates the state’s electric utilities, and CAISO manages the regional grid and wholesale electricity market.
Detroit, the historical heart of the American automotive industry, is now pivoting towards electric vehicle manufacturing and clean energy technologies. The city’s medium voltage sub-transmission infrastructure must support the electricity needs of these industries, accommodate the increasing adoption of EVs, and integrate renewable energy resources. The Michigan Public Service Commission (MPSC) oversees the state’s electric utilities, while MISO manages the regional grid and wholesale electricity market.
Seattle, with its focus on sustainability and renewable energy, requires a medium voltage sub-transmission network capable of supporting energy storage solutions and demand response programs. These technologies will help balance the electric grid, optimize energy consumption, and manage peak demand periods. The Washington Utilities and Transportation Commission (WUTC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, and BPA oversees transmission operations in the Pacific Northwest.
New Orleans’ medium voltage sub-transmission infrastructure must support the city’s recovery from natural disasters and adapt to the changing climate. Integrating energy storage solutions and demand response programs can help enhance grid reliability and resilience. The Louisiana Public Service Commission (LPSC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, while the SERC Reliability Corporation ensures the reliability of the regional grid.
Boston’s medium voltage sub-transmission network must support the city’s growing focus on clean energy, climate resilience, and smart city technologies. The integration of microgrids and smart grid technologies can enhance the reliability and efficiency of the local grid, while also supporting the increasing adoption of EVs and DERs. The Massachusetts Department of Public Utilities (DPU) regulates the state’s electric utilities, and ISO New England manages the regional grid and wholesale electricity market.
Austin, a hub for technology and innovation, requires a medium voltage sub-transmission infrastructure capable of supporting the integration of microgrids, smart grid technologies, and renewable energy resources. These advancements can help improve grid reliability and resilience, as well as support the growing demand for electricity from the expanding tech sector. The Public Utility Commission of Texas (PUCT) regulates the state’s electric utilities, and ERCOT manages the regional grid and wholesale electricity market.
Montpelier’s medium-voltage subtransmission network must support the city’s growing focus on clean energy and climate resilience. The integration of small-scale renewable energy resources like community solar projects and small hydroelectric plants can enhance the reliability and sustainability of the local grid. The Vermont Public Utility Commission (VPUC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, and ISO New England manages the regional grid and wholesale electricity market.
Madison requires a medium-voltage subtransmission infrastructure capable of supporting the integration of renewable energy resources and local clean energy initiatives. These resources can help improve grid reliability and resilience, as well as support the growing demand for clean electricity from the city’s residents and businesses. The Public Service Commission of Wisconsin (PSCW) regulates the state’s electric utilities, and MISO ensures the reliability of the regional grid.
Ithaca’s medium-voltage subtransmission network must support the city’s growing focus on clean energy and climate resilience. The integration of small-scale renewable energy resources like community solar projects and small hydroelectric plants can enhance the reliability and sustainability of the local grid. The New York State Public Service Commission (NYSPSC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, and the New York Independent System Operator (NYISO) manages the regional grid and wholesale electricity market.
Boulder requires a medium-voltage subtransmission infrastructure capable of supporting the integration of renewable energy resources and local clean energy initiatives. These resources can help improve grid reliability and resilience, as well as support the growing demand for clean electricity from the city’s residents and businesses. The Colorado Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, and the Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC) ensures the reliability of the regional grid.
In states like Minnesota and Colorado, community solar gardens are increasingly popular as a means to provide solar energy access to residents who cannot install solar panels on their property. Medium-voltage subtransmission lines help connect these solar gardens to local distribution networks, enabling more people to benefit from clean energy.
Microgrids are localized energy networks that can operate independently from the main grid, often using a combination of renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and energy storage systems. Medium-voltage subtransmission lines are essential for connecting microgrids to the larger grid, ensuring energy reliability and resilience during emergencies or grid disruptions.
Medium-voltage subtransmission lines are crucial for rural electrification efforts, which aim to bring reliable and affordable electricity to remote and underserved communities. These projects often involve connecting smaller-scale renewable energy projects like wind turbines or solar arrays to the main grid via medium-voltage subtransmission lines.
With the rapid growth of electric vehicle adoption, the need for reliable and accessible EV charging infrastructure is on the rise. Medium-voltage subtransmission lines are necessary for connecting fast-charging stations to the grid, enabling EV owners to charge their vehicles quickly and conveniently.
