ELECTRIC, WITH AN EDGE
The 3 phase transformers are widely used to generate, transmit and distribute electrical power to industrial and commercial businesses, but are they practical? In this article, you will have a better understanding of the functions of a three-phase transformer. This will also give you further information about the 3 phase transformer before making an actual purchase.
When it comes to generating and transmitting electrical power to your business establishment, transformers can furnish sufficient energy to run your business efficiently. Nonetheless, there are many different types of transformers that you can choose from nowadays. Thus, it is best to pick the most suitable transformer based on your needs.
If you are a business owner that owns a manufacturing business or other industrial or commercial establishments, the 3 phase transformer is for you! This transformer is more practical when it comes to supplying large loads and large power distribution.
Although most of the utilization pieces of equipment are connected by single-phase transformers, these are not ideal for large power distribution in the viewpoint of practicality. So, if you are looking for a high-quality transformer for your business, it is best to look for it through trusted transformer manufacturers like Daelim.
DAELIM is one of the most renowned transformers suppliers around the globe. The company is committed to render only the best services and high-quality transformers that meet the client’s expectations and needs. DAELIM also offers reasonable quotes to each of their clients based on their corresponding requirements.
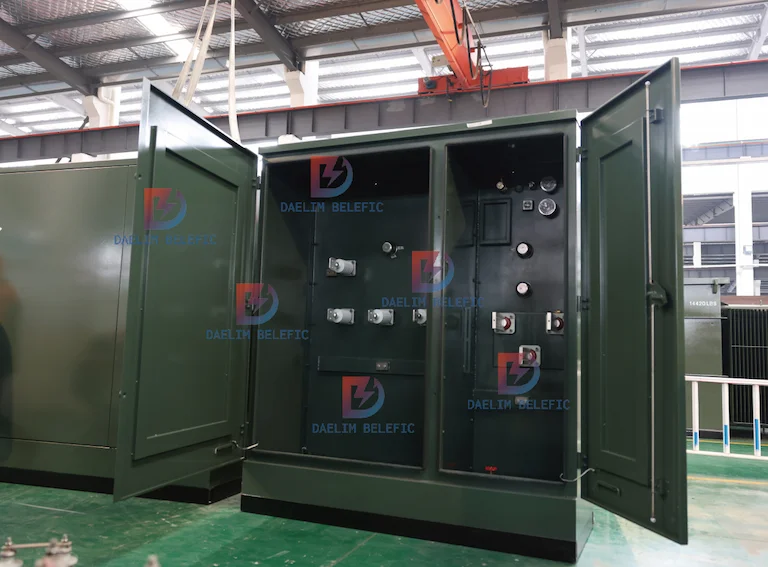

The 3 phase transformer is a transformer that runs with a three-phase electrical system. Basically, this transformer is utilized to step up or step down the high voltages in different stages of the energy transmission system. This transformer has been invented since 3-phase electricity is widely used for power distribution due to its capability to provide a balanced load.
These types of transformers are built by winding three single-phase transformers on a single core. After that, they are put into an enclosure filled with dielectric oil, which executes various functions.
Since dielectric is a nonconductor of electricity, it can render insulation between the voltage windings and the case. It also assists in cooling and preventing the formation of moisture that can dwindle the winding insulation.
The working principle of three-phase transformers is the same as the single-phase, Faraday’s Law of Induction. Single-phase and three-phase transformers only differed in wiring configurations. To further explain this, it is better to take a look at three-phase electrical systems.
A three-phase transformer is a power generator and distributor of electricity. It is a conventional method of alternating current (AC) electric energy that generates, transmits, and distributes large-scale power to furnish the energy requirement of large industries and establishments. It can also be utilized to increase or decrease the voltage in a three-phase system as needed.
The three-phase transformer uses a polyphase system, which distributes alternating current (AC) electrical power while regular power transfer is present during an electrical cycle. This is why it’s generally used by electrical grids worldwide. It’s highly capable of running large motors and other heavy loads
The fundamental operating system of a three-phase transformer is comparative to a single-phase, such as on induction. The alternating supply is supplied to the main windings and generates an EMF( electric magnetic field) in the secondary winding. The generated amount of electric-magnetic field will depend on the count of secondary turns, be it a step-up or step-down transformer.
