ELECTRIC, WITH AN EDGE
Transformers are essential in providing electrical power to our places. Plus, they make sure that our appliances function safely to reduce the risk of electric shocks and other accidents. There are many types of transformers available on the market, One of which is a 500 kVa pad-mounted transformer.
We’ll talk about what it is, how it works, and what makes it a unique type of transformer you might need.
DAELIM is the world’s top professional transformer and electrical equipment manufacturer; it has been a reliable and trusted brand for more than 15 years.
Following international standards like ANSI, IEEE, IEC, CSA, AS/NZ, etc.,
DAELIM upholds these standards with affordable but high-quality products.

Learn more now:Seven Technical parameters of Pad-mounted Transformers
14+FAQ ABOUT THE PAD MOUNTED TRANSFORMER
-FIND THE BEST PAD-MOUNTED TRANSFORMER GUIDE ON THE WEB ALL IN ONE PLACE. SEE OUR LIST OF 14+FAQ RIGHT HERE.
How to ground the pad-mounted substation
– Regarding the grounding problem of the pad-mounted substation, first of all, we must correctly select the low-voltage public grounding bus, and the grounding grid of the box-type substation should be buried below 1m.
Seven Technical parameters of Pad-mounted Transformers
– About the small knowledge of pad-mounted transformers, here are the seven technical parameters of pad-mounted transformers, including short-circuit capacity (kVA), rated current (kV), rated voltage (A) and other parameters for your reference.
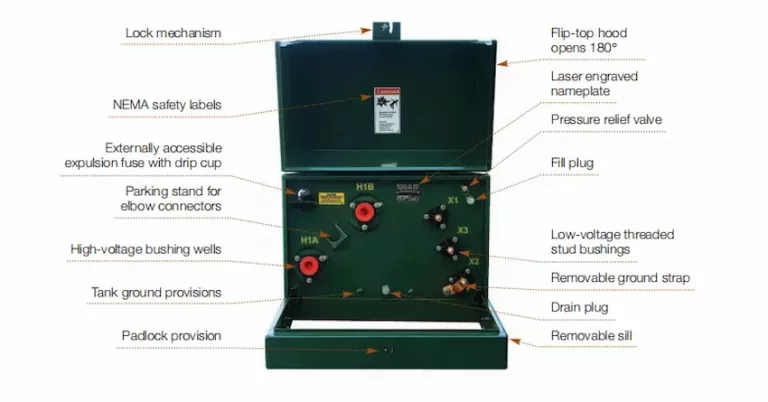
Pad-mounted transformers are ground-mounted utility distribution transformers commonly enclosed in locked metal cabinets.
These cabinets are placed on small concrete pads.
500 kVa pad-mounted transformers, on the other hand, are a kind of pad-mounted transformers capable of transforming high electrical power up to 500 kVa to supply safe voltage levels needed in residential areas.
These pad-mounted transformers are installed in service drops to allow them to step down primary to the secondary voltage on utility distribution lines.
Different specifications of 500 kVA pad-mounted transformers vary depending on the manufacturer and the brand.
However, there are some features and designs that are similar across almost all types of pad-mounted transformers.
Common pad-mounted transformers are available both in electrical and mechanical configurations.
They operate on medium-voltage distribution systems and can either be single-phase or three-phase.
500 kVA pad-mounted transformers can only be installed outdoors because they are oil-filled units.
With this, their coils are immersed in a steel oil-filled tank to maintain the desired temperature for their maximum function.
Pad-mounted transformers also contain bayonet-mount fuses placed in high voltage compartments.
The fuses protect against transformer overloads and secondary faults.

The design and dimensions of pad-mounted transformers are subjective to the manufacturer’s preferences.
Sizes will also depend on whether a pad-mounted transformer is single-phase or three-phase.
Single-phase 500 kVA pad-mounted transformers consist of two windings on each side called the primary and secondary windings.
These pad-mounted transformers are typically used to supply residential areas and smaller industrial settings.
Thus, single-phase 500 kVA pad-mounted transformers can weigh approximately 4000 lbs.

