ELECTRIC, WITH AN EDGE
The demand for different types of transformers have risen significantly due to a lot of people staying at their homes. Transmission transformers and power transmission transformers are one of the most highest demand transformers, and learning about the Transmission transformer connection is a great way to understand distribution transformer rating.
Why is it important to learn these? For starters, it helps broaden the knowledge about the different types of transformers since transformers are a complicated and vast subject for some. But with the help of DAELIM, a company that has been specializing in Transmission transformers, you will be able to extensively learn about this topic.

Looking for a reliable transmission transformer manufacturer to provide you with high-quality and efficient power solutions? Look no further than Daelim Belefic, a leading transformer manufacturer with over 20 years of experience in the industry.
Our advanced production equipment and technology, combined with our commitment to quality and customer satisfaction, have made us a trusted name in the industry. We produce a wide range of transmission transformers in compliance with various international standards, including IEC, GB, AS NZS, CSAC88-16, ANSI/IEEE, and GOST R.
At Daelim Belefic, we understand the importance of reliable power supply, which is why we design our transmission transformers to provide high efficiency, stability, and a long service life. Our transformers are widely used in power systems, industrial production, and commercial and residential buildings.
We also provide comprehensive technical support and services to ensure that our customers receive the best possible solutions. Our team of experts can help you choose the right transmission transformer for your specific needs, and we offer installation, testing, and maintenance services to ensure that your transformer is operating at optimal performance.
When you choose Daelim Belefic as your transmission transformer manufacturer, you can trust that you are receiving a high-quality, reliable, and cost-effective solution. Contact us today to learn more about our products and services, and let us help you find the perfect transmission transformer for your needs.
To begin with, answering this question is the very first step to grasping a better understanding of what these electrical devices truly are.
Some might be familiar with what electrical transformers are but in case you did not know, here are the fundamentals of what electrical transformers are in general.
Electrical transformers are basically machines that have the ability to transfer electricity from circuit to circuit with voltage that is frequently changing. Although the changing voltage is rampant, electrical transformers do not go through a frequency change as the transferring process begins.
Nowadays, electrical transformers are manufactured to be used in alternating current supply or better known as A.C supply. This means that the fluctuation in the supply voltage is affected by the current. This means that there is an increase in the current which will result in the increase of the voltage as well. (Applicable vice versa).
Moreover, electrical transformers are designed to enhance the safety and efficiency of power systems. This is done through the process of increasing and decreasing voltage levels when there is a need to do so.
Transformers are the reasons why there is a supply of electricity to buildings, which is why they are commonly used for residential and industrial applications. Furthermore, this goes the same for the distribution and regulation of the power as well since transformers provide electricity to countless buildings even at long distances.
Not all transformers have these parts since there are different types of transformers with different functions, mechanisms, and purposes. But the majority of these types do have some of the parts. Including but not limited to:
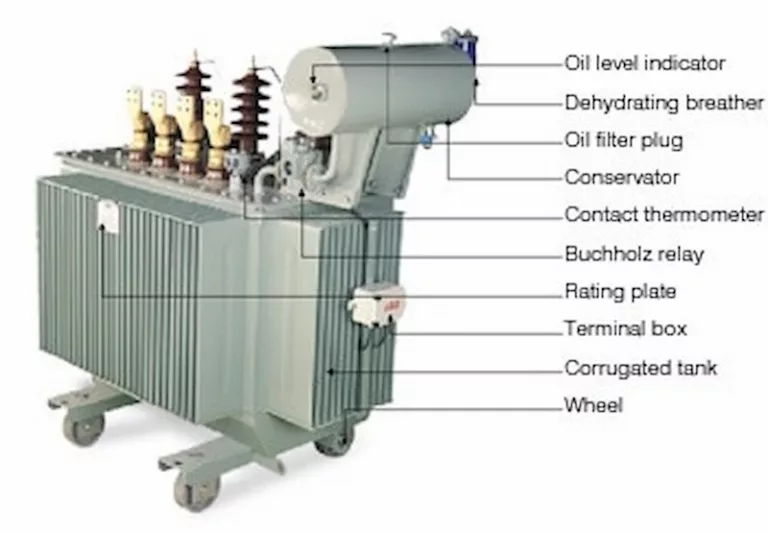
The magnetic core will be responsible for relating the flux to the secondary winding, and the purpose of this is to create a magnetic circuit that is capable of closing the flux. In terms of the low reluctance path, this is placed within the core to maximize flux linkage.
