ELECTRIC, WITH AN EDGE
As the demand for power transformers in substations continues to rise, knowing the function of power transformers in substations, transformer substation types, electrical substation components, and transformer substation diagram are important. With the help of DAELIM, one of the best transformer manufacturers in the world, you will be able to fully comprehend its purpose.
In this article, you will go through sections related to power transformers, substations, and the purpose or function of power transformers in substations. This will guarantee you to make a well-thought purchase decision instead of randomly buying a transformer.
But before going through what is the purpose power transformers in substations, it is important to know what are the different types of transformers first. The purpose of this is for you to easily digest the information that is given as we go deeper into the article.

For starters, transformers can basically be categorized into different families and this heavily depends on what their purpose, construction, and use are. There are even times that this way of categorizing mix with one another. For instance, some transformers can both be a three-phase transformer and a step-up transformer at the same time.
But nevertheless, the classifications below are usually what international standards follow.
Step-up transformers are transformers that basically convert low voltage (L.V) and high current from the primary side of the transformer towards the high voltage (H.V) and low current value on the secondary side of the transformer.
In other words, step-up transformers are used to increase the primary voltage to secondary.
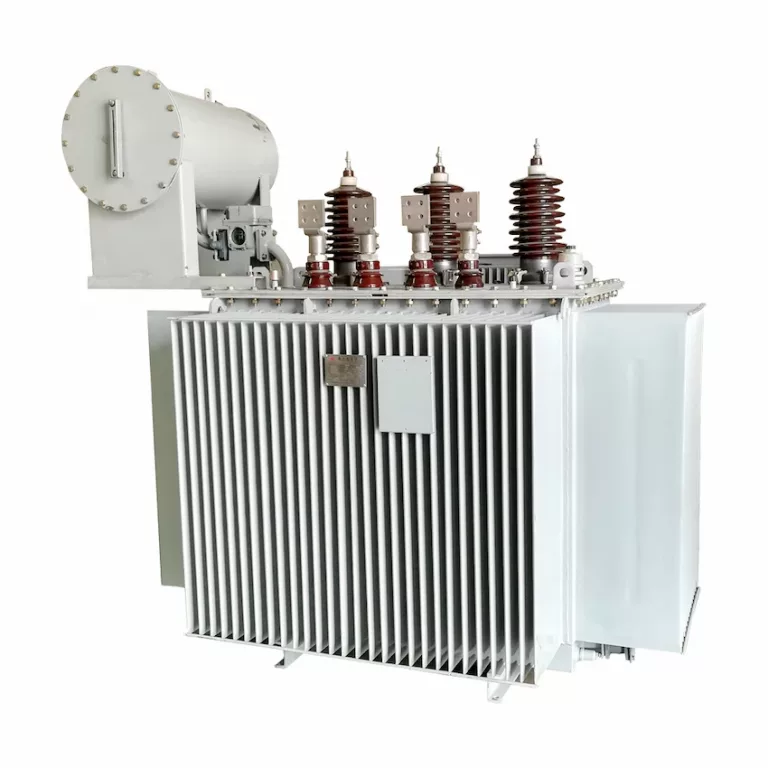


On the other hand, step-down transformers are transformers that convert L.V and high current from the primary side to the H.V and low current value on the secondary side of the transformer.
In simpler terms, step-down transformers are used to reduce the primary voltage to secondary, which is the complete opposite of step-up transformers. A power transformer in substation can have the ability to both increase or decrease the voltage levels. However, this heavily depends on the situation and purpose of the power transformer in substation.
Three-phase transformers like some DAELIM power transformers are commonly used in projects that have a three-phase power system since this is more cost-effective compared to single-phase transformers.
In terms of size, it is important to use a bank of three single-phase transformers since it is much easier to transport one of these electrical devices.
Understanding Live Front Three-Phase Pad-Mounted Transformer


When it comes to single-phase transformers, this type of transformer basically utilizes single-phase A.C or alternating current. DAELIM single-phase transformers heavily depend on a voltage cycle that operates in a unified time phase.
In other words, the ratio of primary windings to the secondary winding will determine what changes in the current.
You may have heard of distribution transformers before since they are widely used and very popular around the world. DAELIM Distribution transformers have the ability to step down the voltage for the purpose of domestic or commercial use.