On the other hand, three-phase 500 kVA pad-mounted transformers consist of three single-phase units attached to a single three-phase system.
The common dimensions of a three-phase 500 kVA pad-mounted transformer are 68” by 62” by 70,” and it typically weighs around 5000 lbs with approximately 200 gallons of mineral oil.

The proper installation of 500 kVA pad-mounted transformers will contribute to their optimum function and performance.
Several transformer companies offer installation services to save you time and hassle.
We have listed the procedure for the proper pad-mounted transformer installation.
All new transformers should be subjected to the different standard transformer tests before installing them. These tests are the following:
For transformers stored for more than six months, additional tests should be performed, including:
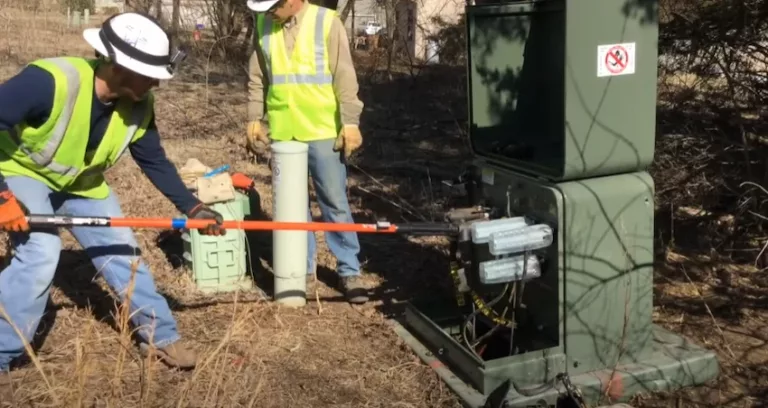

