ELECTRIC, WITH AN EDGE
A power Step-Up substation is a facility where electricity converts from transmission to distribution.
This is a technology from Daelim that will change the way to use power.
Power from the transmission grid is stepped down to the distribution grid for use in homes and businesses.
The grid is a network of interconnected power systems that supply power to the population.
In this article, the step-up substation from Daelim, one of the important parts of the power grid, will be discussed.
Daelim is a well-known Chinese electrical component and solution.
Check them out if you’re seeking high-quality, well-made items that can provide remarkable results.
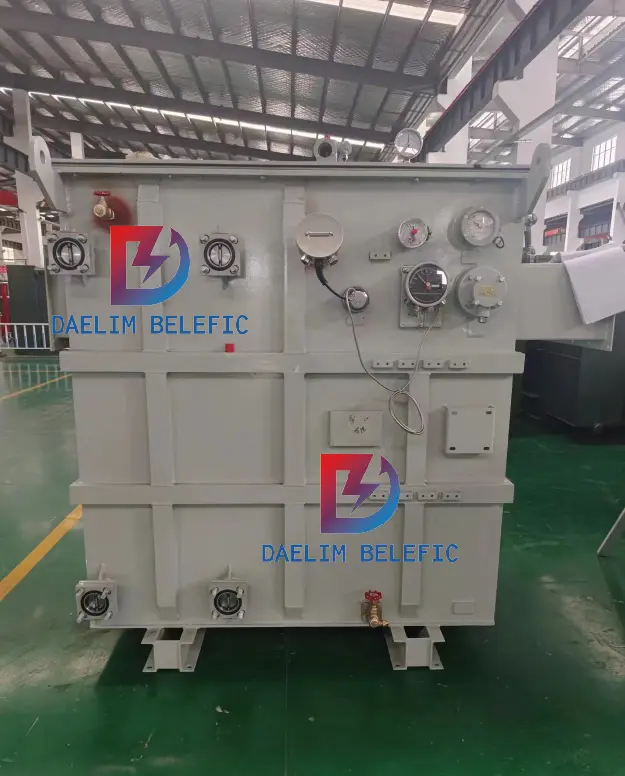

Looking for a reliable and efficient solution for your power substation needs? Look no further than Daelim Belefic, the leading manufacturer of high-quality step-up substations. With over 15 years of experience in designing, engineering, and producing electrical equipment, we provide our clients with cutting-edge service and speed, thanks to our professional customization skills and adherence to our core concept, “DAELIM EDGE+ ADVANTAGE.”
At Daelim Belefic, we are dedicated to becoming the world’s leading manufacturer of electronic equipment. We achieve this by investing in research and development, which allows us to provide efficient and professional transformer product solutions that help our clients reduce costs and create new values. Our developments meet the technical requirements of our clients and are efficient, safe, environmentally friendly, and low in life cycle cost.
We have a team of expert engineers, electrical engineers, CAD draftsmen, and more, who are familiar with international transformer standards, including IEC, IEEE/ANSI, CSA, and others. We use the latest technology, machines, and modern facilities to produce high-quality step-up substations, all while using qualified standard materials that meet the standards of world-renowned suppliers through international procurement.
We take quality seriously at Daelim Belefic, and we implement the ISO 9001 quality management system to ensure that our products meet the highest standards. We subject our products to type tests, FAT tests, and inspection tests to confirm their reliability, safety, and quality. We also offer customized solutions to meet our clients’ unique needs, and we are committed to continuous improvement through quality guidelines and practices.
Our dedicated customer service, product innovation, engineering excellence, and strong social and environmental responsibility have made us a trusted power solutions partner for the global electric industry. We aim to become a leader in the transformer industry in China, and we believe that our commitment to quality and innovation will help us achieve this goal.
Trust Daelim Belefic for all your step-up substation needs. Contact us today to learn more about our products and services, and how we can help you achieve your power solutions goals.
A step-up substation is a type of substation that gets its power supply from a near-producing facility.
It uses a large power transformer to enhance the voltage level for transmitting to a remote location.
In the step-up substation, power transmission can be done by using a transmission bus to transmission lines.
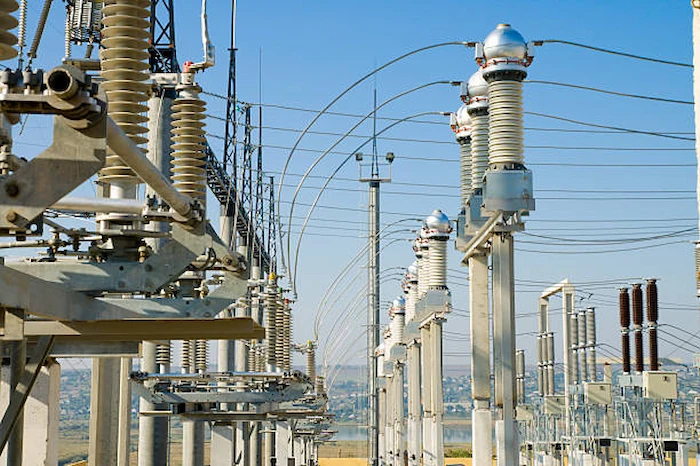

