
ELECTRIC, WITH AN EDGE
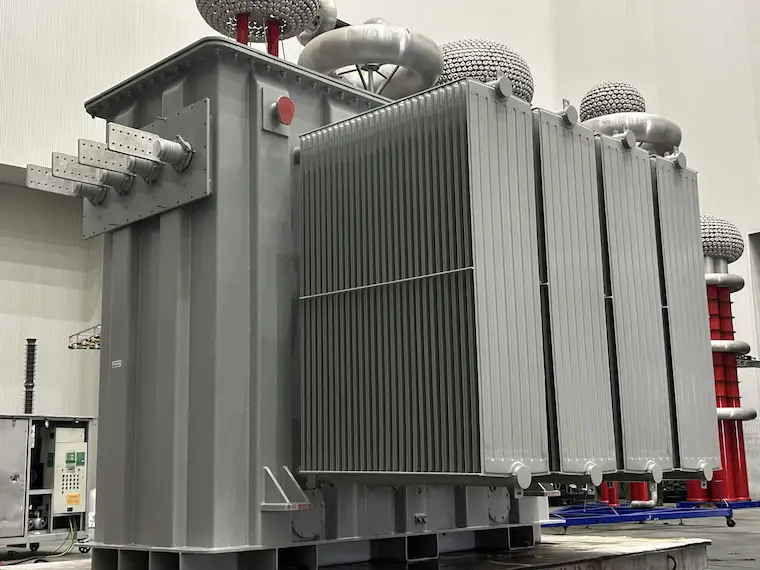
Substation transformers have been around for decades and the most common type of them is the distribution substation transformer. In this article, DAELIM, one of the top substation transformer manufacturers in the world, will provide you details about substation transformer ratings, substation transformer diagrams, substation transformer capacity, and many more.
This is crucial for consumers to learn these elements in order to make a clear purchase decision on which substation transformer they should choose from. There are several characteristics you should learn first before proceeding with what substation transformers are.
For instance, since you will learn about what distribution substation transformers are, it is vital that you understand first what distribution transformers are for you to easily understand the characteristics and components of distribution substation transformers.
Pofessional Manufacturer of Pad Mounted Transformer Substation Transformer,HV Power Transformer Single Phase Transformer IEEE/ANSI,CSA,DOE,AS/NZS,IEC and etc。standards
Daelim, an experienced producer of distribution transformers, acknowledges the important duty that substation transformers play in the efficient circulation of power across various infrastructural networks. To meet diverse power needs, we provide a thorough series of transformers, from 500kV main transformer for large power grids to single-phase distribution transformers for centered applications. Our transformers are designed to ensure a smooth and trusted power supply, making them the backbone of power circulation systems.
Substation transformers are essential for changing the voltage degrees from high to low or the other way around, making it possible for the efficient transmission and distribution of electric power. These transformers can be seen in different formats– oil-cooled transformers, liquid-filled transformers, and three-phase dry-type transformers to name a few.
The option of a transformer is commonly affected by a combination of variables, consisting of the details usage case, the amount of power required, and any restrictions enforced by the place where it will certainly be utilized.
In specific regions, pad-mounted transformers are liked for their sleek look and capability to blend in with the surrounding setting, while ground-mounted transformers are commonly selected for their functionality and toughness in industrial parks with adequate exterior room.