The Buffalo Niagara Medical Campus (BNMC) microgrid project relies on medium-voltage subtransmission lines to integrate on-site renewable energy generation, energy storage, and energy-efficient buildings, enhancing grid resilience and sustainability.
The Borrego Springs Microgrid project uses medium-voltage subtransmission lines to connect renewable energy resources, such as solar panels and energy storage systems, to a localized grid that can operate independently from the main grid during emergencies or grid disruptions.
The island of Kauai has several medium-voltage subtransmission lines connecting its renewable energy projects, such as the Koloa Solar Farm, to the local grid. These projects help the island move towards its goal of reaching 100% renewable energy by 2045.
The city of Newark is working to develop microgrids that use medium-voltage subtransmission lines to connect renewable energy resources and energy storage systems to the local grid, improving resiliency during power outages and other grid disruptions.
The University of Alaska Fairbanks operates a microgrid that uses medium-voltage subtransmission lines to connect on-campus renewable energy generation sources like solar panels, biomass, and energy storage systems. This microgrid serves as a testbed for emerging technologies and grid management strategies.
The Lansing Board of Water & Light (BWL) is investing in grid modernization efforts, including the upgrading of medium-voltage subtransmission lines to better accommodate renewable energy projects like solar arrays and wind farms, as well as improving grid reliability and efficiency.
Arizona Public Service (APS) is working on several medium-voltage subtransmission line projects to support the integration of renewable energy resources, such as solar and wind farms, into the grid. These projects help Arizona meet its renewable energy goals and improve the overall stability and reliability of the grid.
Rocky Mountain Power, a subsidiary of PacifiCorp, is investing in grid modernization projects to upgrade medium-voltage subtransmission lines across Utah, facilitating the integration of renewable energy resources and improving grid reliability for customers.
South Carolina Electric & Gas (SCE&G) is upgrading medium-voltage subtransmission lines to integrate distributed renewable energy resources, such as solar and wind projects, into the grid. These efforts help improve grid reliability and support South Carolina’s clean energy goals.
Oklahoma Gas & Electric (OG&E) is investing in grid modernization projects, including the upgrading of medium-voltage subtransmission lines to better accommodate the increasing number of renewable energy projects like wind farms, which are prevalent in the state due to its abundant wind resources.
Duke Energy, a major utility company in North Carolina, is working on grid modernization projects, including upgrading medium-voltage subtransmission lines to support the integration of renewable energy resources like solar and wind power, improving grid reliability and resilience for customers.
Indianapolis Power & Light (IPL) is focusing on grid modernization efforts, such as the upgrading of medium-voltage subtransmission lines, to better accommodate renewable energy projects and improve the overall stability and reliability of the grid.
American Electric Power (AEP) is working on several medium-voltage subtransmission line projects in Ohio, aiming to support the integration of renewable energy resources like solar and wind projects and improve overall grid reliability and resilience for customers.
Commonwealth Edison (ComEd) is investing in grid modernization initiatives, including upgrading medium-voltage subtransmission lines to accommodate the growing number of renewable energy projects like solar arrays and wind farms, ensuring a more reliable and sustainable energy future for Illinois residents.
Wisconsin Electric Power Company (WE Energies) is focusing on grid modernization efforts, such as upgrading medium-voltage subtransmission lines, to better integrate renewable energy projects and improve the overall stability and reliability of the grid.
Entergy Mississippi, a major utility company in the state, is working on grid modernization projects, including upgrading medium-voltage subtransmission lines to support the integration of renewable energy resources like solar and wind power, improving grid reliability and resilience for customers.
Ameren Missouri, a major utility company in the state, is investing in grid modernization projects, including the upgrading of medium-voltage subtransmission lines to better accommodate renewable energy projects like solar arrays and wind farms, ensuring a more reliable and sustainable energy future for Missouri residents.
MidAmerican Energy, a leading utility in Iowa, is focusing on grid modernization efforts, such as upgrading medium-voltage subtransmission lines, to better integrate renewable energy projects and improve the overall stability and reliability of the grid, particularly given the state’s prominence in wind power generation.
Entergy Arkansas is working on grid modernization projects, including upgrading medium-voltage subtransmission lines to support the integration of renewable energy resources like solar and wind power, improving grid reliability and resilience for customers.