A step-up substation is an essential component in the electricity supply chain, responsible for transforming the voltage level of power from a lower voltage to a higher voltage suitable for transmission over long distances. The main function of a step-up substation is to increase the voltage level of electricity from a generator so that it can be transmitted to long distances over high voltage power lines, reducing power loss during transmission. This type of substation receives power from a generator and raises its voltage to transmission levels, typically in the range of 115-765 kilovolts. A step-up substation typically consists of transformers, switchgear, and associated equipment to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the substation. These substations are often located near the power generation plant or energy source, such as wind or solar farms, and are critical for efficient power transmission over long distances.
Moreover, it can also be a knock on the incoming power as received by generation plants.
This power plant is capable of supplying power to the operation of apparatus in the plant.
It also includes circuit breakers for switch generation and transmission circuits in and out of service as required.


1 MVA Three phase Pad-Mounted transformer 250mva 220kv – Daelim

Step-up substations are used in areas that have higher voltages than the power grid. They are used to convert high voltage electricity into lower voltage electricity. Here are two examples of two uses of it:
In generating stations, a high voltage of between 11 and 66 kV is used.
This output is fed to the step-up transformer in the step-up substation.
It increases the high voltage to ultrahigh voltage levels above 132 kV.
This enables the electricity to be transmitted on the primary transmission lines for a very long distance.
This substation is either closely located to the generating station or within the premises of the generating station itself.
The primary objective is to increase the voltage drop the current by at least a hundred times.
Thus, it can be transmitted for long distances without hearing loss.
This is made possible through thinner wires that not only increase transmission efficiency but also reduce heating losses.
Most railroads and some specific Metro Rails utilize a high voltage of 25 kV AC single phase.
This is to provide traction to the locomotives that use high power induction or BLDC motors.
Because the overhead railway traction power lines are long, a voltage drop over longer distances is possible.
Thus, it results in the locomotive not being able to get the entire 25 kV voltage supply.
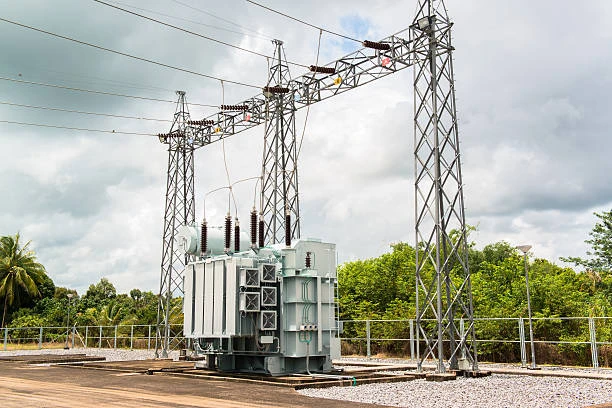