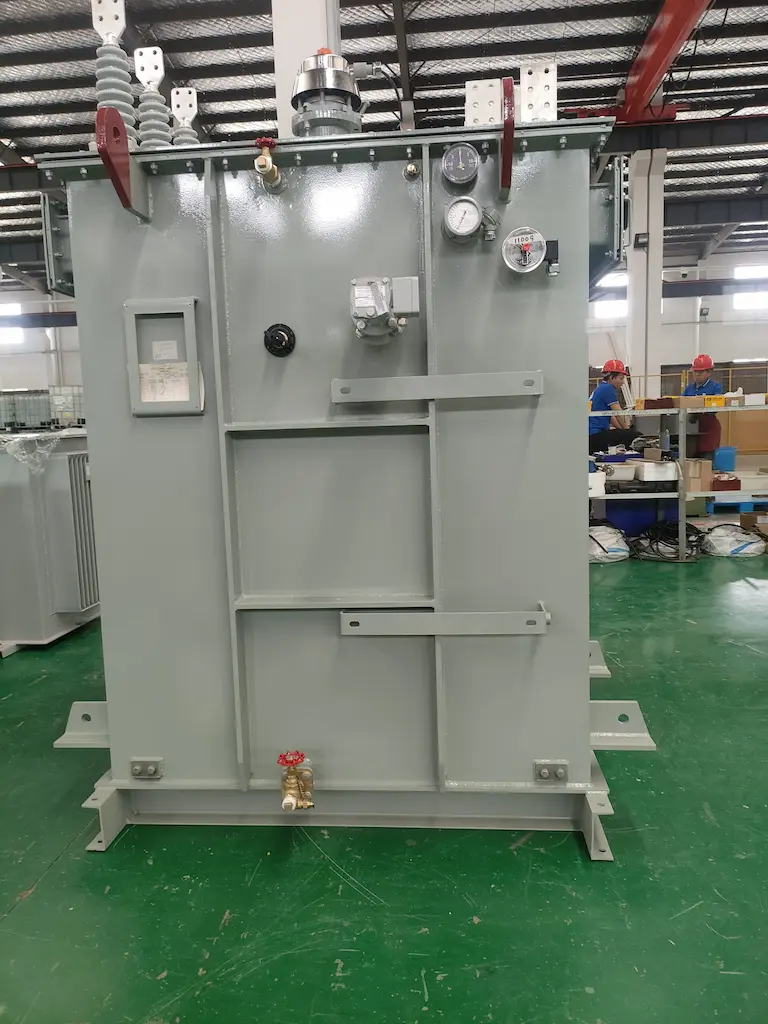

Substation transformers can be customized according to the certain power requirements of different markets, such as the distribution transformer solution for papermaking ventures, or the distribution transformer ability remedy for refining factory.
Daelim also offers a thorough description of 10kV transformers and specs, underlining our commitment to consumer education and openness in operations.
Daelim is your go-to resource for transformers for sale in Canada, providing a wide variety of solutions to satisfy your particular needs. Whether you’re looking for transformers for residential, industrial, or commercial use, we have a selection of alternatives offered, consisting of pad-mounted transformers made for residential applications. Our team takes pride in supplying customized services that guarantee integrity and effectiveness.
In the next part of this article, we will delve deeper into mobile transformer substations, high-voltage circulation transformers, and much more. Remain tuned to discover these exciting topics.
The working principle of distribution transformers is similar to the substation transformer diagram. The main working principle operation of a transformer relies on mutual inductance that is between two circuits, in which, it is linked by a magnetic flux.
In the case that the second coil circuit is closed, You can expect that current will still flow in it, and this makes electrical energy transferred through the laws of magnetism from the first coil to its secondary coil.
Distribution Transformer Solution for Papermaking Enterprises
Generally, distribution transformers like distribution substation transformers have the ability to transform high voltage level electricity to low voltage electricity in a matter of seconds for consumer use (i.e., like houses and other establishments.)
Distribution transformers have no problem distributing electrical energy to large industries with less voltage of under 33 kV and 440 V to 220 V for common domestic purposes.
Before you learn what a distribution substation transformer is, it is highly recommended that you familiarize other distribution transformers first. This is another amendment to make things easier for you to understand.
Single-phase transformers are primarily used in applications that do not need a three-phase source. This type of transformer is commonly used for repairing overhead distribution powers. The most common scenario would be residential cases.
This type of transformer is also used in commercial loads, power applications, industrial lighting, and many more. However, for applications that have a three-phase source, a three-phase distribution transformer is needed for a successful operation.