Basically, it has a good voltage regulation that operates the whole day with a typical max efficiency at 50%of full load.
Selection of Power Distribution Main Transformer in 110kV Substation Design
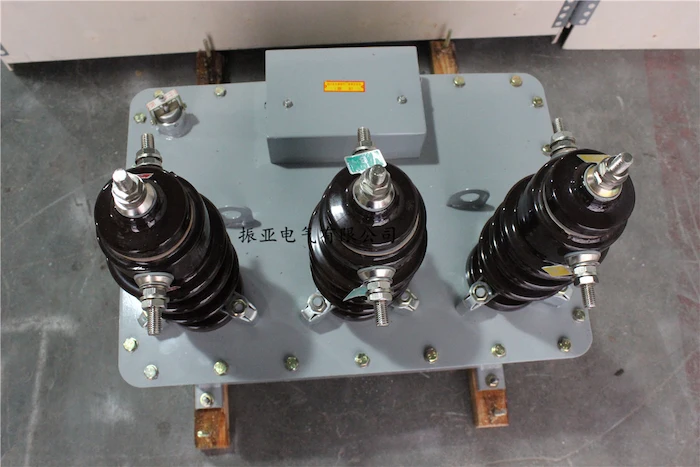


Instrument transformers are basically transformers that have a mix of both current transformers and potential transformers that are commonly used or applied for the purpose of decreasing high voltages and currents to mitigate values that can be measured with the use of conventional instruments.
As the name suggests, outdoor transformers are transformers that are designed to operate outside and far from houses and other buildings. Usually, this type of transformer has transformer oil or mineral oil in them that are highly flammable.
Power Transformer: The Ultimate FAQ Guide
Because of that, outdoor transformers do not pass the fire codes of most buildings.
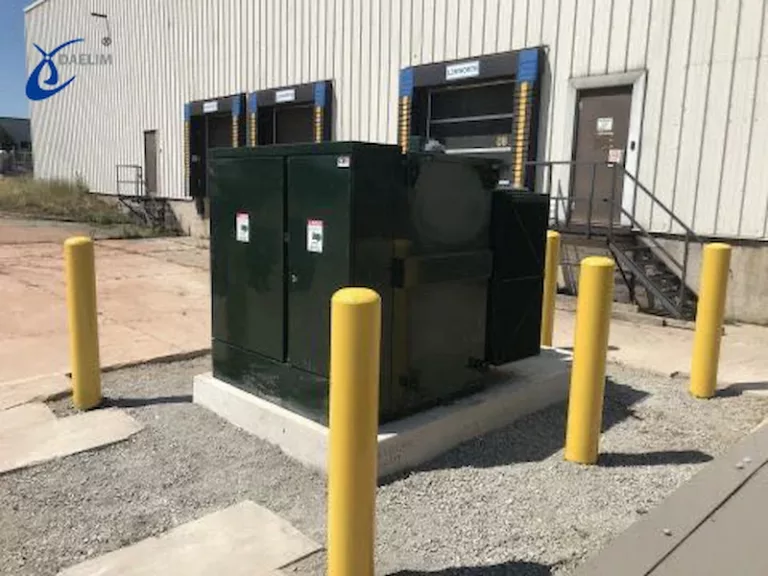

When it comes to indoor transformers, they can be installed indoors and the usual transformers for this type of application are DAELIM Dry-type transformers, wherein there is no flammable involved during its operation.
As aforementioned, oil-type transformers are basically a type of transformer that utilizes transformer oil or mineral oil for its cooling. Moreover, oil cooling is the most effective medium to cool a transformer compared to dry-type cooling.