Public Service Company of New Mexico (PNM) is investing in grid modernization initiatives, including upgrading medium-voltage subtransmission lines to accommodate the growing number of renewable energy projects like solar arrays and wind farms, ensuring a more reliable and sustainable energy future for New Mexico residents.
Xcel Energy, a major utility company in Colorado, is working on several medium-voltage subtransmission line projects to support the integration of renewable energy resources like solar and wind projects, improving overall grid reliability and resilience for customers.
The Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA), a federally owned corporation that serves the state, is investing in grid modernization projects, including the upgrading of medium-voltage subtransmission lines to better accommodate renewable energy projects like solar arrays and wind farms, ensuring a more reliable and sustainable energy future for Tennessee residents.
Louisville Gas and Electric Company (LG&E) is focusing on grid modernization efforts, such as upgrading medium-voltage subtransmission lines, to better integrate renewable energy projects and improve the overall stability and reliability of the grid.
Basin Electric Power Cooperative is working on grid modernization projects in North Dakota, including upgrading medium-voltage subtransmission lines to support the integration of renewable energy resources like wind power, given the state’s abundant wind resources.
As the United States’ electric power system continues to evolve, the integration of renewable energy resources at various voltage levels, including medium-voltage subtransmission lines, becomes increasingly critical in addressing emerging challenges and opportunities. Laws and regulations at the federal, state, and regional levels must adapt to promote the development and deployment of clean energy solutions, ensuring a more resilient, sustainable, and efficient electric power system for the future.
low voltage transmission line are essential for delivering electricity to end-users, and the integration of distributed renewable energy resources, such as rooftop solar installations and small wind turbines, can play a significant role in enhancing grid reliability and sustainability:
Medium-voltage subtransmission lines are essential for connecting smaller-scale renewable energy projects to the grid and ensuring that clean energy can be reliably delivered to local communities:
New York City’s dense distribution network, which supplies electricity to millions of residents and businesses across the five boroughs.
San Francisco, where low voltage distribution lines provide power to residential neighborhoods, commercial districts, and the city’s iconic cable car system.
low voltage transmission line play a crucial role in delivering electricity to end-users, including residential, commercial, and industrial customers. As the United States continues to incorporate more renewable energy sources and distributed generation, upgrading and modernizing low voltage transmission line is essential to ensure a reliable and sustainable electric power system. Here are eight city or state examples showcasing various renewal efforts in low voltage transmission line:
Seattle’s low voltage distribution lines provide electricity to residential neighborhoods, commercial areas, and the city’s thriving tech industry. The Washington Utilities and Transportation Commission (WUTC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, while the Bonneville Power Administration (BPA) manages the transmission of electricity from hydroelectric dams in the Pacific Northwest.
Miami’s low voltage distribution lines serve a diverse range of end-users, from residential customers to the bustling tourism industry. The Florida Public Service Commission (FPSC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, while the Florida Reliability Coordinating Council (FRCC) ensures the reliability of the regional grid.
Atlanta’s low voltage distribution lines provide electricity to residential neighborhoods, commercial districts, and the city’s bustling international airport. The Georgia Public Service Commission (GPSC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, while the Southern Company oversees the operations of the regional grid.
Philadelphia’s low voltage distribution lines serve a wide range of end-users, including residential customers, commercial businesses, and the city’s numerous historical sites. The Pennsylvania Public Utility Commission (PAPUC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, while the PJM Interconnection manages the regional grid and wholesale electricity market.
Austin, a growing tech hub and home to many startups, requires a reliable low voltage distribution network to support the city’s burgeoning tech industry and residential neighborhoods. The PUCT and ERCOT oversee the state’s electric grid and enforce regulations related to power generation and transmission.
Minneapolis has a diverse economy that includes healthcare, finance, and manufacturing. The city’s low voltage distribution lines serve a wide range of end-users, from residential customers to commercial businesses and industrial facilities. The Minnesota Public Utilities Commission (MPUC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, while the Midcontinent Independent System Operator (MISO) manages the regional grid and wholesale electricity market.
Denver’s low voltage distribution lines must serve the city’s growing population and support the increasing adoption of EVs and rooftop solar installations. The Colorado Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, while the WECC ensures the reliability of the regional grid.