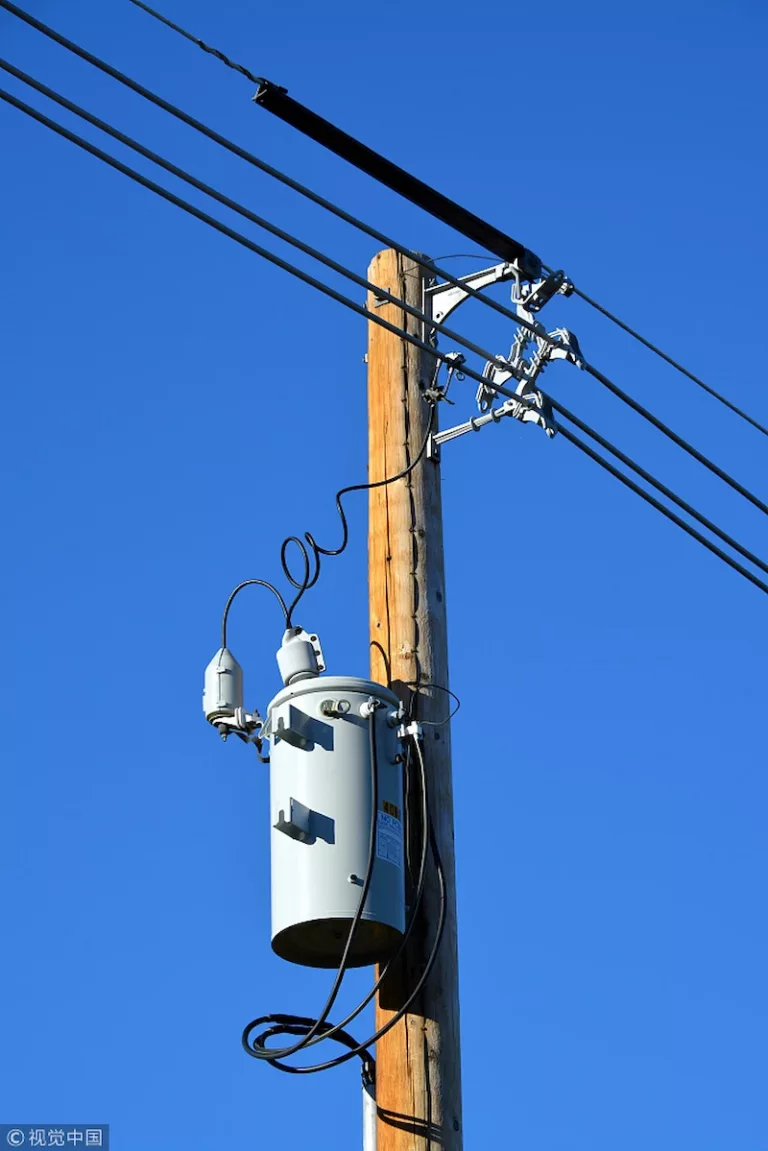

Speaking of three-phase distribution transformers, these are basically transformers that keep electrical energy from basic distribution networks to a distribution user that uses it less. This means that the transformer passes the current to a secondary distribution case that decreases the voltage primary component.
This type of transformer with a three-phase utility decreases the voltage source for the primary network to meet the user’s requirements or needs.
The voltage involved in this is often modified. Moreover, it can be different for consumers of residential and commercial areas since these electrical devices operate based on the level of ratings of frequency and voltage. This is according to the standards of various countries.
So one of the main differences between single-phase distribution transformers and three-phase distribution transformers is the employed residential application, and the pad used in primary underground networks.
There are two common types of pad-mounted transformers that are commonly seen in public, and that is the ground-mounted transformer and the pole-mounted transformer. These two are famous transformers that are safe to be exposed in public. However, they do not have the same functions.
But in general, pad-mounted transformers usually consist of metal housing, and they are set at a location where there is not enough space. For pole-mounted transformers, this simply is not the case since they can be mounted onto utility poles.
Basically, these devices can be employed with electric energy distribution lines at an overhead electrical path for lowering the primary voltage for the purpose of providing the consumers’ electricity,
One of these mounted transformers can actually serve multiple houses or buildings. Supplying electricity to a single building or house is no problem. But for large establishments like industrial buildings or factories, then a transformer of another type is best for that situation.
These transformers can be constructed and secured from corrosive elements that can pose a threat to ordinary transformers. Since they are exposed to the public, this means that outside elements like harsh weather, animals, pedestrians, etc. can easily interfere with the transformer’s operations.
Substations that use transformers can be categorized right into different teams based upon their function and feature in the electric power grid. These groups consist of:
Transmission Substation:
Function: Primarily used in the transmission network to step up or step down voltage.
