ELECTRIC, WITH AN EDGE
Electrical transformers play a vital role in the modern-day lives of every person. It may not be very apparent, but transformers help people operate businesses or power up homes and gadgets. In today’s time, where people are deeply connected with their electrical devices, it cannot be denied that electric use has become ingrained in the function of humanity. Oil-cooled Transformer has been used for many decades, and it is commonly found in electrical companies, factories, and other industries. So, what makes it special? And should you consider purchasing one?
Following international standards like ANSI, IEEE, IEC, CSA, AS/NZ, etc., for more than 15 years, DAELIM has proven itself to be one of the world’s frontrunners in manufacturing professional transformers and other electrical equipment. Daelim offers quality and inexpensive products that are sure to perform well for long periods.
Before we proceed, let’s begin with the basics: just what is a transformer?
There is a variety of transformers available in different shapes and sizes, each made for specific features. While some transformers are big in dimension, others are as little as a barrel. Regardless of their dimension, all transformers share a common purpose of regulating and taking care of currents, voltages, or electricity overall.
They have the ability to move electric power in between circuits and change voltage degrees without influencing the frequency. Currently, they are often utilized with air conditioner source of power.
This indicates that fluctuation in supply voltage is impacted by the fluctuation in the current too.
A surge in voltage implies a rise in present, and vice versa.
Furthermore, transformers boost the safety and security and efficiency of power systems by managing the voltage degrees by either tipping it up (enhancing) or stepping it down (decreasing) when required. They can dispersing and controling power also at cross countries.
Now that you know what transformers are generally used for, let us go to a more specific type of transformer, which are oil transformers.
Oil transformers are basically transformers that use oil to insulate and keep the transformer in healthy temperature levels. These transformers are built to be durable and resist high temperatures and chemical exposures.
Even giving it a full tank of oil is not enough, which is why some people improve the cooling medium of large transformers by adding external radiators which in return, makes oil circulate through the process of natural convection.
Power transformers that have high capacities can also have cooling fans since they operate at full loads but this is normally applied on power transformers that contain thousands of kVA (Kilovolt Ampere).
But for Oil-filled transformers that have a conservator or oil reservoir, you can add a gas detector relay for safety purposes. This detects the increase of gas inside of the transformer due to overheating or internal electric arcs.
In addition, this will cause a circuit breaker to cut off power from the transformer. For transformers that do not have a detector relay, they are normally equipped with another type of relay, specifically; a sudden pressure relay which has a similar function.
To help maintain the lifespan of an electrical transformer, cooling mechanisms or processes are made to help them regulate heat. Too much heat in the transformer can cause malfunctions, or worse – accidents. There are two types of cooling methods: oil and dry. In this article, oil-cooled transformers will be explained.
Dissipating heat within an electrical transformer can be done through the dry (air) method or the use of oil. As opposed to the dry cooling method that uses air as a coolant, the oil cooling method utilizes liquid or oils to minimize heat inside the transformer.
By definition, an oil-cooled transformer is a type of transformer immersed in (mainly mineral) oil that helps regulate the temperature of the transformer. Through the use of a radiator attached to the tank of the transformer, oil can dissipate heat.
Oil-immersed electric transformers are the most commonly used equipment mainly because of their simple structure and reliable operation. It has faster heat dissipation, uniform conduction, and better insulation performance than the dry-type transformer.
They are called oil transformers or oil-type transformers because they use a cooling medium or insulating liquid that is made up of mineral oil. This cooling medium is known for being effective in regulating the transformer’s temperatures compared to transformers that use air as their cooling medium.