A Complete Guide to Oil Immersed filled Distribution Transformer
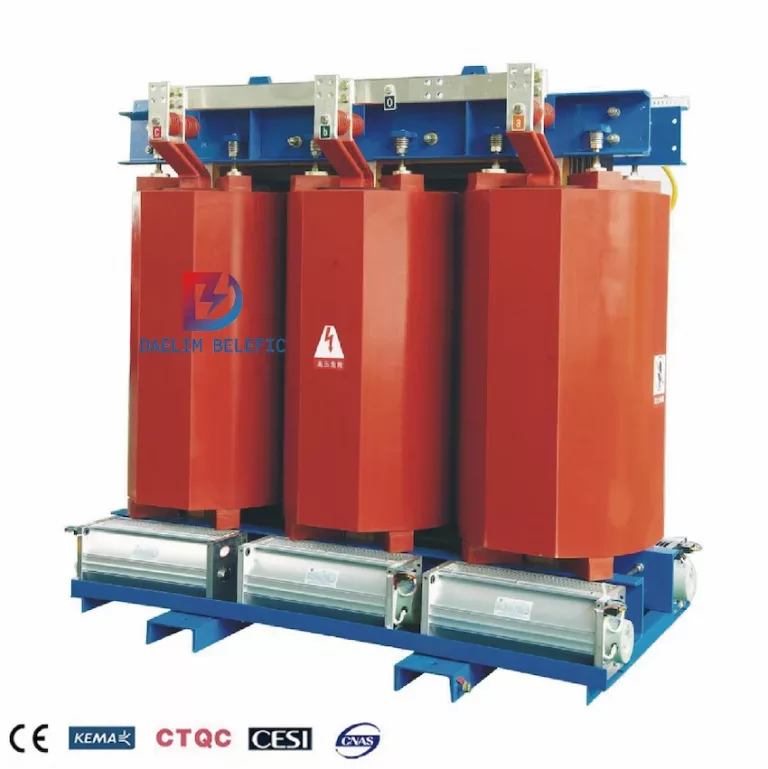


Speaking of dry-type transformers, dry-type transformers basically use forced air or pressurized air to cool down the transformer. It is cost-effective since you do not have to purchase oil anymore. However, both aspects have their advantages and disadvantages.
Your decision should be based on what is your purpose or what type of project are you having.
Detailed explanation of the difference between dry-type transformers and oil-immersed transformers
At this point, it is the best time to talk about power transformers to know what is the function of power transformers in substation. But before going through the different transformer substation types, electrical substation components, and transformer substation diagram it is crucial to learn first what power transformers are in general.
So basically, a power transformer is a static electrical machine or device that is utilized for transforming power from circuit to circuit without changing or disturbing the frequency. Since it has no moving or rotating parts, this transformer is classified as a static device.
Moreover, this electrical device operates on an alternating current supply or better known as A.C. These transformers have similar operating principles to the transformer substation diagram.
Generations of electrical power at low voltages are known to be very cost-effective, which is why it is common for low voltage level power can be transmitted to the receiving end with ease. Low voltage power can easily transmit results that are far greater than line currents that cause more line losses.
But in the case that the voltage level of power is significantly increased, then the current of the power is drastically reduced which results in a reduction in ohmic or l2R losses in the system. There is reduction in cross-sectional areas of the conductor like the reduction in capital cost of the overall system. This improves the regulation of voltage in the system.
Furthermore, the low level power is required to be stepped up for efficient electrical power transmission.
The process of this is done with the help of a step-up transformer at the side of the power system network. High voltage power may or may not be distributed to the consumers direct since this must be first stepped down to the recommended level in order for it to work.
Supply Ability: 100 Set/Sets per Year
Packaging Details: Standard international packages, can be safely shipped through air or sea transportation.
Product Description:
110 kV and 66 kV power transformers are specifically designed and optimized by DAELIM with the help of advanced technologies both national and international assets to enhance the transformer’s core, body, fuel tank, body, or the whole transformer in general.
This feature also utilizes low partial discharge. Meaning there will be less loss and even noise. It is also lightweight compared to other types of transformers. It is highly reliable since this transformer has the characteristics of stability, efficiency, cost-effectivity, and environmental protection.
This is great for big projects, industrial and commercial applications, etc.
Transformer accessories
This transformer comes along with Qualitrol remote installation thermometers, tap changers, A.B.B bushings, and many more!