Functions: Equipped with high-voltage transformers, they frequently have switchgear for controlling high-capacity power circulations.
Function: Facilitate the effective transmission of electricity over fars away by raising voltage to reduce losses (boost) or minimizing voltage for more distribution (step-down).
Distribution Substation:
Function: Located near customer locations to step down the voltage for neighborhood distribution.
Features: Typically equipped with one or several transformers, these substations reduced the voltage to degrees ideal for domestic, business, or industrial use.
Function: Serve as the last voltage makeover stage in the power grid, supplying power at functional degrees to finish customers.
Collection agency Substation:
The converter substation plays an important function in the combination of renewable energy sources into the power grid. Its key objective is to gather and step up power produced from numerous sources, such as wind farms or solar parks, at a reduced voltage level for efficient transmission. This attribute allows the reliable circulation of renewable resource, making it possible to harness the power of nature and convert it right into functional power.
Objective: Convert AC (Alternating Current) to DC (Direct Current) or vice versa in High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) transmission systems.
Attributes: Equipped with gadgets like thyristors and converters for AC-DC conversion.
Function: Enable long-distance and undersea power transmission, and attach grids with various frequencies or inappropriate systems.
Changing Substation:
Function: Mainly made use of for guiding power in the power system without altering its voltage degree. Attributes include making use of switchgear to control the flow of electrical power without the demand for transformers. This help in improving the adaptability and dependability of the grid by making it possible for maintenance, reconstruction, or isolation of particular grid areas.
Goal: Supply power to educate tracks.
Attributes: Adapt the standard power source to the proper format and voltage for train tracks.
Significance: Necessary for running electrical trains, giving secure and consistent electrical energy for trains.
Various kinds of substations serve crucial and distinct functions within the power system, resolving particular needs such as changing voltage degrees, routing power circulation, integrating renewable energy resources, facilitating long-distance power shipment, and sustaining train electrification. Choice and setup of a details substation kind are affected by aspects like website place, power demands, source of power, and grid arrangement.
When it comes to the substation transformer diagram, substation transformers basically follow the rule of thumb of transformers in general as well. Transformers are usually categorized as a passive electrical device that transfers electricity or electrical energy from circuit to circuit through the process of electromagnetic induction.
The substation transformer diagram is commonly used to increase or decrease the voltage levels between the circuits.
Selection of Power Distribution Main Transformer in 110kV Substation Design
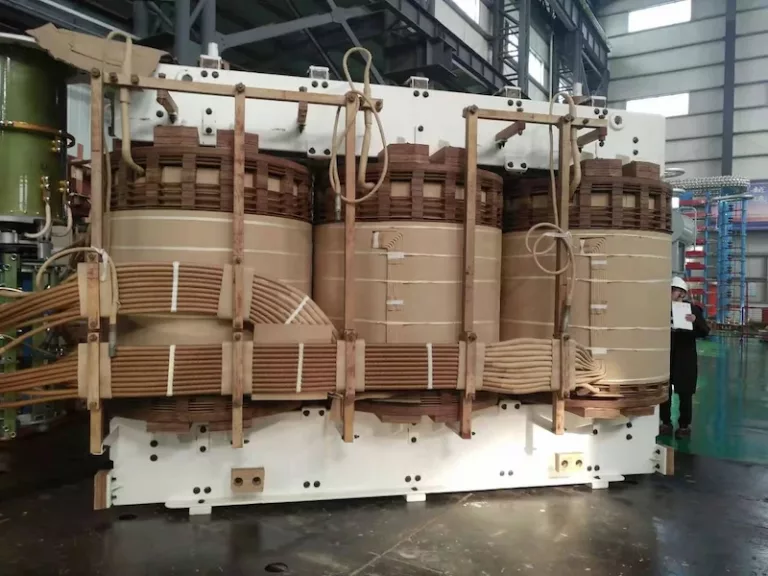

For substation transformer ratings, there is a variety of rating out there since nowadays there are a lot of substation transformers available with different ratings. This could depend on the substation transformer manufacturers if they add or decrease the traditional substation transformer ratings.