The primary winding is the part of the transformer that is responsible for inducing the magnetic flux. This specific part of the transformer is connected to an electrical source. Specifically to where the magnetic flux is produced initially.
These coils are expected to be insulated from each other. After the main flux induction. It is passed to the magnetic core and then linked to the transformer’s secondary winding through a low reluctance path.
What are the types of transformer windings ? What are the types of concentric windings?
The role of the secondary winding here is to help complete the movement of the flux, which basically begins its process on the primary side. Utilizing the core will reach the secondary winding.
The secondary winding is also given the capability to pick momentum since both windings are wound together on the same core,making their own motion. The majority of the different types of transformers have their magnetic core assembled through stacks of limited steel sheets, which leaves the minimum required air-gap between each for optimum continuity of the magnetic path.
Speaking of the different types of transformers, here are some of the different types of transformers available in the market and readily available at DAELIM’s list of products.
A step-up transformer’s sole purpose is to increase the voltage from primary to secondary, and the process of this involves more turns from the secondary winding compared to the primary winding turns.
In terms of the national grid, step-up transformers are basically using this to increase the voltage. However, they can also reduce the current through this process. Step-up transformers (depending on the kVA rating) are fully capable turning 25,000 Volts to 400,000 Volts in a short amount of time whilst decreasing the current.
The lesser the current, the less energy is lost when the wire is heated.
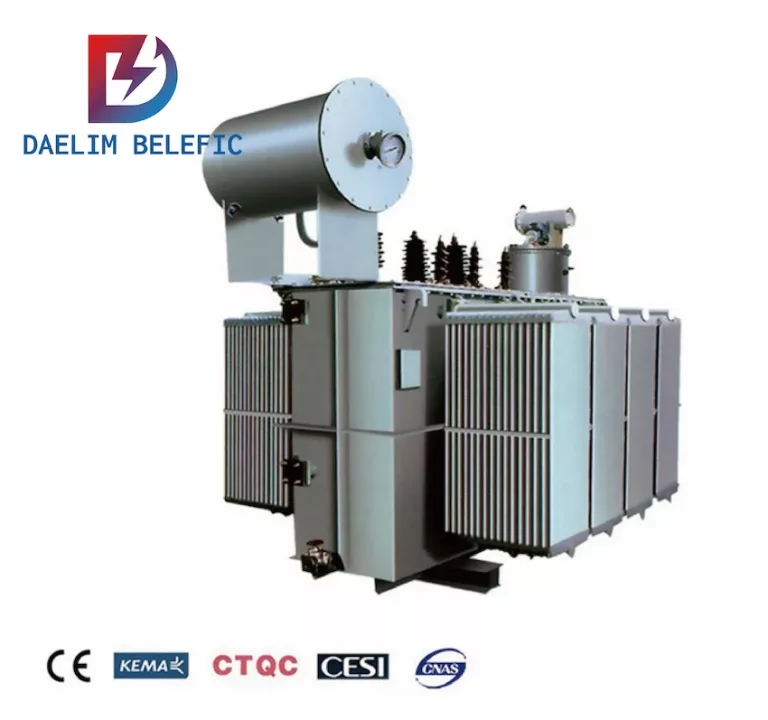


A step-down transformer is basically a type of transformer that reduces the voltage. The same with step-up transformers, this involves the voltage as well but reduced instead of increased from primary to secondary.
When it comes to the transformation ratio, it must be equivalent to the square root of the primary to secondary inductance. ratio.
These transformers are commonly situated at power generation plants that step down the voltage of power streams that is received at the local distribution level.
Basically, power transformers are specifically used for transmitting electrical energy towards any component of the electrical circuit that is between the generator and the distribution primary circuits involved.
These transformers are also used in distribution networks for the purpose of interfering step up and step down voltages. This type of transformer is one of DAELIM’s best sellers.


Speaking of best-selling transformers, distribution transformers are also one of DAELIM’s highly demanded transformers.But what is a distribution transformer for?
Distribution transformers are also commonly used in electrical power distribution and transmission systems for various reasons. For starters, the distribution transformer rating is far from other types of transformers.
