
How to Choose Pad Mounted Transformer?
Table of Contents Selecting the right pad-mounted transformer requires careful consideration of several critical
ELECTRIC, WITH AN EDGE
Transformers are among the most important machines globally, supplying the electrical power you need for your appliances, businesses, and large establishments. The voltage is brought down or up to a level you need through these 63kv transformer.
Transformers have various kinds and classifications depending on their applications, such as the 63kV transformer. To help you understand, let’s talk about what it is, its types, specifications, and its role in mining power supply in this article.
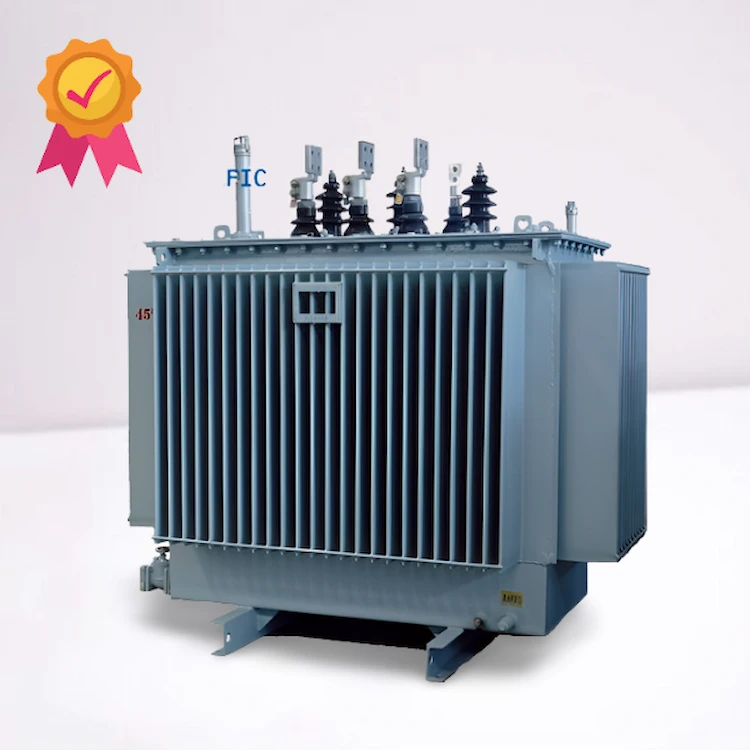

DAELIM is top-notch electrical equipment and transformer manufacturer. For more than 15 years, several clients have trusted this company, as they follow international standards, including ANSI, IEEE, IEC, CSA, AS/NZ, and the like.
These distribution transformers are useful in everyday situations, especially in industrial establishments. Proper handling and maintenance of these machines will allow maintained power generation and distribution, preventing any power disruption that can affect the efficiency of businesses.
At Daelim, we value our clients and want them to experience the best possible transformer they need. With our premium-quality transformers and services, we can guarantee that we offer our products at the most affordable price, staying on top of our competitors.
When choosing a transformer for your system, you will need to consider the size of the project as well as your budget. If you are just starting out in production, it is likely that the cost of other transformers will be prohibitive with this in mind. However, more experienced producers are more likely to have a larger budget that can accommodate these project costs and can choose from a wider range of models and brands.
Many producers around the world are choosing Daelim 63 kV Transformer for a number of reasons. These include the power capacity, the size, and the price. Its size is roughly identical to that of a smaller model and though it may not be as powerful as larger models, it is still capable enough of handling many small to medium-sized projects.
The price ends up being very competitive with other models in its weight class, making it one of the more affordable choices on the market today. Its power capacity of 63KV makes it one of the most powerful units in its weight class and exceeds many other models in terms of output.
When it comes to choosing a transformer for your next project, you want one that will give you as much bang for your buck as possible. It should also be highly reliable and able to last through any number of high-use sessions without breaking down or causing any errors or malfunctions during production.
The Daelim 63 KV Transformer is one of the more powerful choices on the market today, surpassing many other similar models in terms of output. Its solid copper core makes it one of the most reliable and durable options on the market, especially when compared to other types of transformers available. If you are looking for a reliable and highly-efficient power source, this is one model that you should be considering. In fact, some producers are already using it in their projects because it gives them more than they expected when they purchased it.
Many people have also found that this model is an ideal choice for small to medium-sized productions where there can be a higher risk of malfunction or failure with some models in their weight class.
A transformer 63kV is a distribution transformer that directly ventures or steps down a voltage to allow disengagement in essential households, establishments, and large companies. In order to determine the electrical vitality of these distribution transformers, they undergo several circulation transformers, diminishing high voltage levels to meet the levels required on the user’s end.
This power transformer has a rated power of 63 kVA and is a type of small power transformer with a primary voltage of 11kV and a secondary voltage of 0.415kV. This power transformer has a good heat transfer and conductive function. Additionally, it’s designed using advanced technological techniques by utilizing high-quality components and materials, assuring reliable operation.
The 63KV Transformer is one of the most frequently used Transformer. They are often used to step up voltage because they come in a variety of designs with high power and large core sizes. This article will cover the general function of this type of transformer, as well as information on its various parts and how they work together.
63KV Transformers are used in many different applications around the globe. They are designed to increase the voltage from an alternating current to a direct current. The 63KV design uses primarily iron or steel for the bases, with nickel or copper for these coils attached to keep them cool. The main purpose of the transformer is to convert a high voltage input (AC) to a low voltage output (DC).
A transformer is an electrical device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits. The voltages and currents in the circuits are too different to be connected directly, but they can be connected by a transformer.
The core of a conventional transformer consists of two coils of insulated wire wound around an iron magnetic core, many times called a pot core. One coil is known as the primary winding while the other is known as the secondary winding. When power is delivered to the primary winding, it induces a voltage in each turn of the secondary winding due to electromagnetic induction.
To ensure the quality of these distribution transformers, all have undergone the following tests as part of the manufacturer’s standard protocol:

Transformers 63 kV are power transformers mainly utilized to reduce risk during electrical transmission and improve efficiency in electrical power generation and distribution. They can run at full capacity, ensuring no power loss during their operation.
Moreover, the following are the technical 63 kV transformer specifications:
Input Voltage: 61.5 kV system voltage (nominal)
Output Voltage: 63 kV
Maximum Variation from Nominal Voltage (Peak): ±1.00% of Operating Voltage
Minimum Load Current (%): 50% of Output Current at Nominal Input and Output Voltage
Maximum Load Current (%): 100% of Output Current at Nominal Input and Output Voltages
This transformer is generally used to increase the primary voltage up to 63 kV. It can be used in “split phase” or “single phase” connection configurations. The normal operating voltage of this device is 63 kV. The transformer is capable of handling an input voltage in the range of 55-65 kV.
A typical 4-wire transformer configuration consists of two sets of windings whose output produces a complete delta connection. Each set has two windings (A and B) connected in series with two wires connected to the same terminal. Each set has two windings (X and Y) connected in parallel with two wires connected to the same terminal so that XB, XY, and XBY are connected together at the center tap.
The types of 63 kV transformers are subdivided into four classifications: dry type, oil type distribution, single-phase, and three-phase.
The transformer is an electrical device that changes voltage from low to high. There are a wide variety of Transformers, but the most common one is the transformer. In electricity, transformers are rated in kilovolts (kV) and must be capable of carrying heavy current for your power needs.
Most orders for 63kV Transformers range from about 1,000 to 3,000 kVA and larger. There are other types of transformers as well like 500KV or 400kV which you may find suitable if you have smaller electrical demands.
There are generally four types of 63 kV three-phase transformers developed for this purpose namely: a) low voltage transformer, b) medium-voltage transformer, c) high voltage transformer, and d) super-high voltage transformer.
Dry-type transformers do not require liquid incorporation to allow excess heat to dissipate and meet the standard temperature needed for a transformer’s maximum function. Instead, the transformer coils undergo construction within a gaseous medium or dry insulation.
Air is created through vacuum pressure impregnation in polyester, silicone varnish, VPI epoxy, or cast resin. The impregnation is important because this allows the transformer to survive in harsh environmental conditions.
Additionally, dry-type transformers need constant inspection and maintenance. This includes regular checking of operators’ grills, louvers, and slits to ensure that they are clean with no blockages. When these power transformers are not routinely inspected, the transformer can overheat and fail to function.
The ultimate advantage of dry-type transformers over other types is that you do not need to perform routine oil analysis on them. They have also preferred locations indoors as well as areas with higher fire-related risks. Generally, there are three types of dry-type transformers:
Vacuum-pressure-impregnated dry-type transformers are mainly used in commercial and industrial establishments. These transformers have insulation ranking in O and K classifications, withstanding extreme temperatures.
Vacuum–pressure impregnated transformers are built using temperature-resistant components and moisture-resistant polyester sealant applied by impregnating with vacuum pressure.
The main difference between encapsulated transformers with VPI transformers is the material used in their development. Instead of polyester resin, vacuum-pressure encapsulated transformers utilize silicone-based resins.
These transformers can withstand harsher environmental atmospheres because resin generally develops into a thicker varnish that is resilient to moisture, salt, and high humidity. Vacuum-pressure encapsulated power transformers are mainly used in areas vulnerable to acids, alkalis, and chlorides.
Open wound transformers are manufactured through the dip and bake method. The transformer coils are heated before dipping in extremely hot varnish during their development to undergo the baking process.
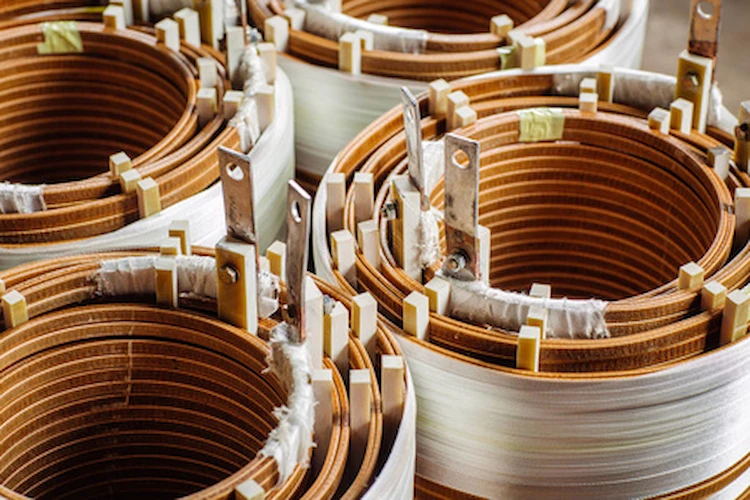