Selection of Power Distribution Main Transformer in 110kV Substation Design
This also goes the same for the substation transformer capacity because substation transformer manufacturers can nerf or tweak this aspect of the substation transformer. A typical substation transformer would normally be rated somewhere between 69-13 kV and 20 MVA.
This means that the primary voltage is usually around 69 kV. On the other hand, the secondary voltage would be around 13 kV. The substation transformer capacity has a power rating of 20 MVA or 20,000 kVA.
Selection and Capacity Calculation of Transformers Used in Substations
The connections of substation transformers indicate how three phases of transformer winding are associated with one another. There are basically two connections of the windings, the Delta which is where the end of each phase winding is linked to the start of the following phase, and the Star that connects two ends of each phase are connected with one another.
Normally, substation transformers are connected with a delta formation at the high-voltage aspect and wye for the low voltage aspect. The delta connection also isolates two systems when it comes to giving the harmonics space.
However, these are not preferred by the system. The wye connection on the other had established a convenient neutral point for the purpose of connecting it to the ground.
Connection Mode of Working Winding of Three-phase Transformer
This indicates that the transformer is capable of changing the low voltage side voltage in order to maintain nominal voltage at customer service points. The voltage at customer service points can fluctuate as a result of either primary system voltage fluctuation or excessive voltage drop due to the high load current.
Transformer taps effectively change the transformation ratio and allow voltage regulation of 10–15% in steps of 1.75–2.5% per tap. Transformer tap changing can be manual or automatic.
However, only under-load type tap changers can operate automatically.
Now that you know the fundamentals of substation transformers, it is time to move on to what are distribution substation transformers.
For starters, distribution substation transformers are transformers that usually operate at 2.4 – 34.5 kV voltage levels. Moreover, distribution substation transformers deliver electric energy or electricity directly to residential consumers. For industrial consumers, this is also possible as well.
Distribution feeders also transport power from the distribution substations for the purpose of delivering it to the homes of the consumers. Basically, these feeders are capable of serving multiple buildings or establishments.
In the case of the consumer’s premises, the distribution substation transformer will be responsible for transforming the voltage to the service level voltage that is directly used in households and industrial plants that are usually rated from 110 volts to 600 volts.
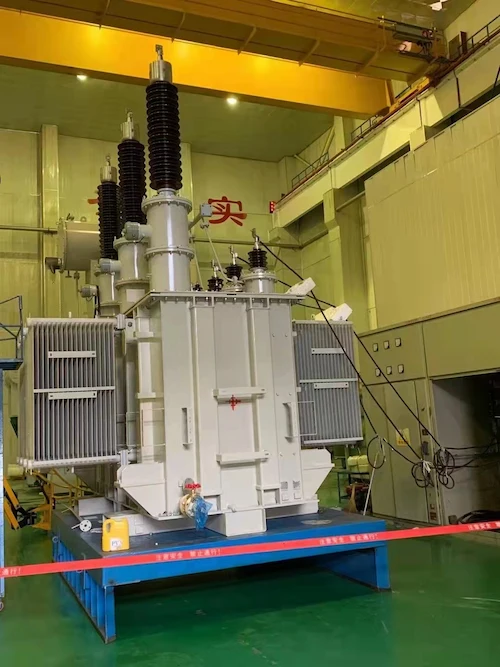

When it comes to the distribution substation transformer’s supply line, the distribution substation transformer is basically connected to a sub-transmission system with one supply line. This is referred to as the “primary feeder”.
However, keep in mind that it is normal for distribution substation transformers to be supplied with two or more supply lines. The purpose of this is to increase the reliability of the power supply in the case that a supply line is accidentally disconnected.
These supply lines are connected to the substation transformer through high voltage disconnecting switches. This is to prevent isolated lines from the substation in order to do maintenance or any repair work.
substation transformer ratings are usually expressed through kilovolt amperes or kVA. But they can be expressed in MVA as well, which means megavolt ampers. This basically indicates the amount of power there can be when there is a transferring process through the transformer.
substation transformers usually range from 3 kVA to 25 MVA.
In terms of the voltage rating, it is a different aspect from the power rating, and it is governed by the sub-transmission and distribution voltage levels in which the transformer is connected. Furthermore, there are voltages that are governed by applicable standards as well.