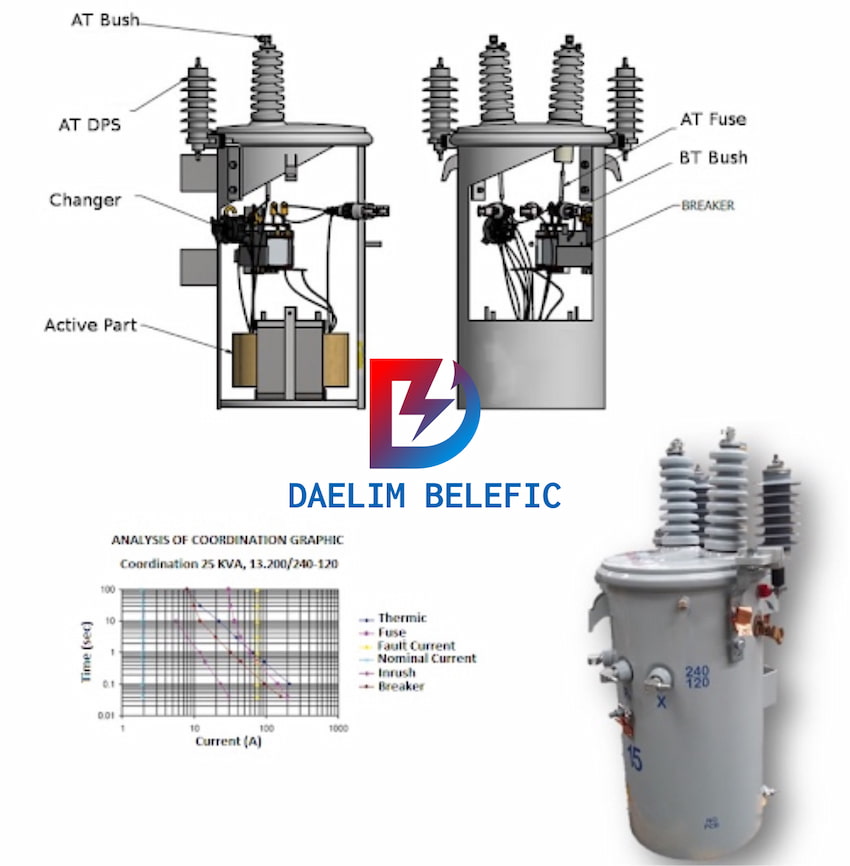
Because of its efficiency, an oil-cooled transformer is used in almost all types of usage that needs around 50 MVA rating and above. Since it can absorb and dissipate more heat, it is typically used in transformers with more oversized electrical loads.
However, due to the oil’s proneness to catching fire, oil-cooled transformers are advised not to be used in closed or indoor spaces. Transformers that usually use this cooling method are placed or installed outside the building away from people and other fire hazards.
Regardless of the cooling medium used, oil-type and liquid-type transformers are known to have better cooling than dry-type transformers. This is because liquid is considered a more effective cooling medium.
They are highly efficient cooling mechanisms that are widely used as well.
As previously mentioned, there are two types of transformers based on their cooling method or capability: the oil-cooled transformer and the dry-type transformer. Below is a gist of the difference between the two: their features, advantages, and disadvantages.
This type of cooling method of transformers uses mineral oil for heat dissipation and better insulation. It is categorized into types: Open Type transformers and Sealed Type transformers.
Oil cooling transformers also have different methods, all using oil as their primary coolant. They are as follows:
In this method, heat from the core and windings is transferred to the oil. The oil then flows upwards in the radiator, following the principle of convection. Cooled oil will then fill up space. The oil’s heat will dissipate in the atmosphere because of the natural airflow around the transformer. It is usually used for transformers rating up to 60 MVA.
Here, the oil is forced circulated through the heat exchanger using a pump. Then, compressed air is moved with the use of fans. Heat exchangers can be built separately from the tank and connected via pipes on the top and bottom. It is mainly used on higher rating transformers.
It is similar to the OFAF method. However, it uses water flow to dissipate heat from the heat exchangers instead of air. The heated water is cooled on a separate cooler. This method is used in large-scale transformers having hundreds of MVA.
The essential advantage of an oil-cooled transformer, as it is an excellent electrical insulator, is that it has good thermal conductivity for absorbing heat. On the downside, they are also considered a fire hazard and are strongly advised not to be used indoors. An oil leak can also cause pollution to the environment.