There are mainly two types of step-up substations:
Conventional Step-Up Substation: This type of substation is designed to step up the voltage of electrical power from the generator to the transmission level. These substations typically consist of a transformer, circuit breakers, switches, and other protective equipment. They are used to connect power plants to the high voltage transmission network and are typically located near the power plant.
Mobile Step-Up Substation: This type of substation is used for temporary power supply during maintenance or in emergency situations. These substations are mounted on trailers and can be easily transported to the desired location. They are designed for quick deployment and can be connected to the grid within a short period of time. They are also used in construction projects where temporary power supply is required.
Some other types of step-up substations include distribution substations, collector substations, switching substations, and transmission substations. The type of substation used depends on the specific requirements of the power system and the location.
Substations are used to improve power transmission efficiency and reliability.
The step-up transformer is a part of this category, which is designed to raise voltage levels.
There are many different types of substations.
Find out more about them here.
This type of substation is located at different points in an electrical network.
It supports the distribution and transmission of power.
Moreover, they can be connected to any part of the network and source sub-transmission or distribution lines.
This functions as the main source of electric power supply for a specific business customer.
The technical requirements and the business case for this facility greatly depend on the customer’s requirements.
This type of substation is where the main voltage distributions are stepped-down to supply voltages using a distribution network.
The voltage of any two phases will be 400 volts.
Meanwhile, the voltage between neutral and any phase will be 230 volts.
Selection of Power Distribution Main Transformer in 110kV Substation Design
An underground distribution substation is the most widely used and common type of substation.
The primary purpose of this substation is to provide all the functionality of a conventional substation while minimizing the area occupied above the ground.
Electrical substation components are essential for the installation of the substation. It is designed to prevent dangerous ground potential in areas where personnel operate switches or other apparatus.
Some of the important substation parts are powered by batteries. The size of the battery bank depends on the voltage required for operations of the DC circuit.
The two basic types are acid-alkaline batteries and lead-acid batteries.
The lead-acid batteries are of the most common type, providing high voltages at a cheaper cost.


The busbar is one of the most important elements of a substation.
It is a conductor that carries current to have numerous connections with it.
In other words, it is a kind of electrical connection where the incoming current and outgoing current take place.
It is defined as a set of multiple identical capacitors connected either in parallel or in an enclosure and utilized to correct power factors and protect circuitry, such as a transformer substation.
The main purpose is an economical technique for power factor maintenance and for correcting power lag problems.
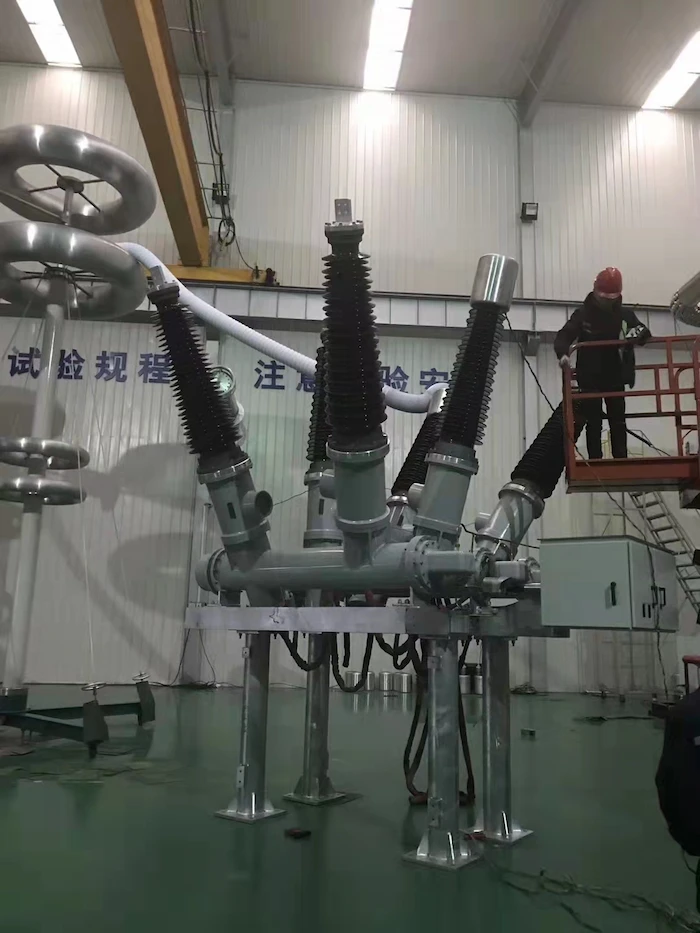