This is one of the reasons why the voltage rating is showcased by the substation transformer manufacturers
The voltage rating is what dictates the construction and insulation of the requirements of the transformer. This is for the transformer to be able to withstand the rated voltage or higher when the system is in operation.
In terms of the cooling medium, as mentioned there can be two possible cooling mediums used by transformers, which are mineral oil and pressurized air.
The cooling medium basically dictates what the transformer’s power rating is capable of, as well as inspecting the level of temperature it can withstand during peak demands. Transformer rating involves self-cooling ratings at specified temperatures during operations.
A pad-mounted transformer is a type of transformer that is installed on a concrete pad, typically at ground level. It is designed for outdoor use and can be seen in residential, commercial, and industrial areas. It is typically used to step down the voltage from a medium voltage to a low voltage that can be used by buildings or homes. These transformers are relatively small, and they can range in size from a few kVA to around 3000 kVA.
On the other hand, a substation transformer is a larger transformer that is typically used in electrical substations. These transformers are designed to step down the voltage from a high voltage to a lower voltage that can be distributed to homes and businesses. They are much larger than pad-mounted transformers and can range in size from a few hundred kVA to several MVA.
The main difference between a pad-mounted transformer and a substation transformer is their size and location. Pad-mounted transformers are smaller and located on the ground, while substation transformers are larger and located within electrical substations. Pad-mounted transformers are often used for local distribution, while substation transformers are used for higher voltage transmission and distribution.
Pad-mounted transformers are also typically more visible to the public, as they are often installed in areas where they are more easily seen. Substation transformers are typically located in fenced-in areas and are not as visible to the public.
Overall, both pad-mounted and substation transformers play an important role in the electrical grid, as they help to step down voltage for local use. Understanding the difference between the two can help customers to make more informed decisions about their power needs.
When it comes to substation transformers, it is important to choose a reliable and experienced manufacturer that can deliver high-quality products. Here are some reputable substation transformer manufacturers that have a strong track record in the industry:
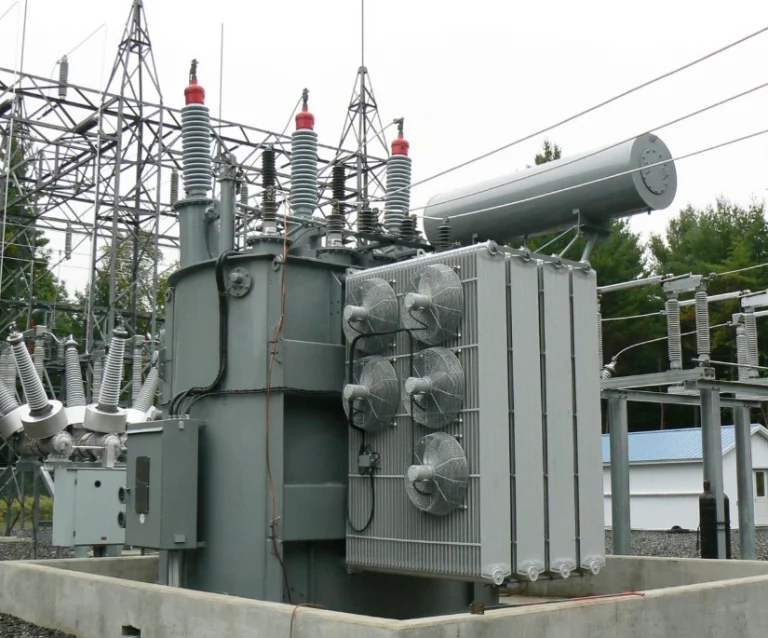

DAELIM BELEFIC TECH CO. LTD. is a well-known manufacturer of substation transformers with more than 15 years of experience in the field. Their substation transformers are designed, engineered, and produced with a focus on high-quality electrical equipment. DAELIM BELEFIC’s substation transformers are also known for being efficient, safe, environmentally friendly, and have low lifecycle costs. They strictly implement the ISO 9001 quality management system and conduct multiple quality tests to ensure that their transformers meet the required standards.
ABB Group is a leading manufacturer of substation transformers and offers a wide range of products and services related to power transmission and distribution. ABB Group has extensive experience in the design, engineering, and production of substation transformers for a variety of applications.