This type of transformer is considered high-class since it has the highest power. Also, you can consider a distribution transformer to have the highest volt-ampere transmission systems. Power ratings are measured, determined, or scaled by what type of cooling medium the transformer uses.

Unlike power transformers and distribution transformers, pad-mounted transformers are actually located or situated in public places since their build is safe for outdoor exposure. You see these metal boxes almost everywhere, especially in residential areas or even in the streets.
This type of transformer is commonly used in residential areas and it works the same way as distribution transformers do but with limits since its size is only capable of a lesser distribution transformer rating.
Pad-mounted transformers basically lower high voltages to household voltage levels that are enough to power one or several buildings, along with the electrical appliances in them.
Another popular type of transformer that is commonly seen outdoors but above ground level are pole-mounted transformers. These single-phase transformers are basically those barrel-shaped metal objects you see on utility poles on the streets.
They are common breadbox transformers that are utilized to convert distribution voltages to 120/240-volt power that is a sufficient amount to supply homes and other buildings that are of low electrical volume.
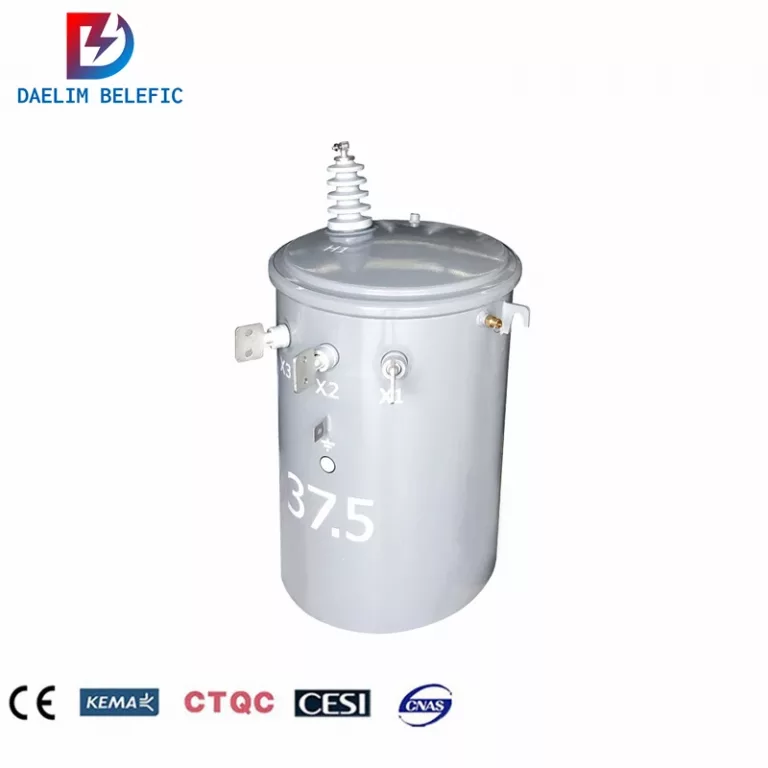

But what about transmission transformers? What are they for and how does a transmission transformer connection work? And what is the difference between a power transmission transformer versus an ordinary one?
In this section, we go through the answer of each question and elaborate it thoroughly so that it will be easier for you to understand what it is.
A transmission transformer is basically another term for a power transformer. You must remember that so as to not confuse yourself with these terminologies. But to elaborate more on transmission transformers, they are commonly used for transmission that are utilized as a step-up device.
A transmission transformer is a type of power transformer that is used to transfer electrical energy from one voltage level to another. It is typically used in power transmission systems to step up the voltage of electrical energy for efficient transmission over long distances.
This is in order to minimize that l2r loss for a given power flow. This type of transformer is specifically designed to make use of its core to a maximum in order to operate near the knee point of the B-H curve.

Three-phase transmission transformer connections are generated with the help of using three single-phase transformers or by directly using one three-phase transformer. The advantage of this is that there will be less cost, weight, floor space, and even lower losses compared to using three single-phase transformers.
This is basically how transmission transformer connections are established. Depending on what your project or purpose is, you may go for three single-phase transformers or one three-phase transformer. Either way, it performs and operates decently.
When it comes to the advantages and disadvantages of a transmission transformer, there are some factors that you should look out for. This section also aims to help you make a purchase decision.