This type of transformer uses air as its cooling medium instead of oil; that is why it is called the dry type. This type of cooling method is categorized into two:
It is used mainly on small transformers up to 3 MVA. Natural air flow surrounding the tank or the transformer is used to cool down the machine.
In this method, the air is forced into the core and windings using fans or blowers. To prevent dust from accumulating, air filters are used. It is usually used for transformers with ratings up to 15 MVA.
The most apparent feature of dry-type transformers is that their core is wholly exposed instead of inside a tank. This is to allow the air to flow in and out of the core and windings freely. Another notable advantage it has over the oil-type transformer is that it reduces fire hazards; thus, it is often used in indoor spaces.
Choosing between an oil-cooled and dry type transformer would mainly depend on your budget and safety requirements. Even though oil-filled transformers are considered more efficient, you still cannot use them in some fire-prone regions. However, dry-type transformers are more prone to overheating if they experience overload. That is why in choosing which is best, consider its usage as well. Both are great transformers in their ways.
Oil transformers generally work the same with other transformers, but instead of air as its cooling medium like dry type distribution transformers, oil transformers use transformer oil as its cooling medium.
Transformer oil is an oil that is mineral-based. It is suitable for transformers because of its chemical properties and dielectric strength. It serves as a cooling medium or cooling agent to oil-type transformers.
However, it is worth noting that oil will degrade overtime which can cause faults and costly repairs in the long run.
The oil used in oil transformers are mineral oils. Specifically naphthenic, silicone, and bio-based oil.
These three transformer oils are commonly used in oil type transformers because of their compatibility. Mineral oil is simply superior compared to the other oils since it has better electrical and cooling properties.
They can be expensive, but are very worthwhile since it is considered the most efficient way to cool oil-type transformers. You can use alternatives but they can be just as expensive and less effective.
Mineral oils are common in the industry. Mineral oil is great for transformer oil because it is the most compatible oil available out there. However, it does have its disadvantages or drawbacks, one of which is that its low flashpoint.
If the mineral oil leaks, there is a huge possibility that it can start a fire. This is because mineral oil is highly flammable. For buildings, there is fire code that requires their transformers to use less flammable liquid or oil.
This where dry-type transformers are of great use because of their cooling medium. Air or pressurized air is what dry-type transformers use for them to cool down, which means there is no oil that can leak from it since it has none.
Mineral oil is also considered an environmental contaminant, and if water is accidentally mixed it will drastically degrade. This is the reason why transformers have a design that keeps water far from the oil.
This duo is known to be a common mineral oil alternative for environments that are at high-risk of fire like laboratories, constructions, inside establishments, etc. Pentaerythritol tetra fatty acid and natural and synthetic esters are more expensive than mineral oil.
So, what makes it an alternative?
Transformers need a special design change to be compatible with pentaerythritol tetra fatty acid natural and synthetic esters, which means using it can be a hassle. Natural esters have very poor oxidation stability. As a result, natural esters are the only viable solution to hernmertically sealed transformers.
Silicone or fluorocarbon-based oils are less flammable oils that are compatible with oil-type transformers. However, they are more expensive than esters and they are less biodegradable as well.
There are researchers experimenting with vegetable-based formulations as well. For instance, coconut oil. However, they are not suitable for cold climates and voltages that are over 230 kV.
Even nanofluids are being experimented for transformer use. These are commonly used as additives to improve stable and thermal and electric properties.
New bio-based transformer liquids were also introduced back in 2019. It has a low viscosity that makes it a better cooling medium that could reduce the transformer’s winding hot temperature, and improve loading capabilities.
However, since it is new, it is not widely available yet.
Transformers with oil coolants use mineral oils mainly for their chemical properties and dielectric strength. It is an excellent agent to act as an insulator and coolant for your transformer. A dielectric or dielectric material is an electrical insulator that is polarized by an applied electric field. It stops or repels electricity charged through the material.