This type of switch is used to close or open a circuit when a fault occurs within the system. Circuit breakers have 2 mobile contacts that are in “off” condition in normal situations.
It will send a tripped command to the circuit breaker that moves the contacts apart when a fault occurs.
Hence, avoiding possible circuitry damages.
Preventive measures for tripping of three-side switch of 110kV main transformer
The current transformer is used for transforming higher value currents into lower values.
It is utilized analogously to that of AC instruments, control apparatus, and meters.
Also, it is used for maintenance and installation of current relays for protection purposes in substations.

The instrument transformer is a device used for reducing higher currents and voltages.
For safe and practical usage, it is measurable with traditional instruments such as digital multimeters and more.
Analysis of Performance Data of High Voltage Distribution Transformer
The Insulators do not allow the flow of electrons through them. Examples of insulators are shackle, strain type, suspension type, and stray type.
They are used in substations for avoiding contact with humans or short circuits.
The main factors affecting the insulation performance of transformers
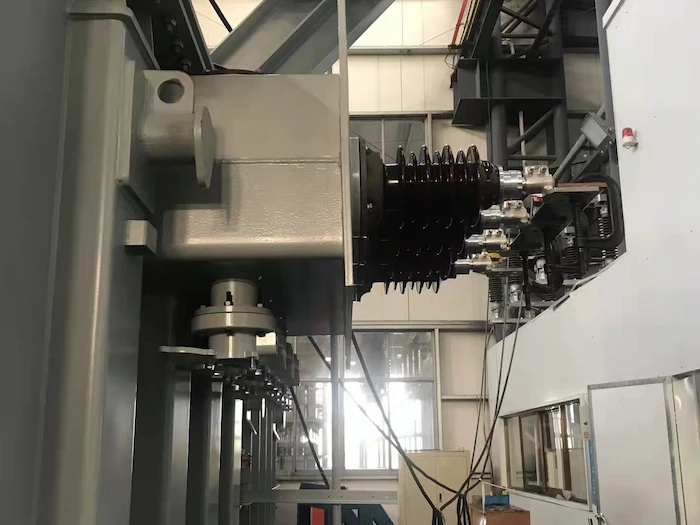


The isolators in substations are mechanical switches deployed for isolating circuits when there is a current interruption.
These are mechanically operated switches.
Lightning arresters have the function of protecting substation equipment from high voltages and are also restricting the amplitude and duration of the current’s flow.
These are connected amid earth and the line.
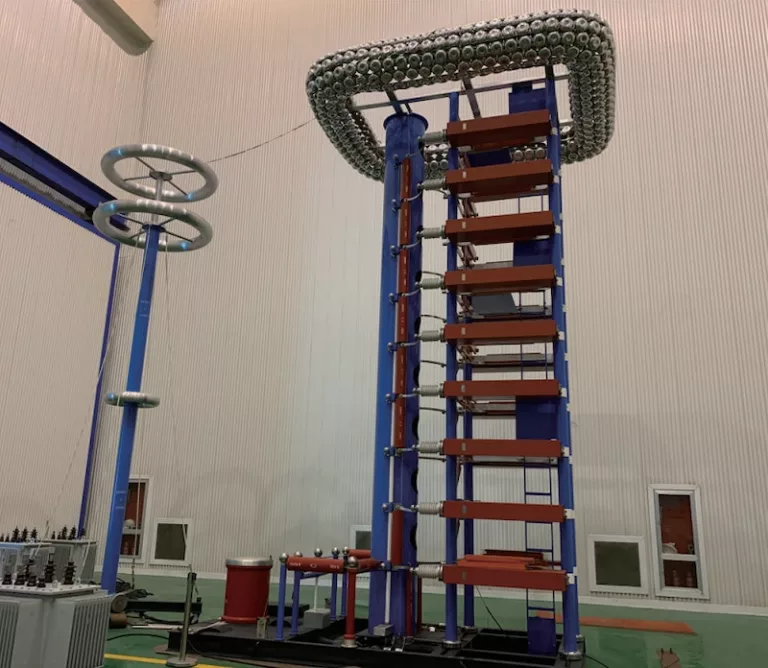