A good site for transformer installation is a place that complies with all safety codes and should not interfere with the movement of materials, personnel, and equipment.
The chosen site should also not pose any risks and hazards to the transformer.
Evaluation of foundations for the transformer includes examining the soil characteristics and concrete work.
Most soils can bear a pressure of 2500 lbs/ sq ft.
You should also note that clay soils are highly compressible, which may require you to stabilize back-fill.
Once the transformer is delivered and received, inspecting it for possible damage during shipment is important.
The preliminary examination should be done before the transformer is removed from the car or truck.
File a claim with the carrier in case you find any evident damage.
An internal inspection should also be done after removing the covers and panels of the transformer.
Examine for any damage, loose connections, dirt, or possible presence of moisture.
The transformer should always be inspected first before installation.
Make an inventory of all tools and hardware used in the preliminary inspection and testing of the transformer.
After making an inventory, complete verification to ensure that all the items used are properly accounted for.
Grounding is a protective measure that prevents static electricity from damaging the transformer windings.
It serves as protection when the transformer windings come in contact with the transformer core.
When lifting transformers, they should be moved and lifted in an upright manner.
All transformers are designed to provide a good grip during lifting, jacking, and rolling.
Nonetheless, it will always depend on the transformers’ weight, size, and mechanical configuration.
When the transformer is properly placed on the preferred site, make a thorough final inspection before using the transformer.
Only qualified personnel should perform the final inspection and installation of conductors.
In electrical terms, kVA stands for kilovolt-ampere, a unit of apparent power. Apparent power, measured in kVA, is the combination of real power (measured in kilowatts, or kW) and reactive power (measured in kilovolt-amperes reactive, or kVAR).
Understanding the concept of kVA is crucial in the electrical industry, particularly when dealing with transformers. It helps in determining the capacity of equipment, designing electrical systems, and improving energy efficiency.
Real power is the actual power that’s used to do work, while apparent power is the product of the current and voltage in an AC circuit. The ratio of real power to apparent power is known as the power factor.
The power factor indicates the efficiency of power usage in an electrical system. A power factor of 1 means that all the power is being used effectively, while a lower power factor indicates that some power is being wasted.
Transformers are typically rated in kVA because they have to handle both the real and reactive power in an electrical system. Therefore, a 500 kVA transformer has a capacity of 500,000 volt-amperes.
By understanding and managing the kVA in an electrical system, it’s possible to improve energy efficiency. This can lead to cost savings and a reduction in environmental impact.
The amount of power that a 500 kV line can carry depends on several factors, including the line’s impedance, length, and the current it can safely handle.
A 500 kV line can carry a significant amount of power, often in the range of several hundred megawatts. However, the exact amount can vary depending on specific line characteristics and operating conditions.
The impedance of the line affects how much power it can carry. Lower impedance allows for more current to flow, which can increase the line’s power capacity.
The length of the line also impacts its power capacity. Longer lines have more resistance, which can reduce the amount of power they can carry.
The current rating of the line is another key factor. Lines that can handle higher currents can carry more power.
The voltage level of the line, in this case, 500 kV, is a major determinant of its power capacity. Higher voltage lines can carry more power.
The prices of 500 kVA pad-mounted transformers depend on the manufacturer and key specifications.
Generally, 500 kVA pad-mounted transformers cost around $10,000 to $60,000.
The prices depend on the design, brand, and additional features that make specific transformers unique and different from their competitors.
Pole-mounted transformers are utility distribution transformers mounted on electric service poles.
They are commonly used in residential and commercial areas with industrial lighting that require light power loads.
On the other hand, pad-mounted transformers are utility distribution transformers encased in locked metal or steel cupboards that sit on small concrete pads.
You can commonly see them in places that lack space for fenced enclosures.
Additionally, pad-mounted transformers are commonly used with overhead electric power lines.
They are focused on stepping down a primary voltage to a safe level to use by consumers.
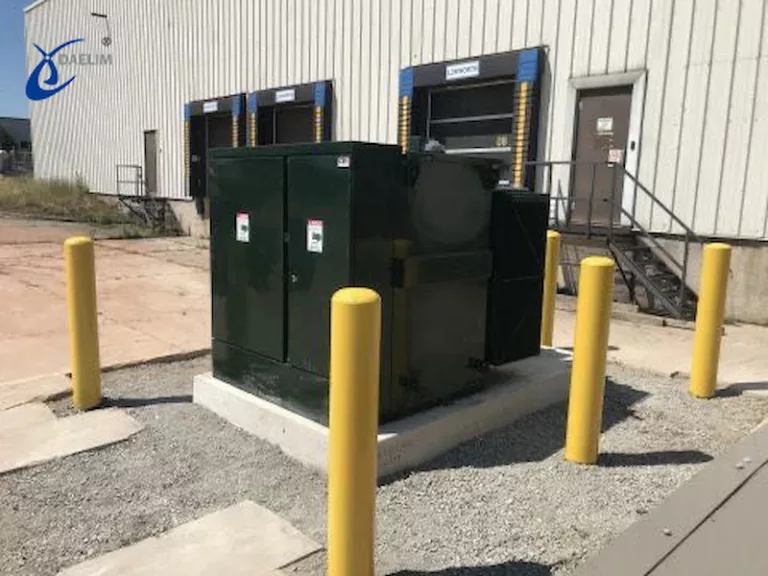
To minimize the visibility of the concrete pads with pad-mounted transformers, you can place plants near them.
You can place shrubs, grass, flowers, and other ornaments to hide pad-mounted transformers.
Place these decorations can still allow crew members to work or regularly inspect your transformers.
Before placing anything to cover pad-mounted transformers, remember the 10-feet clearance at the opening and four-foot clearance at the rear and sides of the transformer’s housing.
These clearances are important, especially when crew members will have to do maintenance or inspection.

Pad-mounted transformers are not protected in the way overhead lines and substations are.
They are electrical equipment and cans that pose an electrical risk to anyone who comes close to it.
With this, it’s important always to keep a safe distance from pad-mounted transformers to avoid any unforeseen accidents.
If you have kids, remind them not to use these transformers as playgrounds or obstacle courses.
If you find that the existing distribution transformer types or power cannot meet your requirements. You can choose to tell Daelim. Daelim has a team that has always had a wealth of design transformers, and can give you a specific design plan in the shortest time.
Daelim’s distribution transformers comply with IEEE, ANSI, CSA, IEC certification, and are used in North America (such as Canada, the United States, Mexico), South America (such as Ecuador, Chile), Europe (such as Spain, Lithuania) and some Asian countries. Daelim even has a professional installation team that can provide you with installation services.
ELECTRIC, WITH AN ENGE-- DAELIM BELEFIC
After filling in the contact information, you can download the PDF.