The oil in the transformer serves as an insulator and cooling agent for the transformer. The acid will form a sludge that settles on the windings, resulting in heat dissipation.
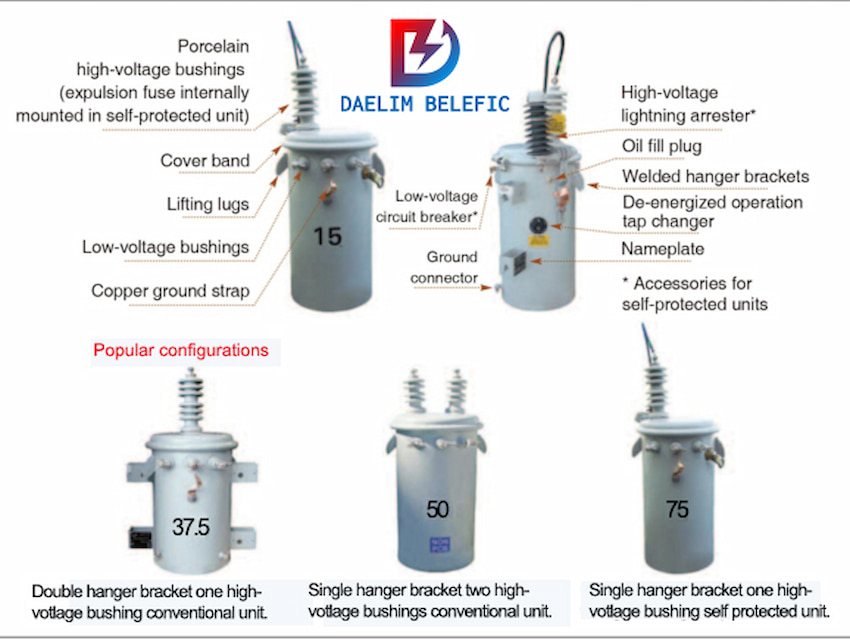

The oil in the transformer is to insulate and cool the oil transformer. They heavily depend on the oil to keep the temperatures at moderate levels to not overheat while it is operating. The oil has the ability to stay stable at high temperatures, and because of its insulating properties it regulates the transformer’s temperature.
This oil is also used in high-vo;tage capacitors, switches, circuit breakers, and even fluorescent lamps.
Aside from insulation, another function it offers is that it suppresses corona discharge and arcing. The most common transformer oil is mineral oil, but there are alternative formulations out there that are starting to make a reputation for themselves in hopes of replacing traditional mineral oil.
No, not all transformers use oil. Take dry-type transformers for instance, they utilize air or forced air as their cooling medium or cooling agent. It does have its pros and cons, which we will discuss deeper in the article.
But it is for certain that not all transformers use mineral oil to keep transformers cool.
There is not a specific transformer out there that is considered the best. However, there are transformers that are best suited for a specific environment. Take for example oil-type transformers, they are great for outdoor uses but are not advisable indoors due to their flammable components.
At this point, If you are still not sure which transformer is best for you, you may contact DAELIM’s team of professionals to help you with your concerns and confusions.
If in the case that oil runs out, the transformer can still operate but not for long as its temperature will continue to rise without insulating oil. This can also damage the transformer if it is not stopped immediately.
The oil for transformers is composed of polychlorinated biphenyl, which is a toxic chemical content that is dangerous to both humans and animals. This is why it is highly recommended that you take extra precautions when applying the oil to the transformer.
In case you didn’t know, DAELIM offers after-sale services so that you will be assisted on how to correctly apply oil to your transformer.
In this section, you will get to learn the advantages and drawbacks of oil transformers. This will help you decide if you should or should not purchase one. This greatly helps your purchase decision.
Let us first start with the advantages.
Below are the key advantages to using oil transformers
The insulating oil used to cool the transformer is highly efficient, and it has never been replaced by an alternative so far because it simply does a better job. Some alternatives are too pricey, yet less effective.