DAELIM Electric suggests that you should consider the disadvantages as well before you make a purchase decision as it might not meet your standards for your purpose of project.
Starting with the main or key advantages of transmission transformers, below are the following:
If you are looking for a transformer that requires no start-up time, then transmission transformers are for you since they can operate immediately without delay whatsoever. The only time that this transformer consumes is the transportation and installment of the transformer.
After installation, it is just as good to plug-to-play.
Of course, efficiency is out of the question here since transmission transformers are upgraded to more efficiency due to several improvements made on it. They rarely encounter losses. But although this type of transformer is considered highly efficient, this does not mean they are 100% efficient. But nevertheless, its efficiency is well over 95%.
Well, they certainly are not called transmission transformers for no reason. This transformer allows electricity to be transmitted over long distances at amazingly low prices. Increasing the voltage is required for the current to be transmitted while the resistance on its line is reduced.
This helps ensure that there are little losses as it moves. On the other hand, a different case would mean that there would be power losses on transmission lines which would affect the passing of the electricity.
As mentioned, this transformer does not have a starting time, and you would be thrilled to know that transmission transformers also has a continuous operation feature, which means that unlike other electrical machines, they do not need to be switched off.
Turning off a transmission transformer could affect its performance, especially if this is done repeatedly. This is the main reason why they are commonly used in distribution power systems.
Another great feature that the transmission transformer has is low maintenance. Transmission transformers may have a no starting time and no stopping function but this does not mean that they require frequent maintenance.
However, you do need to monitor its oil, contacts, and components. But that is basically it. Moreover, this does not involve a lot of effort and money to do so.
When it comes to the disadvantages, the following are the drawbacks of transmission transformers.
Unlike dry-type distribution transformers, transmission transformers need a cooling medium or insulating oil, which can be costly and highly flammable.Since it is operating all the time, you would have to monitor its oil if there is any left.
It is not possible to shut it down and wait for it to cool as this might easily affect the transformer’s performance.
transmission transformers can be large, even lesser rated ones can still be big, and this could be a problem to some, especially if there is a limited amount of space available. Remember, the size of the transformer has a lot to do with its voltage level capacity.
The higher it is, the larger the transformer. So if your purpose or project requires a high voltage transformer, then expect that you would need a large space for it.
Transmission transformers are good for large projects that involve high voltage ratings and long distance supplying. However, if this does not seem to be fit for your purpose or project, there are countless types of transformers you can choose from DAELIM’s list of products.
However, if you are still unsure at this point. Do not hesitate to contact DAELIM’s team of professionals for immediate assistance.
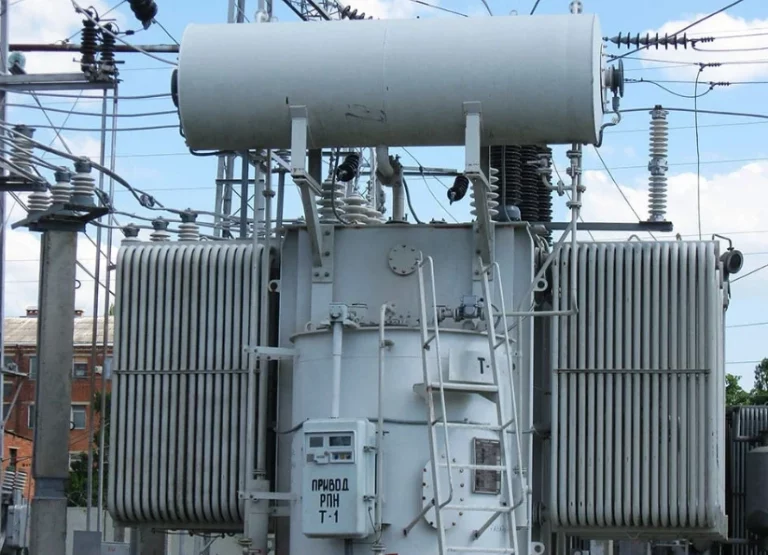

Power transformers are used in high-voltage transmission networks to step up or step down the voltage of electrical energy. Distribution transformers are used to step down the voltage of electrical energy for distribution to homes and businesses.
Power transformers and distribution transformers are both types of electrical transformers, but they have different functions and are used in different parts of the electrical grid.