Minneapolis’s low voltage transmission line must serve the city’s diverse population and support the increasing adoption of DERs, such as rooftop solar installations and small-scale energy storage systems. The integration of these resources can help enhance the resilience and flexibility of the local grid, while also contributing to the state’s ambitious clean energy goals. The Minnesota Public Utilities Commission (MPUC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, and the Midcontinent Independent System Operator (MISO) manages the regional grid and wholesale electricity market.
Atlanta’s low-voltage distribution network serves a wide range of end-users, including residential customers, commercial businesses, and educational institutions. The city’s focus on clean energy and sustainability requires a reliable distribution system that incorporates distributed renewable energy resources like rooftop solar installations and small wind turbines. The Georgia Public Service Commission (GPSC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, and the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) ensures the reliability of the regional grid.
Nashville’s low voltage distribution network serves a wide range of end-users, including residential customers, commercial businesses, and the city’s thriving music industry. The Tennessee Public Utility Commission (TPUC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, and the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) manages the transmission and distribution of electricity in the region.
Tampa’s low voltage distribution lines must serve the city’s growing population, support the increasing adoption of EVs and rooftop solar installations, and maintain grid reliability during extreme weather events like hurricanes. The FPSC regulates the state’s electric utilities, while the FRCC ensures the reliability of the regional grid.
Albuquerque’s low voltage distribution network serves a diverse range of end-users, including residential customers, commercial businesses, and research institutions. The city’s focus on clean energy and grid modernization requires a reliable and resilient distribution system. The New Mexico Public Regulation Commission (NMPRC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, and the WECC ensures the reliability of the regional grid.
Baltimore’s low voltage distribution lines must serve the city’s diverse population, support the increasing adoption of EVs and DERs, and maintain grid reliability during extreme weather events like hurricanes. Integrating energy storage solutions and demand response programs will be critical to ensuring the stability and resilience of the local grid. The Maryland Public Service Commission (MPSC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, while PJM Interconnection manages the regional grid and wholesale electricity market.
Omaha’s low voltage distribution network serves a range of end-users, including residential customers, commercial businesses, and agricultural operations. The city’s focus on clean energy and grid modernization requires a reliable distribution system that incorporates energy storage and demand response solutions. The Nebraska Public Power District (NPPD) oversees the state’s electric utilities, and SPP ensures the reliability of the regional grid.
San Diego’s low voltage distribution lines must serve the city’s diverse population and support the increasing adoption of EVs, rooftop solar installations, and DERs. The integration of microgrids and smart grid technologies can help enhance the resilience and flexibility of the local grid, particularly during events such as wildfires and extreme weather. The CPUC regulates the state’s electric utilities, and CAISO manages the regional grid and wholesale electricity market.
Minneapolis’ low voltage distribution network serves a wide range of end-users, including residential customers, commercial businesses, and educational institutions. The city’s focus on clean energy and sustainability requires a reliable distribution system that incorporates microgrids, smart grid technologies, and energy storage solutions. The Minnesota Public Utilities Commission (MPUC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, and MISO ensures the reliability of the regional grid.
Sacramento’s low voltage distribution lines must serve the city’s diverse population and support the increasing adoption of DERs, such as rooftop solar installations and small-scale energy storage systems. The integration of these resources can help enhance the resilience and flexibility of the local grid, while also contributing to the state’s ambitious clean energy goals. The CPUC regulates the state’s electric utilities, and CAISO manages the regional grid and wholesale electricity market.
Raleigh’s low voltage distribution network serves a wide range of end-users, including residential customers, commercial businesses, and educational institutions. The city’s focus on clean energy and sustainability requires a reliable distribution system that incorporates distributed renewable energy resources like rooftop solar installations and small wind turbines. The North Carolina Utilities Commission (NCUC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, and the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) ensures the reliability of the regional grid.
Seattle’s low voltage transmission line must serve the city’s diverse population and support the increasing adoption of DERs, such as rooftop solar installations and small-scale energy storage systems. The integration of these resources can help enhance the resilience and flexibility of the local grid, while also contributing to the state’s ambitious clean energy goals. The Washington Utilities and Transportation Commission (WUTC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, and the Bonneville Power Administration (BPA) oversees transmission operations in the Pacific Northwest.
Orlando’s low-voltage distribution network serves a wide range of end-users, including residential customers, commercial businesses, and educational institutions. The city’s focus on clean energy and sustainability requires a reliable distribution system that incorporates distributed renewable energy resources like rooftop solar installations and small wind turbines. The Florida Public Service Commission (FPSC) regulates the state’s electric utilities, and the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) ensures the reliability of the regional grid.