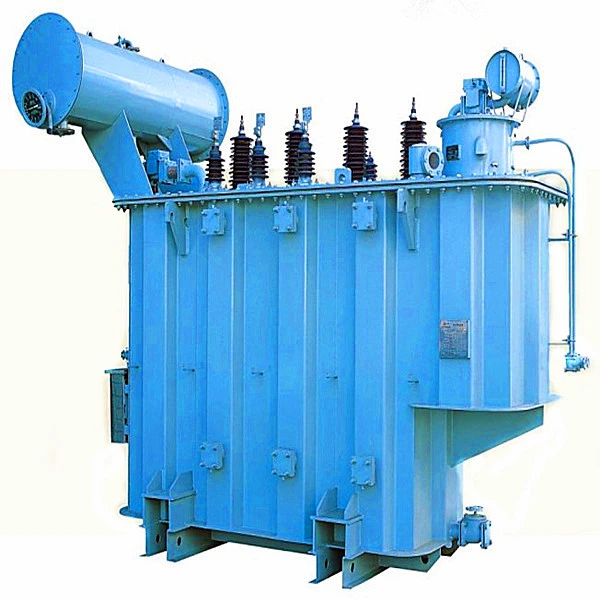

Supply Ability: 50 Set/Sets per Year -110KV class three-phase power transformer
Packaging Details: Standard international packages, can be safely shipped through air or sea transportation.
Product Specifications:
The DAELIM 220kV, 110kV, and 66kV transformers are all designed to be low-loss through the use of national and international advanced technologies. This in return results in low local discharge, strong protection, low loss, and overall high reliability.
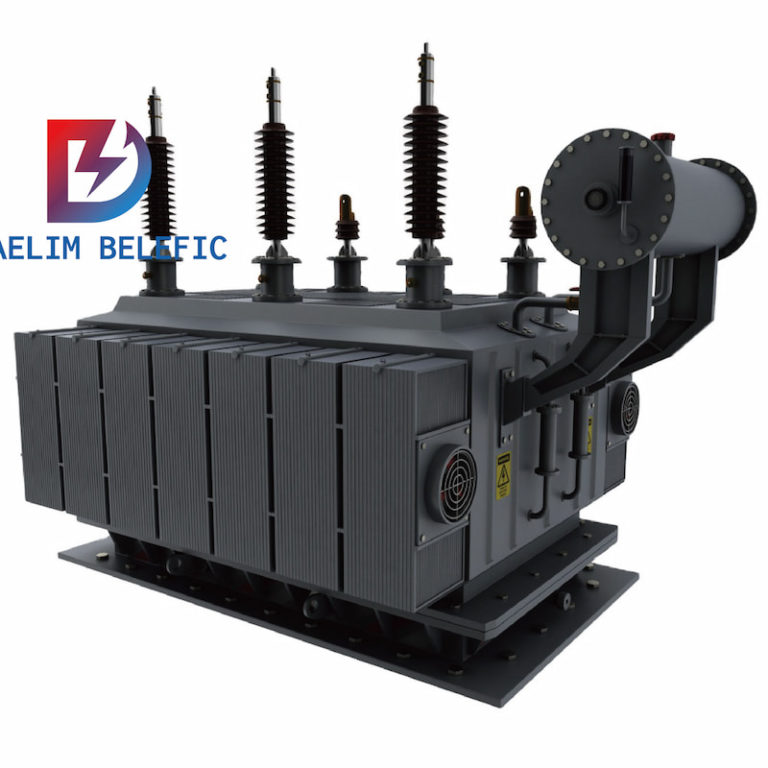

Supply Ability: 20 Set/Sets per Month – Three-phase low-loss NLTC oil-immersed 66kv 5mva power transform
Packaging Details: Wood case or according to client’s requests. The transformer can be shipped air and sea transport.
Product Specifications:
The DAELIM 66kV three-phase two winding NLTC power transformer has the lowest kilovolt ampere rating among the low-loss power transformer series in DAELIM but this does not mean it is not worth considering.
The DAELIM 66kV three-phase two winding NLTC power transformer is still an outstanding power transformer, and it is more compact and lightweight compared to the higher-rated power transformers in the DAELIM low-loss series of transformers.
Noise: The transformer is rated 63mva and below is lower than 58db(an)
Power loss: There is a no-load loss 30% lower than that of the I.E.C standard.
Reliability: It is 100% guaranteed that the transformer is safe and in brand new condition that is built and ready for optimum performance.
Short circuit withstanding: Model SFZ11-50000/132 smoothly passed the short circuit withstanding test of the national transformer quality supervision and inspection center and also passed the holland KEMA quality control system.