Power transformers are used in the transmission network to step up or step down the voltage levels in order to reduce the electrical losses during long distance transmission. They are typically high voltage and high power transformers that operate at a higher frequency and are designed for large power capacities.
Distribution transformers, on the other hand, are used to supply power to residential and commercial areas, and are located near the point of use. They are low voltage and low power transformers designed for smaller power capacities and operate at a lower frequency. Distribution transformers are responsible for stepping down the voltage from the high voltage transmission system to the lower voltage distribution system that is used to power homes and businesses.
In summary, the main difference between a power transformer and a distribution transformer is their usage in the power system. Power transformers are used for long-distance transmission of high-voltage and high-power electrical energy, while distribution transformers are used for supplying low voltage and low power electrical energy to residential and commercial areas.
A transmission transformer steps up the voltage of electrical energy to reduce losses during transmission over long distances. It is also used to step down the voltage of electrical energy when it reaches its destination.
A transmission transformer plays a crucial role in a power transmission system. It is responsible for stepping up the voltage of the power generated at the power plant to a level suitable for long-distance transmission. The high voltage transmission reduces energy loss and enables the electricity to travel long distances with less resistance.
The transmission transformer is typically placed at a substation where the voltage is increased from the generator voltage to a high voltage that can be efficiently transmitted over long distances. The high voltage power is then transmitted over power lines to other substations where it is stepped down by another transformer to a lower voltage that is appropriate for local distribution.
In summary, the transmission transformer helps to reduce energy loss during long-distance transmission, and also enables the power generated at a power plant to be distributed to far-reaching areas. It is a critical component in ensuring efficient and reliable power transmission, and the choice of a high-quality transmission transformer is essential to ensuring the safe and effective operation of the entire transmission system.

The common connection types for transmission transformers include delta-delta, delta-wye, wye-delta, and wye-wye.
Transmission transformers can be connected in a variety of ways, depending on the specific power transmission system and requirements. The most common connection types for transmission transformers are:
Delta-Star Connection: In this connection, the primary winding is connected in delta, and the secondary winding is connected in star. This type of connection is used when the voltage at the primary side is higher than the voltage at the secondary side.
Star-Delta Connection: In this connection, the primary winding is connected in star, and the secondary winding is connected in delta. This type of connection is used when the voltage at the secondary side is higher than the voltage at the primary side.
Delta-Delta Connection: In this connection, both the primary and secondary windings are connected in delta. This type of connection is used when the voltage at the primary and secondary sides are equal.
Auto-transformer Connection: In this connection, a part of the winding is shared between the primary and secondary sides. This type of connection is used to step up or step down the voltage by a small amount.
The choice of the connection type depends on various factors, including the voltage levels, power requirements, and the location of the transmission transformer in the power transmission system. The right connection type can help ensure efficient power transmission and reliable performance of the transformer.
The distribution transformer rating refers to the maximum amount of power that a transformer can deliver to a load. It is typically expressed in kilovolt-amperes (kVA) or megavolt-amperes (MVA).
The distribution transformer rating refers to the maximum amount of power that a distribution transformer can handle without overheating or causing damage. It is typically expressed in kVA or kilovolt-amperes, which is a unit of apparent power that takes into account both the voltage and the current flowing through the transformer.
The rating of a distribution transformer is an important factor to consider when designing and installing a power distribution system. It is determined based on the expected load demand in the area where the transformer will be installed, as well as the available capacity of the electrical grid that supplies power to the transformer.
In general, distribution transformers have ratings ranging from a few kVA to several hundred kVA. The exact rating needed for a particular application will depend on a variety of factors, such as the size of the area to be served, the types of loads that will be connected, and the expected growth in demand over time.
It is important to choose a distribution transformer with the appropriate rating to ensure reliable and efficient operation of the power distribution system. Using a transformer with too low of a rating can lead to overloading and overheating, while using a transformer with too high of a rating can result in unnecessary costs and inefficiencies.

The key specifications of transmission transformers include the rated power, rated voltage, impedance, efficiency, and temperature rise.
Transmission transformers have several key specifications that are important to consider in their design and selection. Some of the most important specifications include:
Voltage rating: This refers to the voltage level at which the transformer is designed to operate. In a transmission system, the voltage levels can be extremely high, so the transformer must be designed to withstand these voltages.
Power rating: This refers to the amount of power that the transformer can handle. In a transmission system, the power levels can be very high, so the transformer must be designed to handle these loads without overheating or failing.