When it comes to transformers, a three-phase has several advantages compared to the single-phase based on the following characteristics:
A three-phase transformer has a lesser mass compared to a single-phase.
A three-phase transformer is smaller in size compared to a single phase. It will only take a small portion of your space, which means you have extra space for your other things.
The three-phase transformer price is lesser than three single-phase transformers, although they are of equal ratings. You may check reputable transformer manufacturers like Daelim for reasonable prices.
A 3 phase transformer is already pre-wired. This means you’ll not have any difficulty in assembling and installing your own transformer.
When it comes to practicality, the three-phase transformer won’t disappoint you. They can furnish large loads of power and distribute them to big industries and establishments that need a high power supply. This will not also affect your energy consumption and increase your electricity bill. Your electricity consumption will stay the same as they depend on the wattage of your machines, not on the electricity connection.
Another advantage of the three-phase transformer is that it’s capable of supplying steady electricity power, which means you’ll never run out of energy.
Compared to the single-phase, three-phase only utilizes less conducting materials to send or distribute electrical power. Thus, you’ll only have to pay for fewer materials and end up saving some money on supplies.
Both single-phase and three-phase electrical systems utilize alternating current or better known as AC. AC is an electricity type, which regularly alters direction and amplitude, typically portrayed by a sine wave.
AC signals are composed of three main properties; period, frequency and amplitude. Both period and frequency define the time component of the wave, whereas amplitude determines the strength and magnitude of the electricity.
In the three-phase systems, the current has three peaks and three troughs running on three separate conductors. Alternating currents are out of phase by 120° from each other. In these types of electrical systems, the highest amplitude is reached more frequently for a given period. This helps produce power at a relatively steady rate.
This type of transformer operates with six windings, three for the primary and another three for the secondary. Each winding can be linked in either star or delta configurations. These windings can be seen as separate single-phase windings.
Therefore, three single-phase transformers can be attached to build a three-phase transformer. There are three fundamental parts of a transformer and these are the following:
The primary winding takes electrical power and generates magnetic flux when it is attached to an electrical source.
This refers to the magnetic flux generated by the primary winding. The flux crosses through a low reluctance path connected with secondary winding forming a closed magnetic circuit.
The secondary winding supplies the desired output voltage due to shared induction in the transformer. The construction of a three-phase transformer is quite similar to the single-phase transformer. Its core is also constructed either in core type or shell type. The low voltage (LV) and high voltage (HV) windings of the 3-phases are put on the three limbs of the core.
In the core type of 3 phase transformer, the core is split into three limbs. Each limb conducts both high voltage (HV) and low voltage (LV) windings of the three phases. Now, the generated flux made by the primary winding will then be linked to the secondary windings.
The low voltage winding (LV) is placed on top of the core limb and the high voltage winding(HV) is placed on the low voltage (LV) winding. This is because the amount of insulation needed is low to insulate the low voltage winding from the core.
The three-phase winding consists of three core limbs that are 120° apart from one another. In a core type, three-phase transformer, one limb functions as the return route for the magnetic flux of the two limbs. The total of fluxes in two limbs is equal to the flux in one limb that serves as the return track.
The construction of the shell type three-phase transformer is not typically used. This type of three-phase transformer has five limbs where the core encloses the windings built on the three limbs. The other two limbs found between phases keep the three limbs together, forming a unit. This also provides a return route for the fluxes.
The construction of this type is comparable when three single-phase transformers are placed on each other’s side. In contrast to core type construction, each phase has its individualistic magnetic circuit and return way for flux. Therefore, the three phases are more independent in shell-type form.
The three-phase transformer configurations have two primary forms, the delta and star. In order to understand these two better, see the given details below.
In the Delta or mesh connection, three windings are attached on both ends, creating a closed loop. Both ends are connected to a terminal, having no neutral point and use ground connections instead.
This connection type can also be configured as a high leg system by grounding the focal point of one phase. The voltage in this configuration measured across the line opposite to the center-tapped phase and ground is higher than measured across terminals.
In a Star connection (wye connection), there are three windings and four terminals. One end of the three windings is fastened to a regular neutral point or terminal, while the others form the three phases of the circuit.