Substations are commonly found above ground since there are some substations that can be found underground. Both in which have similarities in their construction that usually involve wooden poles or utility poles, tube metal structures, etc.
Substations that are situated in large areas are commonly supported by steel lattice towers that are known to be cost-effective. On the other hand, small substations are found in suburbs, and their appearance is a huge factor for purchase decisions.
Transformer substation types can have different insulations. Some are gas-insulated and some are just covered in metal for low voltages. As mentioned, substation appearance matters since they are basically designed to blend with the environment they are in.
Speaking of transformer substation types, each classification has its own voltage class, power system, insulated connections, build, and other unique elements.
Transmission substations are basically substations that are utilized to intertwine two or more transmission lines that are of the same voltage that is passing through them. This is the reason why this power transformer in substation has high voltage switches to assist the clearing of faults safely.
power transformers in substations, specifically transmission substations, have power transformer between the voltages, reactors, capacitors, etc. This is one of the main functions of power transformer in substation. This manages power flow much easier.
These can also be considered simple or complicated, but this depends on the voltage level. A well-known example of this is a transmission substation in need of a bus or circuit breakers to operate.
Some transmission systems may need a larger area and as well as a number of voltage levels, fuses, circuit breakers, and other protective equipment to operate.
The purpose of distribution substations is to transfer power from the transmission system to the distribution system of a certain or given area, This is a popular cost-effective method since it is expensive to connect electricity to the consumers through the main network.
Moreover, this requires a lot of power which is why there are power transformers in substations. This can also be dangerous as well. A safer alternative method is to let the distribution systems do their work in reducing the voltage intensity into lower distribution levels.
Distribution systems usually have two transmission lines, and when it comes to the output, the majority runs through a number of feeders. In terms of the voltage levels, they are usually kept at a medium.
Distribution Transformer Solution for Papermaking Enterprises
A power transformer is a crucial component of an electrical substation that is responsible for transferring electrical energy between different voltage levels in a power system. Its main function is to step up or step down the voltage of electrical energy, thereby facilitating its efficient transmission and distribution throughout the network.
A power transformer in a substation typically consists of a core and two or more winding coils. The core is made of high-grade magnetic material that helps to produce a magnetic field when current flows through the winding coils. The winding coils are made of insulated copper wire and are wound around the core. The number of turns in the winding coils, as well as their position on the core, determines the voltage ratio of the transformer.
Power transformers are usually classified based on their voltage rating, which can range from a few hundred volts to several hundred kilovolts. They are designed to withstand high electrical stresses and extreme environmental conditions, such as high temperature, humidity, and vibration.
Overall, a power transformer is a critical element of an electrical substation, enabling the efficient and reliable transmission and distribution of electrical energy to customers.
There are several types of transformer substations, each serving a specific purpose and designed to operate under certain conditions. Here are the most common types of transformer substations:
Step-up transformer substation: This type of substation is used to increase the voltage level of the electrical power coming from the power plant to the transmission system.
Step-down transformer substation: This type of substation is used to decrease the voltage level of the electrical power before it is supplied to the distribution system.
Distribution transformer substation: This type of substation is used to supply electrical power to residential, commercial, and industrial consumers.
Underground transformer substation: This type of substation is designed to be installed underground, making it ideal for urban areas with limited space for above-ground installations.
Mobile transformer substation: This type of substation is designed to be easily transported to different locations, making it ideal for emergency power supply or temporary power needs.
Each type of transformer substation has its unique design, specifications, and features. It’s essential to choose the right type of transformer substation that fits your specific needs to ensure reliable and efficient power supply.
Main Power Transformer Solution for Coal Mine
Substation transformers come in various ratings that determine their power and voltage capacity. The ratings of substation transformers can be classified based on their power and voltage levels.
Power rating refers to the maximum amount of power that the transformer can handle continuously without overheating. Substation transformers are available in different power ratings, ranging from a few kilovolt-amperes (kVA) to several hundred megavolt-amperes (MVA). The power rating of a transformer depends on various factors, including the size of the transformer, its core and winding design, and the cooling system used.