Impedance: This refers to the resistance that the transformer presents to the flow of current. In a transmission system, the impedance of the transformer must be carefully designed to ensure that the voltage drop across the transformer is minimized.
Efficiency: This refers to the amount of power that is lost in the transformer as it converts the voltage and current levels. In a transmission system, it is important to minimize these losses to ensure that the system operates as efficiently as possible.
Cooling: Transmission transformers generate a significant amount of heat, so it is important to have an effective cooling system in place. This can be accomplished through a variety of methods, including forced air or liquid cooling.
Noise level: The noise level of a transformer is an important consideration in many applications. In some cases, it may be necessary to limit the noise level to prevent disturbance to nearby residents or sensitive equipment.
Size and weight: Transmission transformers can be very large and heavy, so it is important to consider the physical space and weight limits of the installation site when selecting a transformer.
By carefully considering these specifications and selecting a transformer that meets the specific needs of the application, it is possible to ensure reliable and efficient operation of a transmission system.
Transformers are used in transmission lines to step up the voltage of electrical energy for efficient transmission over long distances. They are typically located at substations along the transmission line.
Transformers play a crucial role in power transmission systems. They are used to step up the voltage of electrical power generated at power plants, so it can be transmitted over long distances with minimal losses. At the receiving end, the voltage is stepped down to a safe level for distribution to homes and businesses.
In transmission lines, transformers are typically used to step up the voltage to very high levels, ranging from 138 kV to 765 kV. This high voltage is required to minimize the amount of power lost as it travels long distances over power lines. When the power reaches its destination, transformers step down the voltage to a lower level, typically between 4 kV and 35 kV, for distribution to homes and businesses.
Transformers used in transmission lines are designed to handle high voltages and high power levels. They are typically much larger and more complex than transformers used for distribution. Transmission transformers are usually located at substations, where they connect to the power lines and distribute the power to the local distribution system.
Overall, transformers are a critical component of power transmission systems, allowing power to be generated and distributed efficiently and reliably.
A transmission transformer plays a pivotal duty in the power circulation network. Its main function is to step-up or step-down the voltage degrees, guaranteeing effective power transmission over fars away.
Voltage Regulation: The transformer maintains a constant voltage level, stopping fluctuations that can harm electric tools.
Energy Efficiency: By readjusting voltage levels, transmission transformers minimize power losses throughout transmission.
Safety and security: They offer isolation in between the key and secondary circuits, making sure customer safety.
Transmission transformers play an essential duty in integrating renewable energy resources, such as wind and solar power, into the grid, allowing a cleaner and extra sustainable energy future.
Flexibility is enabled by the capacity to connect different voltage degrees across the grid.
Integrating a converter transformer in HVDC systems guarantees direct existing (DC) is converted to alternating existing (AIR CONDITIONING) and the other way around, facilitating long-distance power transmission with marginal losses.
Transmission transformers are planned for high voltage applications and are made use of to send power over cross countries, while circulation transformers are meant for lower voltage applications and are in charge of distributing electrical power to consumers.
Voltage Levels: Transmission transformers run at higher voltages, while distribution transformers operate at reduced voltages.
Place: Transmission transformers are typically located at nuclear power plant or substations, whereas circulation transformers are discovered closer to residential or business locations.
Dimension & Capacity: Transmission transformers are normally larger and have a higher capability than circulation transformers.
Cooling Methods: Due to their dimension and ability, transmission transformers usually require advanced air conditioning techniques.
The difference between power transformer and distribution is vital for professionals in the electrical industry to understand, making sure the appropriate equipment is used for the appropriate objective.
There are various kinds of transmission transformers offered, each customized to meet specific demands and applications. A few of the normal selections include:
Voltage Boosting Transformer: Enhances the power supply for effective long-distance transmission.
Step-Down Transformer: Reduces the voltage degree for circulation to end-users.
Three-Phase Transformer: Used in three-phase power systems, typical in industrial applications.
Single-phase transformers are used in single-phase power networks and are commonly seen in household setups.
Autotransformer: A solitary winding transformer that can function as both step-up and step-down.
The diagram of the transmission transformer aesthetically highlights the various kinds of transformers, aiding engineers and technicians in comprehending exactly how they are developed and feature.