The whole core structure, be it a core type or shell type, is placed inside the transformer tank saturated with oil with their windings. The three-phase winding connections are made inside the transformer tank. The primary and secondary terminals of the three phases are taken out of the tank by bushings for outside connections. The most generally used three-phase transformer winding connections are, Star-to-Star, Delta-to-Delta, Star-to-Delta, and Delta-to-Star.
Star-to-star connection type works on both small currents and high voltages, making it cost-effective for transformers. In this type of connection, the primary and secondary terminals of three-phase windings are linked, forming the letter Y.
In delta-to-delta connection, one end of a three-phase winding coil is attached to the end of another coil. When connected this way, you will notice that it will take the form of a delta, typically seen as a triangle. The delta-connected windings can produce large currents with low rates of voltages.
Star-to-delta connection is a type of winding connection used when you need to reduce the voltage levels. In this connection, the transformer’s neutral primary winding is earthed.
The delta-to-star connection is a combination of delta-connected winding on the primary side and star connection. The delta-star connection is utilized when there is a need to increase the voltage levels.
This connection type is most suited for distribution purposes because of its 3-phase and 4-wire system at the secondary side. However, its applications are restricted due to the existence of a phase shift between the primary and secondary winding.
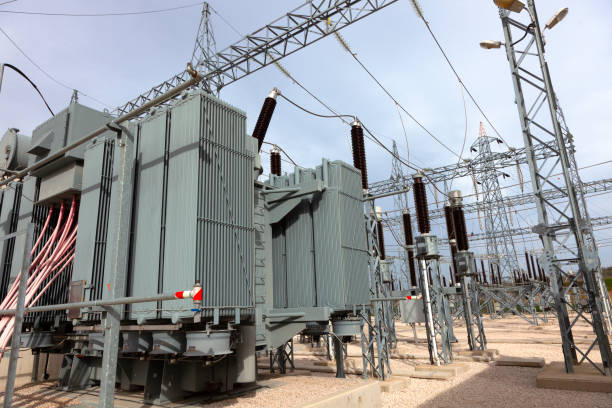

3 phase transformers are used in many industries, including manufacturing, health care, electrical contracting and many more. These mentioned industries need a reliable and consistent source of power to keep their operations running smoothly, which can be found in three-phase transformers.
These transformers can carry large loads and large power distributions efficiently that are highly required by many large industries. Most power generating channels are in three-phase nature, and the voltages range from 13.2 kV to 22 kV.
To decrease the power loss to the distribution end, the power is transmitted at much higher voltages like 132 kV to 400 kV. So, if there’s a need for higher voltages, a three-phase step-up transformer is used.
On the other hand, at the end of transmission, a step-down three-phase transformer is used to step down these high voltages to levels 6600, 400, 230 volts, etc. This is why 3 phase-transformers are ideal when it comes to power distribution for large industries as they can balance the power perfectly.
These transformers are highly dependable in converting substantial amounts of energy from the primary source into a form they can utilize for various machines and building utilities.

One of the disadvantages of a three-phase transformer is the entire unit shuts down when one phase is at fault. This is due to the core that is shared for all three units. In other words, if one unit is broken, the core of the faulty unit would instantly drench due to the absence of an opposing magnetic field.
Without the opposing magnetic field, there will be an immense escape of magnetic flux to the metal’s core enclosures. This can increase the metallic parts’ heat that can cause fires in some cases. Thus, it is critical to remember to shut down the three-phase transformer if you find that one of the phases is faulty.
Other disadvantages of this transformer are the following:

Since the three-phase unit is composed of three single phases, you can expect that it will incur higher charges as there are three phases in total that draw power from the electrical grid instead of one.
The three-phase transformer has three units that shared a common core. So, when a unit is faulty or damaged, the three units must be shut down entirely. This is why the cost of defective units is much higher than a single-phase since there are three units to repair.
A three-phase transformer is self-cooled, which means whenever it gets hot, it cools itself at the expense of your transformer’s capacity. So, whenever its temperature rises, you can expect that the power of your transformer is reduced.
Voltage regulators are used to alter the output voltage. Throughout loaded conditions, the output voltage of the transformer may recede. Thus, there is a need to regulate the voltage ratio by adjusting the tapping turns. The adjustment is done by using a tap changer, depending on the frequency with which it is needed to change the output voltage.