Dry-type transformers use epoxy resin that has poor heat dissipation. It is incomparable to mineral oil, in terms of heat dissipation performance.
Oil transformers are suitable for high voltages but for dry-type transformers, they are only adaptable to voltages that are below 35 kV, which is a big difference.
Depending on what oil transformer you are getting, there is without a doubt that oil transformers from DAELIM are of high-quality. You can expect the materials to be solid, which means you will not have to worry about common threats such as leaks, degrading, etc.
Below are the drawbacks of oil transformers, if there is an element that bothers you, do reconsider or contact DAELIM for clarifications.
Since you are using oil as a cooling medium, you can expect to spend more on oil transformers than of dry type transformers since dry type transformers are using air as their cooling medium. Although not that efficient, it is costly when it comes to price.
You need to keep in mind that maintaining oil transformers is a must to keep it in good condition. Regardless, oil transformers can have extended longevity if taken care of properly.
Despite its advantage to heat dissipation, the cooling medium or the mineral is flammable, and it can easily catch fire and potentially explode. In the case that an overpressure incident occurs, the engine oil spill could risk environmental pollution.
As mentioned, oil transformers usually do not pass the majority of the building fire codes nowadays, this is because its highly flammable content can easily catch on fire, and could easily spread inside establishments.
The answer is yes and no. No, because transformer oil rarely catches fire because of the structure of the tank itself. If manufactured or designed well, an oil-cooled transformer will most likely not catch fire. But since mineral oils are highly flammable, unfortunate circumstances may still cause a fire. For the following reasons, transformer oil can catch fire:
1. If a transformer is manufactured poorly, the coil insulation could be damaged and cause short circuits.
2. Local high-temperature fire caused by poor connections or connectors lead by excessive contact resistance.
3. If the iron core is damaged and current and temperature rise, internal combustibles could burn.
4. If an overload occurs and the protection of the device fails, it can cause the transformer to overheat
5. Oil quality deteriorates over time which can affect heat circulation of the oil and heat dissipation. It could lead to overheating and fire.
6. Natural phenomena like lightning strikes could ignite combustible materials.
7. If an animal tampers with the low voltage bushing of the transformer, a short circuit could start and cause a fire.

Transformer oil could be harmful to humans and animals for several reasons. First, the main component of transformer oil, polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB), is highly toxic to humans. Exposure to PCB could cause hepatotoxicity and neurotoxicity.
As also previously mentioned, if the oil quality is not maintained correctly, it could cause the transformer to malfunction and overheat. It, then, could lead to fire or combustion that is very harmful not only for humans but also for the environment.
It is a type of transformer with its primary and secondary windings completely covered with epoxy resin, preventing moisture from penetrating.
The oil in the transformer serves as an insulator and cooling agent for the transformer. The acid will form a sludge that settles on the windings, resulting in heat dissipation.
A typical transformer has several secondary windings or coils. These coils are insulated wire conductors wrapped in the laminated steel core.
In sum, oil-cooled transformers are great at dissipating heat. It is considered the most efficient type of transformer compared to the dry-type transformer. An oil-cooled or oil-immersed transformer is also categorized into three mechanisms, the OFAF, ONAN, and OFWF.
In choosing which type of transformer, you will significantly depend on your budget and usage. Also, consider the environment or surrounding where you will place the transformer.
If you are looking for a transformer that is great for outdoors, then oil transformers are definitely for you! However, if you are planning on placing it indoors or inside establishments, be aware of the fire code since one of the drawbacks of this transformer is its highly flammable oil.
If you are still undecided on which one to get, visit DAELIM and ask about which is best for your needs. Their experience in the electrical product industry will surely help you get the most efficient yet less expensive transformer to suit your needs
ELECTRIC, WITH AN ENGE-- DAELIM BELEFIC
It is a type of transformer with its primary and secondary windings completely covered with epoxy resin, preventing moisture from penetrating.