The link of a transmission transformer in a power grid is vital for the seamless circulation of power. These transformers are purposefully placed within the grid to ensure reliable power transmission and distribution.
Substation Integration: Transmission transformers are predominantly located in substations, where they get power from generating stations.
Grid Interconnection: They assist in the affiliation of grids operating at various voltage levels, ensuring a constant power supply.
Parallel Operation: Multiple transmission transformers can run in alongside manage high power needs.
Safety Features: Our transformers are created with sophisticated protective steps, consisting of breaker and relays, to prevent electric breakdowns and make certain safe procedure.
Electric engineers carefully strategize the connection of the transmission transformer to assure the security and integrity of the grid.
A transmission transformer representation gives a thorough picture of its inner operations, showcasing the different parts and their relationships. The diagram includes numerous essential elements, consisting of:
Key and Secondary Windings: These are coils that receive and provide electrical energy, respectively.
It is constructed from iron or ferrite and acts as an avenue for the electromagnetic field.
Tap Changer: Adjusts the transformer’s result voltage based upon the lots requirements.
Cooling System: Ensures the transformer continues to be within operational temperature restrictions.
Insulation: Prevents electrical leaks and short circuits.
The visual representation of a transmission transformer’s inner workings, referred to as a representation, works as a useful resource for technical specialists, assisting in different jobs such as setting up, keeping, and detecting problems with the tools.
Worldwide, numerous manufacturers concentrate on transmission transformers, ensuring high quality and compliance with worldwide criteria. Some remarkable names include:
Daelim Transformer has solidified its setting as a relied on sector leader, flaunting over twenty years of quality in production and an unwavering dedication to conference and exceeding UL criteria.
Siemens: A global titan in the electrical industry, Siemens offers a variety of transformers catering to numerous applications.
ABB: Known for its cutting-edge solutions, ABB’s transformers are used worldwide.
General Electric (GE): With an abundant background in electric engineering, GE’s transformers are synonymous with dependability.
Schneider Electric: Their transformers are created for performance and sustainability.
Ensuring the highest degree of high quality, imagination, and consumer joy, transmission transformer producers commit themselves to providing remarkable items.
Converter transformers in HVDC (High Voltage Direct Current) systems are essential for long-distance power transmission. Their primary function is to convert rotating present (AIR CONDITIONER) to guide current (DC) and the other way around. Trick aspects consist of:
Minimal energy loss over long distances is ensured by HVDC transmission, made possible by the use converter transformers, which improve the process.
Flexibility: These transformers make it possible for the transfer of energy between grids operating at inconsonant regularities, suiting different power systems and enhancing general grid resilience.
Lowered Infrastructure: HVDC systems call for less transmission lines, resulting in cost savings.
Security: Converter transformers improve grid security by avoiding the spread of electrical disturbances.
Integrating a converter transformer in HVDC systems is a testimony to the developments in electrical design, paving the way for effective and dependable power transmission.
The Guanella and Ruthroff transformers are both utilized in transmission lines, however they have distinct differences in style and capability.
The Guanella transformer flaunts multiple winding arrangements, whereas the Ruthroff transformer includes a single winding design.
Guanella transformers can work as 1:1 baluns, efficiently transforming balanced signals to out of balance ones.
Frequency Range: Guanella transformers are recognized for their broad frequency array, making them ideal for various applications. Ruthroff transformers, on the other hand, have an extra minimal frequency array.
The Guanella transformer is generally more complex in layout because it involves numerous winding setups, whereas the Ruthroff transformer is simpler with its single winding style.
Applications: Guanella transformers are frequently found in superhigh frequency (RF) applications due to their vast transmission capacity. Ruthroff transformers are typically utilized in insusceptibility matching situations.
Experts in the field need to realize the distinctions in between the Guanella and Ruthroff transformers to see to it they choose the ideal transformer for specific usages.
Transmission transformers serve as the backbone of power transmission lines, making certain electrical power is communicated effectively and securely over huge ranges. Their significance includes:
Voltage Regulation: They readjust voltage degrees, making certain power is transmitted with marginal losses.
Safety and security: By giving seclusion between circuits, they avoid electrical mistakes and safeguard devices.
Combination: They help with the smooth incorporation of different power resources, such as renewables, right into the grid.
They guarantee nonstop power supply also in difficult circumstances by utilizing innovative safety equipment to enhance integrity.