Thermometers are utilized for controlling the oil temperature.
Breathers are utilized to extract moisture from the air space above the oil level of the conservatoire, sustaining the dryness of the transformer oil.
Insulations serve as a barrier system, separating the windings from the core and the two windings from each other.
Transformer oil insulates and cools the generated heat from the core and windings. The oil has a high heat capacity that can carry and expel this heat. Oil flow can be produced either by the thermosiphon effect or by pumping.
The tank shields the cores and the windings from the outside conditions that can affect its functions. It also acts as a vessel for the oil.
An oil conservator is a separate container that holds the expansion of the oil as it can expand when heated.
When the oil absorbs the heat found in the system, it then delivers the heat to the cooling cooler. The cooler or cooling system accumulates hot oils and cools them down via air or water-cooled tubes then reverts them to the windings and core.
The gas actuated relay collects free gas bubbles from the transformer tank. When you notice the presence of free gas, it shows a fault inside the transformer.
These systems are safety devices used to reduce overpressure in oil flashing due to short circuits.
Three-phase refers to a three-wire alternating power circuit (AC), which means there are three alternating currents that are 120 electrical degrees apart from each other in a three-phase. Each leg alternating current can reach the maximum voltage, which is solely separated by ⅓ cycle completion. Simply put, the power production never sinks to zero and remains consistent. This is one of the primary reasons why big industries always opt for three-phase when it comes to transformers.
In the three-phase, there are two classes of circuit configurations: the Delta and the Star. In Delta configuration, it won’t need any neutral wire, only the high voltage systems will put it to use. Star configuration, on the other hand, needs both ground and a neutral wire.
To wire a 3 phase transformer, you need to put the transformer in the midst of the three-phase load and three-phase source. Then, find the three input wires on the three-phase reservoir. Put in mind that each wire stands for each phase. After finding the input wires, you may connect them from the source to the three input terminals, preferably on the primary side of the transformer.
In the three-phase power, you have three conductors and a single voltage connection. You can connect the three conductors for three-phase voltage and any pair for a single-phase voltage.
This connection involves around three hot conductors and a grounded neutral conductor. For 3 phase power, you may connect the three hot conductors while for the single-phase voltage, you may connect two or three hot conductors.
When it comes to power transmission, the three-phase transformer plays a great role in delivering substantial and constant power to various large industries, such as those in shipbuilding, steel industry, industrial manufacturing, in energy types of business like gas drilling, gas reserves, and many more.
This type of power transformer provides great assistance in generating, transmitting and distributing large loads of power supply to various establishments like hospitals, industrial buildings, apartments, transformer stations and more.
One of the distinct differences between a three-phase transformer and a single transformer is their wire count. The single-phase only requires two wires: Phase and Neutral. The phase wire is to deliver power from the source to any electrical appliance attached to it. Moreover, the neutral wire transmits the circuit back to the original energy source.
On the other hand, a three-phase transformer operates through three wires, one neutral wire and three-conductor wires. The transformers are placed in an enclosed place, jammed with dielectric oil to reach the specified voltage.
When it comes to the energy supply systems, it has two classifications, namely single phase-system and three-phase system. The single-phase is best used in places where only less power is needed, as this can only carry small loads. On the other hand, three phases are widely used in large businesses, such as factories and other industrial enterprises, where immense energy r is needed.
Another significant disparity between the two is that the single-phase only requires one neutral wire and one conductor whereas the three-phase needs one neutral wire and three conductors for circuit completion. The single-phase is also less efficient and economical compared to the three-phase in terms of power distribution because it only has one unit that operates to generate and transfer power compared to the three units of a three-phase transformer.
The single-phase is best used for home appliances since these only require small power to function, while the three-phase is ideal for large industries and running heavy loads as it has the capability to transmit large power. See the additional differences between the two below.