Siemens Energy is another prominent manufacturer of substation transformers, providing solutions for the transmission and distribution of electrical power. The company offers a comprehensive range of substation transformers, from small distribution transformers to large power transformers for utility applications.
Toshiba Corporation is a Japanese multinational company that has been manufacturing transformers for over 100 years. The company provides a range of substation transformers for various applications, including power transmission and distribution, as well as industrial and commercial applications.
Hyundai Heavy Industries Co. Ltd. is a South Korean company that offers a wide range of products and services related to power generation, transmission, and distribution. The company provides a range of substation transformers for utility and industrial applications, designed to meet the highest standards of quality and efficiency.
Overall, it is important to choose a substation transformer manufacturer with a strong track record in the industry, as this will ensure that you receive high-quality, reliable products that meet your specific needs and requirements.
The function of a substation transformer is to transfer electrical power from one voltage level to another. In a power system, electrical power is generated at high voltage levels (usually above 10 kV) and is then transmitted over long distances through transmission lines. However, this high voltage cannot be used directly by consumers. Therefore, at various points along the transmission line, there are substations that step down the voltage to lower levels (usually below 1 kV) that can be used by consumers.
The substation transformer is a key component in the substation that is responsible for stepping down the voltage. It consists of two coils of wire, known as the primary winding and the secondary winding. The primary winding is connected to the high voltage transmission line, while the secondary winding is connected to the distribution line that supplies power to consumers.
The substation transformer works by using the principle of electromagnetic induction. When an alternating current (AC) flows through the primary winding, it creates a magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary winding. The ratio of the number of turns in the primary winding to the number of turns in the secondary winding determines the amount of voltage step-down.
Substation transformers come in a range of sizes and specifications to suit different voltage levels and power demands. They are designed and manufactured by specialized transformer manufacturers, such as Daelim Belefic, who have the expertise and experience to produce high-quality, reliable transformers that meet the specific requirements of their clients.
Substation transformers come in a range of sizes and specifications to meet various power distribution needs. The size and specifications of substation transformers depend on several factors such as the level of voltage required, load demand, and the type of substation.
In general, substation transformers can be classified by their power rating, which is measured in kilovolt-amperes (kVA). The power rating of a substation transformer can range from a few kVA to several hundred MVA.
The physical size of a substation transformer is also an important consideration. The size of a substation transformer is typically determined by the amount of insulation required for the voltage level and load demand. Larger transformers will generally require more insulation and therefore have a larger physical size.
Substation transformers are also available in different specifications depending on the specific application requirements. Some common specifications include the type of cooling system, such as forced air or liquid, and the type of insulation, such as oil or dry-type.
Other specifications that can vary between substation transformers include the number of phases, the frequency, and the voltage class. The most common voltage classes for substation transformers are 69 kV, 115 kV, 138 kV, 230 kV, and 345 kV.
When selecting a substation transformer, it is important to consider all of these factors to ensure that the transformer meets the specific requirements of the application. Consulting with a reputable substation transformer manufacturer can help in selecting the appropriate size and specifications for the transformer needed.
The weight of a substation transformer can vary greatly depending on its size, voltage rating, and other specifications. Typically, smaller substation transformers designed for distribution-level voltages (typically up to 69 kV) have a weight of a few thousand pounds, while larger substation transformers designed for higher voltage levels (up to 765 kV) can weigh several hundred thousand pounds.
The weight of a substation transformer is an important consideration when it comes to transportation, installation, and maintenance. Larger transformers often require special equipment for transportation and installation, such as cranes and heavy-duty trucks, while smaller transformers can be transported using standard flatbed trailers.
It is important to consult the manufacturer’s specifications for a particular substation transformer to determine its exact weight, as well as any special transportation or installation requirements.
Substation transformers are excellent electrical devices that are a combination of both a substation and a distribution transformer. Basically, they are capable of doing what substations and distribution do.
This means that if your purpose or project requires distribution operations, then the substation transformer is a great option to choose from.
However, if you have any questions or clarifications about substation transformers, it is best to contact DAELIM’s team of professionals first before making a purchase decision. This is to ensure that you are getting the right type of transformer for your project or usage.
After filling in the contact information, you can download the PDF.