Voltage rating refers to the maximum voltage that the transformer can handle without breaking down or arcing. Substation transformers are available in various voltage ratings, depending on the voltage levels of the power grid. For example, transformers used in transmission substations may have voltage ratings of several hundred kilovolts (kV), while those used in distribution substations may have ratings of several tens of kV.
The ratings of substation transformers are typically specified by the manufacturer and may vary depending on the specific requirements of the project. It is essential to select a transformer with the appropriate power and voltage ratings to ensure safe and reliable operation in the substation. The transformer should also be able to withstand transient overvoltage and other electrical stresses that may occur in the substation.
Substation transformers are a critical component in power distribution, providing the necessary voltage transformation to deliver electricity to end-users. They come in various specifications that are designed to meet specific needs and requirements. Here are some of the important specifications of substation transformers:
Power rating: This refers to the amount of power that the transformer can handle. Substation transformers typically have power ratings ranging from a few hundred kilovolt-amperes (kVA) to several hundred mega-volt-amperes (MVA).
Voltage rating: This is the maximum voltage that the transformer can withstand. The voltage rating of a substation transformer can vary depending on the application, and it is typically specified for both the primary and secondary windings.
Impedance: This is the resistance to the flow of current in the transformer. The impedance of a substation transformer is an important specification, as it affects the voltage regulation and efficiency of the transformer.
Cooling method: Substation transformers can be cooled using various methods, including air, water, or oil. The cooling method used can affect the overall efficiency and cost of the transformer.
Insulation class: This specification refers to the temperature rating of the insulation used in the transformer. It is an important consideration as it can affect the lifespan and reliability of the transformer.
Dimensions and weight: The size and weight of a substation transformer are important specifications, as they can affect the installation process and space requirements in the substation.
Overall, it is important to carefully consider the specifications of substation transformers to ensure that they meet the specific needs and requirements of the power distribution system they will be a part of.
There are many power transformer manufacturers in the industry, but some of the most well-known and reputable companies include:
Siemens: Siemens is a multinational company with a strong reputation in the power industry. They manufacture a wide range of power transformers, including generator transformers, auto transformers, and distribution transformers.
ABB: ABB is another well-known manufacturer of power transformers. They offer a variety of transformers for different applications, including large power transformers for utility and industrial use, as well as smaller transformers for commercial and residential applications.
General Electric (GE): GE is a major player in the power industry, offering a range of power transformers, including distribution transformers, power transformers, and traction transformers.
Hyundai Electric: Hyundai Electric is a global leader in the manufacturing of power transformers, offering a wide range of products including power transformers, distribution transformers, and mobile transformers.
Toshiba: Toshiba is a Japanese multinational company that produces a range of electrical equipment, including power transformers. They offer a variety of transformers for different applications, including large power transformers for utility and industrial use, as well as smaller transformers for commercial and residential applications.
Daelim Belefic: Daelim Belefic is a leading manufacturer of power transformers with over 30 years of experience in the industry. They produce high-quality transformers for a range of applications, including power generation, transmission, and distribution.
Instrument transformers are an important component of substation equipment. They are used to measure high voltage or high current electrical signals, which would otherwise be too dangerous to measure directly. Instrument transformers step down the voltage or current of the signal to a level that can be safely measured by instruments such as voltmeters, ammeters, or wattmeters.
Potential transformers (PTs) are used to measure high voltage electrical signals, while current transformers (CTs) are used to measure high current electrical signals. Both PTs and CTs are typically used in combination with measuring devices such as relays and protective devices to provide control and protection for the power system. PTs and CTs come in various sizes and ratings, depending on the specific application and requirements of the substation.
In summary, instrument transformers play a vital role in ensuring the safe and accurate measurement of high voltage or high current electrical signals in substation equipment.
If your project requires power transformers in substations, then make sure that you are getting the right transformer substation type in order to prevent wasting money and a failed project. Looking into the electrical substation components should be a factor that you should consider looking into thoroughly, and memorizing the transformer substation diagram can also greatly help you.
Should you have any more questions or concerns regarding the function of power transformer in substations, please do not hesitate to contact DAELIM’s team of professionals for immediate assistance.
When you need to find more than just existing transformers, Daelim’s Transformer Service Center can help you design and produce distribution transformers that meet your unique needs.
We have our own factory and a professional team of engineers, which can design and modify application requirements that meet all your conditions.
Download Resource