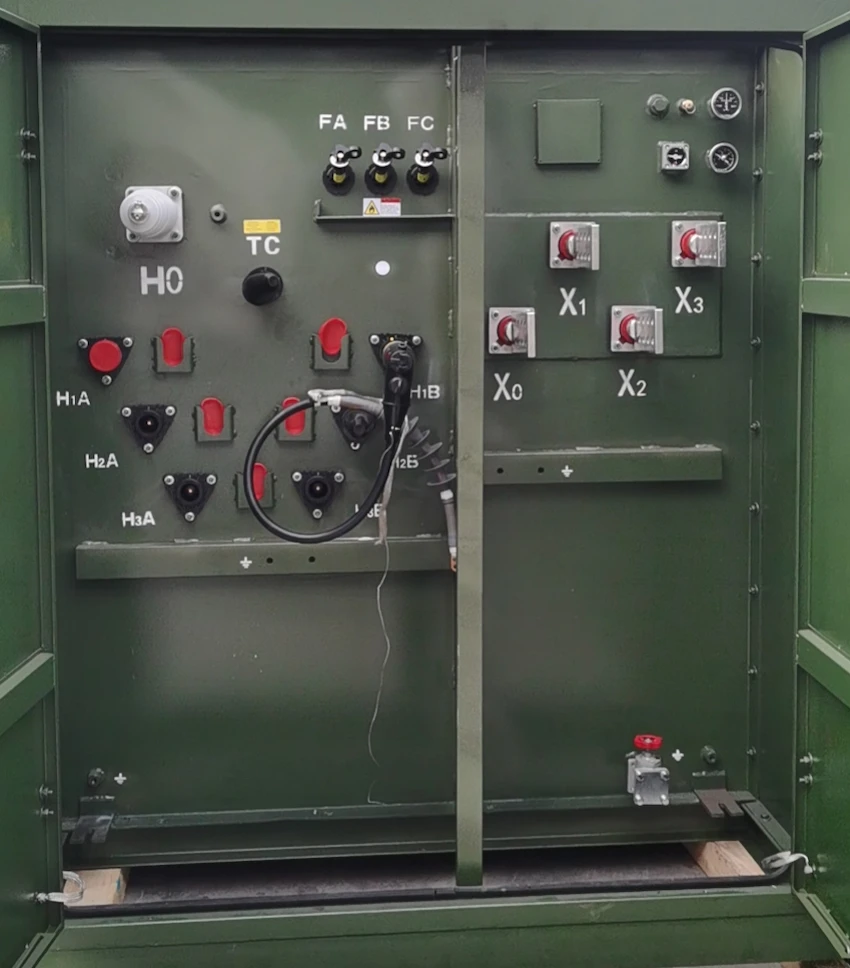

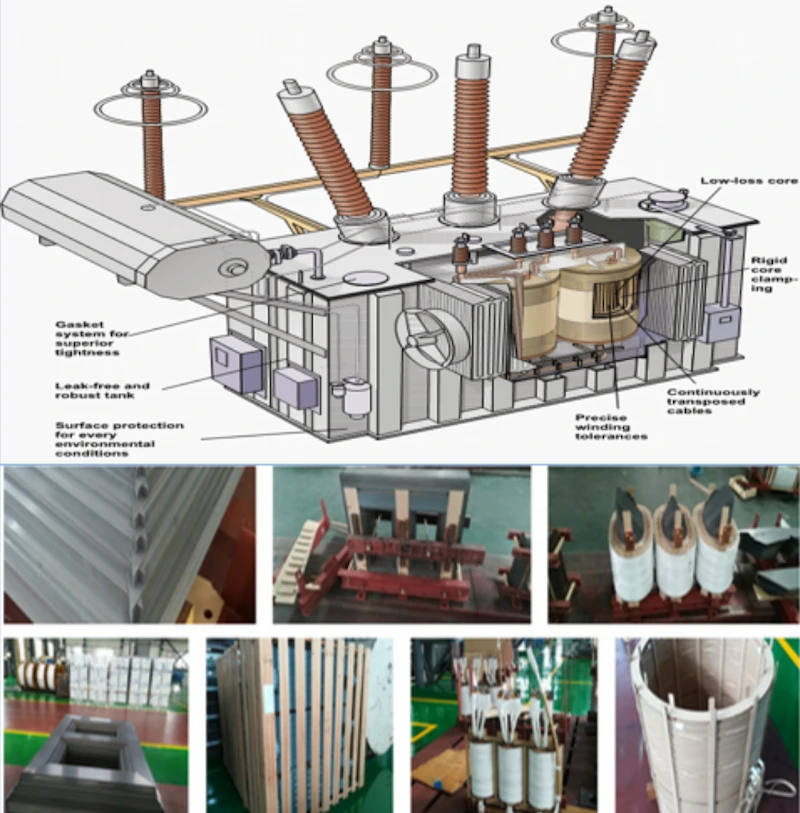
The structure of a three-phase transformer is composed of steel core, transformer enclosures and machine windings.