Power transmission transformers play an important role in the performance of the electric grid, making it possible for the reliable distribution of electrical power to numerous markets, including households, industries, and commercial establishments, and hence, they are vital to the smooth procedure of modern society.
The cost of a Capacitor Voltage Transformer (CVT) can differ dramatically as a result of several market-specific elements that impact its rates.
The rate of the CVT is greatly affected by its specs, including its capacity, voltage score, and features.
Brand name: Established brand names with a reputation for high quality and reliability may regulate greater costs.
Application: Specialized CVTs designed for certain industries or applications can be extra pricey.
Geographical Location: Prices can vary based upon regional need, import tasks, and transport costs.
Extended warranties and solid after-sales sustain from suppliers might cause enhanced prices.
It’s vital to note that while rate is a factor to consider, the integrity, effectiveness, and durability of the CVT transformer need to be vital when making a purchasing choice.
Transmission transformers are classified right into numerous kinds based upon their style, application, and performance. These categories consist of:
Boost and Step-Down Transformers are utilized to customize voltage degrees in order to facilitate efficient transmission and distribution of power.
Seclusion Transformers: Provide electric seclusion to make certain user safety and tools protection.
Phase-Shifting Transformers: Control the power flow in specific grid lines, enhancing grid stability.
Autotransformers: A much more portable style with a solitary winding, using both step-up and step-down functionalities.
Specialty Transformers: Designed for particular applications, such as converter transformers in HVDC systems.
The option of transmission transformer type depends upon the certain requirements of the power system and the wanted results in terms of performance, safety, and integrity.
A power distribution transformer plays a vital role in the electrical power distribution process by minimizing high voltage levels from transmission lines to secure and usable levels for homes, companies, and industries, making sure reliable and trusted power supply.
The working principle of a power distribution transformer is based on electromagnetic induction. When alternating existing (AIR CONDITIONER) streams with the key winding, it creates an electromagnetic field. This magnetic field generates a voltage in the additional winding, which is utilized to supply power to the end-users.
Power circulation transformers are essential for the efficient and safe and secure transmission of power from power stations to consumers. Without these transformers, converting the high voltage from transmission lines to an ideal degree for households and business facilities would be challenging.
Security is ensured by providing the ideal voltage to lower the possibilities of electrical risks.
Effectiveness: By stepping down the voltage, transformers decrease energy losses during transmission.
Flexibility: They fit the diverse voltage demands of a selection of electrical gadgets and equipment.
While all transformers operate on the exact same fundamental concept of electro-magnetic induction, power distribution transformers are particularly developed for the task of dispersing electricity. They are developed to deal with a wide variety of voltage degrees and are commonly extra robust than various other sorts of transformers.
Secret Differences:
Electric Voltage: Power circulation transformers are developed to manage voltage levels that range from moderate to low, whereas power transformers can managing high voltage levels.
Circulation transformers are generally more portable and have a lower capacity when contrasted with power transformers.
Application: They are largely made use of in the last leg of the power circulation system, close to the end-users.
Power distribution transformers been available in a selection of kinds, each customized to satisfy specific needs and conditions. Several of the most often encountered ranges include:
Single-phase Transformers: Used in residential areas and tiny business facilities.
Three-phase Transformers: Commonly used in industrial setups and large commercial buildings.
Transformers mounted on pads are installed at ground level and are commonly made use of in urban settings.
Pole-mounted Transformers: Mounted on utility poles and normally used in backwoods.
Making sure the reputable performance of a power distribution transformer is important for its ideal performance and prolonged lifespan. Sticking to a consistent maintenance schedule, resolving fixing demands in a prompt style, and executing safety nets can substantially prolong the transformer’s life-span.
Maintenance Tips:
Normal Inspections: Check for any type of indicators of wear, tear, or damages.
Oil Testing: Ensure that the transformer oil is devoid of contaminants.
Temperature Level Monitoring: Ensure the transformer doesn’t get too hot.
Validate the transformer’s performance by carrying out a series of electric examinations to assure it’s operating as intended.
When you find that the conventional transmission transformer on the market cannot meet your needs. Daelim has an experienced transformer design team that can design and produce a suitable transmission transformer for you. Because Daelim has fifteen years of design and production experience, and it has been used in more than 20 countries in the world.
Download Resource