Finally, cast coil transformers are the most trustworthy during hard environmental conditions because they don’t need constant maintenance. You can often see them in tunnels, buildings, onboard ships, offshore platforms, production plants, mining services, and nuclear plants.
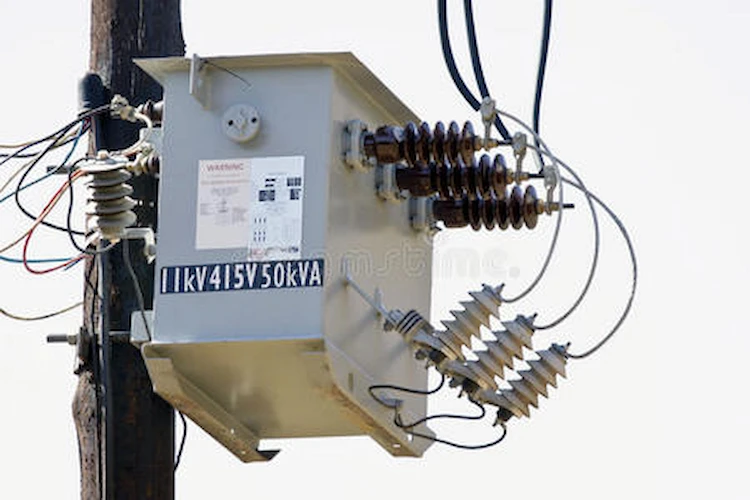