The steel core is one of the vital parts of a 3 phase transformer structure. It consists of three magnetic pillars that task to close the magnetic circuit. The steel core of this transformer type is crafted from electrical steel sheets, covering two sides with an insulating paint and formed collectively into the shape of a cylinder.
Another essential part of the 3-phase structure is its enclosures. The enclosure protects and maintains the life cycle of your transformer. This can be made from steel, iron or plastic, contingent on the structure of the equipment and manufacturer.
Another component of the three-phase structure is the machine winding. It has six windings insulated and wrapped around the cylinder, which receives and transmits power throughout the machine operation.
In terms of efficiency, a three-phase can help you save some cash as it can generate more power without raising your electricity consumption. It can do more for you, especially if you’re a business owner since it can supply a large amount of energy, which means no power interruption in the midst of running your business.
Three-phase transformers are typically used for producing and distributing power. They’re also used in high-power loads like motor drives, rectifiers among other equipment. Furthermore, they can also be utilized in applications that need a step up or step down of transmission lines and electrical grid station power generation.
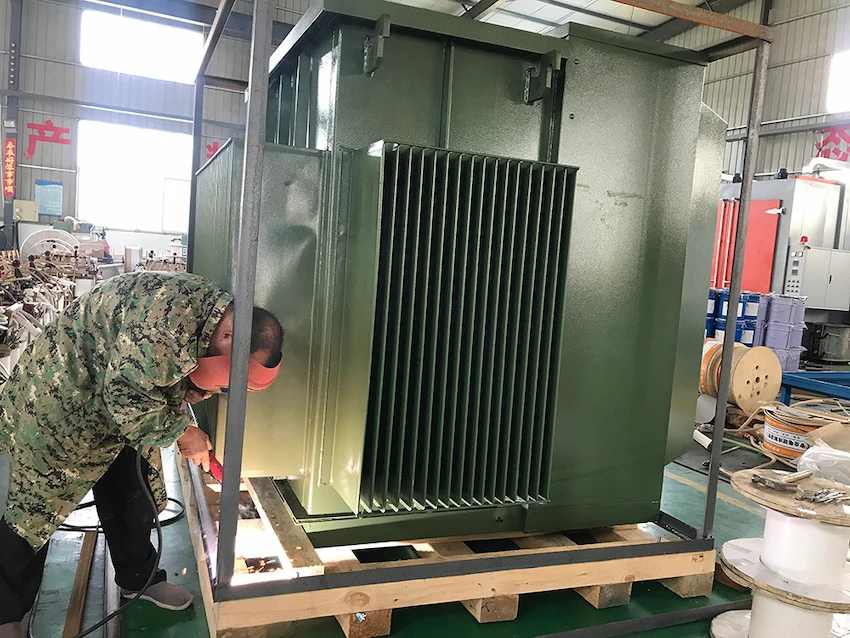

The 3-phase transformer has three types: the sealed-type, the open-type and the dry-type.
The sealed type is capable of cooling itself by expanding its blade. The blades automatically expand when they detect the high temperature in VH. When this happens, the air blows towards the blades, cooling down the machine.
The cooling system of the open-type transformer is in the extra tank and fan blade. The only contrariety between the two is the auxiliary oil tank of the open-type.
This type of transformer has coils wrapped in epoxy resin. Its windings and magnetic cores are pressurized by air, contrary to the regular transformer. This type can make up for the shortcomings of oil transformers. It’s used particularly in circumstances wherein there’s dense pollution, higher air humidity, extra cold surroundings temperature.
Daelim has been dealing with designing, engineering and manufacturing high-quality transformers for more than 15 years. Our company consists of experts and ad professionals in this field. Our team has brilliant researchers and a production team that help form and deliver exceptional and efficient transformers to various businesses and homes.