Pacific Gas and Electric (PG&E) is investing in the modernization of low voltage transmission line to better accommodate distributed energy resources such as rooftop solar panels and battery storage systems, while also improving overall grid reliability and resilience.
Florida Power & Light (FPL) is focusing on upgrading low voltage transmission line to better integrate distributed generation, such as residential solar installations, and improve grid reliability during severe weather events like hurricanes.
Eversource Energy, a major utility company in Massachusetts, is working on upgrading low voltage transmission line to support the integration of distributed renewable energy resources like solar panels and electric vehicle charging infrastructure, while enhancing grid reliability.
Austin Energy is investing in the modernization of low voltage transmission line to accommodate the growing number of distributed energy resources, such as rooftop solar installations and battery storage systems, and to improve overall grid reliability and resilience.
Portland General Electric (PGE) is focusing on upgrading low voltage transmission line to better integrate distributed generation, such as solar installations and energy storage systems, and to improve grid reliability in the face of extreme weather events and increasing demand.
Dominion Energy, a major utility company in Virginia, is working on upgrading low voltage transmission line to support the integration of distributed renewable energy resources like solar panels and electric vehicle charging infrastructure, while enhancing grid reliability.
Xcel Energy, a leading utility in Minnesota, is investing in the modernization of low voltage transmission line to better accommodate distributed energy resources, such as rooftop solar installations and battery storage systems, and to improve overall grid reliability and resilience.
Idaho Power is focusing on upgrading low voltage transmission line to better integrate distributed generation, such as solar installations and energy storage systems, and to improve grid reliability in the face of increasing demand and evolving energy needs.
Rocky Mountain Power, a major utility company in Utah, is investing in the modernization of low voltage transmission line to better accommodate distributed energy resources, such as rooftop solar installations and battery storage systems. These efforts contribute to improving overall grid reliability and resilience while supporting Utah’s clean energy goals.
Public Service Enterprise Group (PSEG), a leading utility in New Jersey, is working on upgrading low voltage transmission line to support the integration of distributed renewable energy resources like solar panels and electric vehicle charging infrastructure. These upgrades enhance grid reliability and help the state achieve its ambitious clean energy targets.
Georgia Power, a major utility in the state, is focusing on upgrading low voltage transmission line to better integrate distributed generation, such as residential solar installations and energy storage systems. These improvements aim to boost grid reliability and support Georgia’s growing clean energy industry.
Arizona Public Service (APS) is investing in the modernization of low voltage transmission line to accommodate the growing number of distributed energy resources, such as rooftop solar installations and battery storage systems. These efforts improve overall grid reliability and resilience, as well as support Arizona’s renewable energy goals.
Entergy Louisiana is working on upgrading low voltage transmission line to support the integration of distributed renewable energy resources like solar panels and electric vehicle charging infrastructure. These upgrades enhance grid reliability and help Louisiana adapt to the evolving energy landscape and the state’s clean energy initiatives.
DTE Energy, a leading utility in Michigan, is focusing on upgrading low voltage transmission line to better integrate distributed generation, such as residential solar installations and energy storage systems. These improvements aim to boost grid reliability and support Michigan’s growing clean energy industry.
Kansas City Power & Light (KCP&L) is investing in the modernization of low voltage transmission line to accommodate the growing number of distributed energy resources, such as rooftop solar installations and battery storage systems. These efforts improve overall grid reliability and resilience, as well as support Kansas’ renewable energy goals.
Omaha Public Power District (OPPD) is working on upgrading low voltage transmission line to support the integration of distributed renewable energy resources like solar panels and electric vehicle charging infrastructure. These upgrades enhance grid reliability and help Nebraska achieve its clean energy targets.
Seattle City Light, a publicly-owned utility company in Washington, is investing in the modernization of low voltage transmission line to better accommodate distributed energy resources, such as rooftop solar installations and battery storage systems. These efforts improve overall grid reliability and resilience, as well as support Washington’s clean energy goals.
Indianapolis Power & Light (IPL) is focusing on upgrading low voltage transmission line to better integrate distributed generation, such as residential solar installations and energy storage systems. These improvements aim to boost grid reliability and support Indiana’s growing clean energy industry.