On the other hand, 63 kv oil immersed Transformers utilize combustible liquids to meet the required temperature. They are suitable for outdoor installation and storage.
Today, recent technologies have started using less-flammable liquids to replace flammable oil in oil-filled transformers. This allows these distribution transformers to be utilized in locations with stricter environmental standards and regulations.
The biggest advantage of 63 kv oil immersed Transformers is their ability to handle higher power ratings. These power transformers also have better cooling capacity than dry-type transformers because the liquid facilitates better cooling purposes. They are also cheaper and easier to assemble, repair, and maintain.
63 kv oil immersed Transformers should regularly undergo transformer oil analysis for their inspection to ensure that the mineral oil is not contaminated or degraded, which can cause a failure in the transformer function.
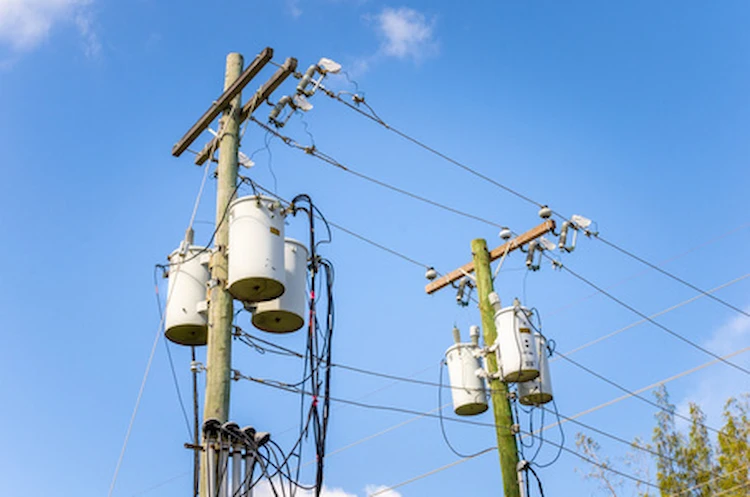

Single-phase 63 kv transformers utilize single-phase alternating currents with two alternating current power lines. They generally use one neutral wire and one conductor for an entire single circuit, forming a single pair of primary and secondary coils and producing the needed voltage.
The 63 kv Single-Phase Transformers have 2 inductive coils wound on a steel or iron core. The primary winding is the coil next to the AC supply, and the other is called the secondary winding. These transformers are mainly used to convert high voltage levels to lower levels in residential areas. Generally, they don’t need cooling systems and contain the following benefits:
Similar to three-phase 63 kV transformers, single-phase types have three common types:
On the other hand, 63 kv Three-Phase Transformers have six coils – three primary and three secondary coils. These coils are all separated at 1200 degrees from each winding. Creating 63 kv Three-Phase Transformers includes winding three single-phase transformers together on one core.
Generally, 63 kv Three-Phase Transformers are placed in dielectric oil-crammed enclosures and are utilized for industrial and heavy-duty purposes. The benefits of these transformers are the following:
The low voltage transformer is a type of electrical machine whose power rating is not more than 63 kW. They are generally used to transform the high voltage current at the interconnection of an electrical substation.
The medium voltage transformer is a type of electrical machine whose power rating ranges from 63-2000kVA. They are used in industrial facilities to limit the number of transformers in a system and also minimize their cost by grouping them together at higher nominal voltages. The medium voltage transformers are connected in parallel to increase the transfer capability of the system and also to increase their capacity.
The high voltage transformer is a type of electrical machine whose power rating is not less than 2000kVA. They are used in industrial facilities to limit the number of transformers in a system and also minimize their cost by grouping them together at higher nominal voltages. The high voltage transformers are connected in parallel to increase the transfer capability of the system and also to increase their capacity.
The super-high voltage transformer is a type of electrical machine whose power rating is not less than 5000kVA. They are used to supply electric energy at public centers like schools, hospitals, shopping facilities, etc.).

A bitcoin mining power system utilizes transformers with a power rating of 63 kV to allow efficient generation and distribution of mining power supply. This power transformer allows medium voltage conversion from a certain substation, giving the ideal power for mining. Generally, crypto mines use transformers with 1000 kVA to 5,000 kVA increments.
Bitocining mining is essential for network generation to allow transaction confirmations, which are essential to maintaining and developing blockchain ledgers.
The operating frequency of a transformer is an essential parameter to help a designer determine the proper core materials needed for transformer construction. Additionally, knowing this parameter also helps an operator identify the machine’s wires and core sizes.