Our team undergoes intensive and methodical training committed to continuous advancement on the quality guidelines and systems. Our mission is also to meet the expectations and needs of our valued customers to earn their trust and fulfill their needs. This way, we can forge a strong and long-term partnership with our clients.
Beijing Daelim Green EP TECH Co. Ltd. is built by the experience and expertise of the people working passionately for the company. Each staff works incessantly with the thought of giving the best possible products to each of our customers. It’s in our best interest to innovate a product like a three-phase transformer to put our clients at an advantage in running their business without any interruptions when it comes to power.
We also offer product customization based on your company’s needs and demands. With us, you can expect high-level products and quick execution abilities without sacrificing the quality of the products. We also ensure that each of our clients feels special with our top-notch customer service. So, if you’re looking for transformers for your home or business, our company is always open for you.
We always stand by our company’s mission, which is to meet our customer’s needs. This is why if you choose us for your transformer’s needs, you will never go wrong with Daelim!




| Connection Type | Application | Voltage Flexibility | Harmonics | Safety |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delta-Delta | Heavy Industrial | High | Better | Medium |
| Star-Star | Low-Medium Industrial | Medium | Average | High |
Industrial Applications:
Production Plants: Used to power heavy machinery and tools.
Information Centers: Provide secure and reliable power for servers and network equipment.
Mining Operations: Power excavation and handling devices.
Business Applications:
Commercial Spaces: Energize heating, air conditioning, and ventilation systems, illumination, and work space devices.
Buying Malls: Serves the power requirements of different stores and amusement facilities.
Power Industry:
Power Plants: In power generation, distribution, and transmission.
Sustainable Power Solutions: Harnessing the Synergy of Solar and Wind Systems.
Healthcare facilities provide electrical energy to essential clinical tools.
"Getting There"
Transport Hubs: Ensure regular power supply for communication, lighting, and crucial operations.
Sprinkling Solutions: Energizing pumps and connected devices for efficient watering.
Laboratories: Providing the specific power demands for r & d.
Friendliness Industry:
Hotels and Resorts: Powering the whole center including home heating, air conditioning, and recreational areas.
Building And Construction Zones: Short-term energy solutions for devices and cars.
Summary:
Three-phase transformers are essential in various commercial and industrial sectors as a result of their efficiency, dependability, and versatility. Their application ranges from manufacturing and data facilities to medical care and hospitality, showing their indispensable role in contemporary facilities.
Comprehending Efficiency: Efficiency is the ratio of the outcome power to the input power, revealed as a percentage.
Key Parameters:
Total Consumption (P_tc): The amount of power taken in by the transformer.
Result Power (P_out): Total power provided to the lots.
Losses: Mainly copper losses in the windings and core losses.
Copper Losses: Can be found utilizing the resistance of the windings.
Core Losses: Associated with the magnetization and demagnetization of the core product.
Integrating Losses:
Instance Calculation:
Suppose P_out = 100 kW, Copper Losses = 2 kW, and Core Losses = 1 kW.
P_in = 100 kW + 2 kW + 1 kW = 103 kW.
Effectiveness = (100/ 103) × 100% ≈ 97.09%.
Quality of products, temperature, tons conditions, and so on.
Assists in selecting the suitable transformer for a details usage situation.
Leveraging sophisticated modern technology, such as wattmeters, to specifically quantify power consumption and ineffectiveness.
Concluding Remarks:
Calculating the performance of a three-phase transformer is a vital step in understanding its efficiency and suitability for particular applications. It requires knowledge of the result power, losses, and the correct use of measurement devices.
Acquaint on your own with the transformer specifications, connection type (e.g., delta or celebrity), and wiring diagram.
Guarantee that the power is shut off.
Use appropriate personal safety equipment (PPE).
Choose from delta, star, or different links depending upon the requirements of the application.
Link the main windings according to the selected configuration, complying with the transformer's handbook and local regulations.
Link the second windings according to the picked configuration, much like the primary winding.
Ensure to attach the transformer to the ground appropriately to avoid electrical dangers.
Look for correct connections, resistance, and insulation prior to activating the power.
Connect the additional windings to the tons, making sure the voltage and present rankings are appropriate.
Regular evaluation and maintenance are critical for secure and effective operation.