We Energies, a leading utility in Wisconsin, is working on upgrading low voltage transmission line to support the integration of distributed renewable energy resources like solar panels and electric vehicle charging infrastructure. These upgrades enhance grid reliability and help Wisconsin achieve its clean energy targets.
South Carolina Electric & Gas (SCE&G), a major utility in the state, is investing in the modernization of low voltage transmission line to accommodate the growing number of distributed energy resources, such as rooftop solar installations and battery storage systems. These efforts improve overall grid reliability and resilience, as well as support South Carolina’s renewable energy goals.
Public Service Company of New Mexico (PNM) is focusing on upgrading low voltage transmission line to better integrate distributed generation, such as residential solar installations and energy storage systems. These improvements aim to boost grid reliability and support New Mexico’s growing clean energy industry.
Central Maine Power (CMP) is working on upgrading low voltage transmission line to support the integration of distributed renewable energy resources like solar panels and electric vehicle charging infrastructure. These upgrades enhance grid reliability and help Maine achieve its ambitious clean energy targets.
Public Service Company of Oklahoma (PSO) is investing in the modernization of low voltage transmission line to accommodate the growing number of distributed energy resources, such as rooftop solar installations and battery storage systems. These efforts improve overall grid reliability and resilience, as well as support Oklahoma’s renewable energy goals.
Alaska Electric Light & Power (AEL&P) is focusing on upgrading low voltage transmission line to better integrate distributed generation, such as residential solar installations and energy storage systems. These improvements aim to boost grid reliability and support Alaska’s growing clean energy industry.
Xcel Energy, a major utility company in North Dakota, is investing in the modernization of low voltage transmission line to better accommodate distributed energy resources, such as rooftop solar installations and battery storage systems. These efforts improve overall grid reliability and resilience, as well as support North Dakota’s clean energy goals.
Delmarva Power, a leading utility in Delaware, is focusing on upgrading low voltage transmission line to better integrate distributed generation, such as residential solar installations and energy storage systems. These improvements aim to boost grid reliability and support Delaware’s growing clean energy industry.
Entergy Arkansas, a major utility in the state, is working on upgrading low voltage transmission line to support the integration of distributed renewable energy resources like solar panels and electric vehicle charging infrastructure. These upgrades enhance grid reliability and help Arkansas achieve its clean energy targets.
National Grid, a leading utility in Rhode Island, is investing in the modernization of low voltage transmission line to accommodate the growing number of distributed energy resources, such as rooftop solar installations and battery storage systems. These efforts improve overall grid reliability and resilience, as well as support Rhode Island’s renewable energy goals.
Northwestern Energy, a major utility in Montana, is focusing on upgrading low voltage transmission line to better integrate distributed generation, such as residential solar installations and energy storage systems. These improvements aim to boost grid reliability and support Montana’s growing clean energy industry.
Green Mountain Power (GMP), a leading utility in Vermont, is working on upgrading low voltage transmission line to support the integration of distributed renewable energy resources like solar panels and electric vehicle charging infrastructure. These upgrades enhance grid reliability and help Vermont achieve its ambitious clean energy targets.
Entergy Mississippi, a major utility in the state, is investing in the modernization of low voltage transmission line to accommodate the growing number of distributed energy resources, such as rooftop solar installations and battery storage systems. These efforts improve overall grid reliability and resilience, as well as support Mississippi’s renewable energy goals.
Rocky Mountain Power, a leading utility in Wyoming, is focusing on upgrading low voltage transmission line to better integrate distributed generation, such as residential solar installations and energy storage systems. These improvements aim to boost grid reliability and support Wyoming’s growing clean energy industry.
As the United States’ electric power system continues to evolve, the integration of renewable energy resources at various voltage levels becomes increasingly critical in addressing emerging challenges and opportunities. Laws and regulations at the federal, state, and regional levels must adapt to promote the development and deployment of clean energy solutions, ensuring a more resilient, sustainable, and efficient electric power system for the future. By understanding the distribution of different voltage levels and the corresponding roles of renewable energy resources, stakeholders, policymakers, and industry participants can better navigate the rapidly changing energy landscape and contribute to the ongoing transformation of the electric power sector.
Download Resource

Table of Contents Selecting the right pad-mounted transformer requires careful consideration of several critical

The primary function of the pad mounted transformer is to serve as a critical distribution

A pad mounted transformer operates through electromagnetic induction, serving as a crucial distribution component that
After filling in the contact information, you can download the PDF.