An inrush current is the first current drawn during the transformer’s initial operation or runtime. The inrush current is instantaneous and lasts for several input supply cycles until it reaches the steady-state flux.
Air-cooled transformers are excellent transformer types for motor loads. Even though the inrush current of these transformers is 5 to 7 times more than the running current, their resultant lower voltages from momentary overloading provide a cushioning effect helpful for motor loads.
The 63 kv Transformers are used to step up or step down voltage. They can be made from three basic materials: iron, copper, and aluminum. Aluminum is the least expensive and has a shorter life span than metal transformers.
The coils of wire inside transformers are made with copper or aluminum. The coils are soldered together so they don’t come apart as easily. They can get hot and if they do, it is corroded or burnt and you can call that a short circuit. This makes the transformer stops working and it must be replaced.
A 63 kv transformer is used in a power station to change the voltage from the generators to supply electricity to your home. A generator is a machine that supplies electricity but not at the right voltage for your home. So stations use transformers to step up (or down) the voltage to supply your home from where it was produced by generators.
There are coils of wire inside a transformer called a primary coil and secondary coil. The coils are joined together with solder so they make sure the copper doesn’t come apart easily.
The connectors on the wires are also connected with solder so you can’t touch the copper but you can still see it.
The windings (coils) inside your transformer are made of copper or aluminum wire, depending on which one is cheaper at the time.
It is important to make sure the windings don’t get too hot because they may burn and short circuit your transformer, making it stop working.
A 63kV transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy between circuits. It is used to convert the voltage of a high-voltage power supply so that it can be used within another circuit. This makes it possible to extend the size of an electrical circuit by using a low-voltage source (such as a battery).
63kV Transformers are not only found in homes but also in hospitals and other businesses where heavy loads may be needed or limited power supplies are found. A standard automotive battery weighs about 40 pounds and stores about 12 volts of electricity. It will provide enough power for your car for about ten minutes when you first start it, but the true test comes when you need more than 10 minutes to get moving again.
63kV Transformers make it possible for elevators and other heavy electrical equipment to be powered by lower-voltage sources. Most of the modern electric power grid is fed from power stations that provide both low-voltage and high-voltage power. This kind of system effectively reduces the loss of electricity during transmission along power lines. High voltage is used to transmit electricity but only low voltage is used at each consumer site. The alternating current (AC) transformers are then used to change this low-voltage electricity into the higher-current direct current (DC).
In a 63KV transformer, the low-voltage power is transferred to the high-voltage side by means of electromagnetic induction. In both types of transformers, the principle of electromagnetic induction remains the same. At least two coils are used to accomplish electricity transfer. One coil is referred to as an inductor and is responsible for transferring power from a low-voltage source to a high-voltage side. This small coil can have its own core or it can be attached directly to another large core. The main purpose of this coil is to transfer power from one circuit to another by means of electromagnetic induction (known as mutual inductance).
There are four parts to this design. The core, coils, and shield. The core and coils comprise most of the current-carrying components of the device. The core and coils are typically soldered together for high voltage applications, but can also be separated into different sections for lower voltages.
The shield is used to protect from excessive voltage build-up in the cores that could cause arcing or short circuits if not insulated properly. If there is too much current in the core, it will heat up and break down which can lead to a problem during operation as well as overheating and eventually breakdown.
The cores are made of laminated steel, which can be broken down into several different parts. The first is a set of vertical and horizontal wire fans, also known as stackers. These are used to separate the vertical and horizontal components of the core. Other parts include the neutral and coil bobbin separator plates.
The coils, which are attached to the cores by welding or soldering, are generally made up of nickel and copper windings. They have a large number of turns, which increase in diameter as they move away from the center ring where they meet the core.
The types of transformers can be differentiated by their construction, application, and performance.
Construction: The transformer is classified on the basis of its construction such as core, shell, and oil-cooled. Core type transformers use rectangular steel laminations for insulation between the windings. Shell-type transformers have an insulating layer wound over them to provide insulation from each other. Oil-cooled transformers are enclosed in a copper jacket where the cooling fluid circulates through tubes inside this jacket to reduce power loss in the transformer due to heat generated by I2R losses.
Application: Transformer is classified on the basis of its application such as step down, step up, autotransformer and distribution. A step-down transformer reduces the voltage from high voltage to medium voltage or low voltage. A Step-up transformer increases the voltage from medium voltage to high voltage. Autotransformers can be used as both step-down and step-up transformers. A distribution transformer is used to supply lower power requirements at a load center.
Performance: Transformer is classified on the basis of their performance such as power rating and efficiency rating. The power rating of the transformer is in terms of kilowatt (kW) or KVA (kVAr). The efficiency rating of the transformer is in terms of losses or power factors.
Download Resource

Table of Contents Selecting the right pad-mounted transformer requires careful consideration of several critical

The primary function of the pad mounted transformer is to serve as a critical distribution

A pad mounted transformer operates through electromagnetic induction, serving as a crucial distribution component that
After filling in the contact information, you can download the PDF.