Conclusion:
Linking and electrical wiring a 3 phase transformer entails a number of critical actions, from selecting the proper link to circuitry the windings and grounding. Complying with the directions, security guidelines, and regular upkeep makes certain a smooth and risk-free operation.
Review the handbook and understand the specifications and security warnings.
Ensure to put on ideal individual safety equipment like gloves, safety glasses, and insulating footwear.
Always isolate the transformer from source of power throughout installation, upkeep, or troubleshooting.
Ensure that the transformer and equipment are appropriately based.
If the transformer includes oil, workout caution, as the oil can posture a danger to safety and security.
Avoiding Overloading:
Constantly make sure that the transformer's load remains within its specified restrictions, as surpassing its capacity can bring about overheating and malfunction.
Inspect regularly for indications of degeneration, damage, or safety worries.
Accredited individuals with the needed abilities and knowledge are the just one that should deal with three-phase transformers.
Guarantee that you have well-defined emergency situation procedures for taking care of electric malfunctions or cases.
Safety is critical when dealing with three-phase transformers. Adherence to safety preventative measures, appropriate use PPE, and regular assessments are crucial to stop crashes and ensure the longevity of the tools.
Make on your own aware of the guidebook, specifications, and precaution of the transformer.
Routine Maintenance:
Look for any type of indications of physical damages, overheating, or oil leakages (if the tools is oil-filled).
Routinely check the insulation resistance to prevent any short-circuits.
Validate the correct performance of the air conditioning system in the transformer, if one is present.
Monitor oil levels and quality. Replace or filter if required.
Continually observe the tons to stop the transformer from being overwhelmed.
Getting too hot: Check for overloads or cooling system failures.
Too much noise can recommend loosened elements or concerns with the core.
Inspect the links and ensure there are no short-circuits to address voltage troubles.
Keep a detailed document of all maintenance tasks, evaluations, and repairs.
Professional Services:
Look for specialist solutions and experienced advice for elaborate issues.
Final thought:
Routine assessments, knowledge of common concerns, and precise documents are important for keeping and troubleshooting a 3 phase transformer. By performing routine upkeep, prospective troubles can be determined early, causing an extensive lifespan for the transformer.
Core Material:
Usually made of silicon steel, which offers high permeability and reduced hysteresis loss.
Windings:
The core is surrounded by either copper or aluminum wires, which are wrapped around it in a spiral style.
Insulation:
Compounds such as paper, varnish, or artificial products can be employed to shield windings from undesirable aspects.
Cooling System:
Solution employing oil or air cooling to eliminate heat.
Bushings:
Insulating materials like porcelain or composite compounds are made use of to secure terminals.
Tap Changers:
Enables changing the turns proportion, controlling voltage.
Safety Devices:
Consisting of integrates, circuit breakers, and temperature level sensing units for security.
Oils tailored for transformer air conditioning and insulation.
Unit:
The metal casing guards the interior parts from the elements.
Verdict:
Three-phase transformers consist of numerous materials and elements, each offering specific features, from the core and windings that promote magnetic change to safety gadgets ensuring safe procedure. The choice of products can considerably impact the transformer's efficiency, expense, and longevity.
Understanding the Load Requirements
:
Take a look at the voltage, existing, frequency, and tons qualities to develop the correct transformer requirements.
Select either delta or celebrity arrangements depending upon the demands of the application.
Evaluate the impact of ambient problems, consisting of temperature, humidity, and available space.
Examining Effectiveness:
Select a transformer with the desired efficiency degree, balancing expense and power savings.
Warranty that the transformer abides by appropriate industry needs and guidelines.
Safety Precautions:
Consider safety functions, such as defense devices and correct grounding.
Stabilize the upfront price with lasting functional costs and cost savings.
Consulting Experts:
Seek expert guidance if the option procedure comes to be complicated.
Take into consideration the accessibility of maintenance services and warranty terms.
Recap:
Choosing the proper three-phase transformer requires a thorough assessment of the application's specs, taking into account factors such as connection type, installation website, performance rating, cost-effectiveness, and safety and security functions. A carefully taken into consideration selection procedure produces a transformer that delivers ideal efficiency and appreciates a lengthy and trouble-free service life.
ELECTRIC, WITH AN ENGE-- DAELIM BELEFIC
After filling in the contact information, you can download the PDF.