The power transformer is used to transmit electrical energy in electronic or electrical circuits between distribution primary circuits and generators.
These transformers are used in distribution networks to interface step down and step up voltages.
The relay is used when the transformer oil is heated due to fault currents and decomposed into gas bubbles.
Switchyards are used for the connection and disconnection of transformers and circuit breakers.
These also have lightning arrestors to protect the substation or power station from strokes of natural lighting.
Preventive measures for tripping of three-side switch of 110kV main transformer
Voltage transformers are devices that convert the energy of one form to another.
It is designed to present negligible load to supplies being measured.
Selection of Voltage Regulation Mode of 1000kV Transformer and Operation and Maintenance
The wave trapper is placed on the incoming lines to trap high-frequency waves.
High-frequency waves coming from nearby substations or other localities are disturbing the currents and voltages.
Wave trappers are tripping high-frequency waves that divert the waves into the telecom panel.
If you are trying to build next to an overhead line, you must consider the voltage safety clearance distances for the finished development and construction.
If the developments are near a substation, you must be very wary about buried cables.
Contact the electricity company and talk to them.
Selection and Capacity Calculation of Transformers Used in Substations

The heart of the transformer is the substation.
The transformer changes the relationship between incoming voltages and currents.
Substation transformers are known for their primary and secondary voltage relationship and their power carrying capabilities.
The electricity distribution companies are responsible for the network of underground cables, power lines, and substations that gathers the electricity going to your home or business in areas where you live.
Daelim has been supplying power and liquid-filled transformers to clients for 15 years.
Daelim products meet international standards and are built with state-of-the-art technology so that you can rely on them to power your electronics.
Step up substations offer various benefits, including:
Increased efficiency: Step up substations help increase the efficiency of power transmission and distribution systems by converting the voltage to a higher level, which reduces the energy loss during transmission.
Improved voltage regulation: By regulating the voltage to a constant level, step up substations help ensure that the electrical equipment downstream operates at the desired level, improving the overall reliability and stability of the power system.
Enhanced capacity: Step up substations are often used in large power systems, and they help improve the capacity of the system by increasing the voltage level and thus allowing more power to be transmitted.
Reduced cost: By reducing energy loss and increasing capacity, step up substations can help reduce the overall cost of the power system, making it more efficient and cost-effective.
Versatility: Step up substations are designed to accommodate various types of power sources and loads, making them highly versatile and suitable for a wide range of applications.
Increased safety: Step up substations are equipped with various safety features such as protective relays, circuit breakers, and grounding systems to ensure safe and reliable operation of the power system.
In summary, step up substations play a critical role in power transmission and distribution systems, offering various benefits such as increased efficiency, improved voltage regulation, enhanced capacity, reduced cost, versatility, and increased safety.
A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system that is used for switching, transforming, regulating, and controlling the flow of electric power. It plays an essential role in the transmission and distribution of electricity from power plants to residential, commercial, and industrial areas. The primary function of a substation is to convert high voltage power into lower voltage power that is suitable for distribution to end-users. Substations may also have equipment to protect and isolate parts of the electrical system for maintenance, repairs, or upgrades. They typically contain transformers, circuit breakers, switches, busbars, and other components that allow electricity to be transmitted safely and efficiently. Substations can be classified based on their function, voltage levels, location, and size.
Step-up substations and step-down substations are two types of substations that perform opposite functions in a power transmission system.
A step-up substation is designed to increase the voltage of electrical power received from a power generation station before transmitting it to a transmission line. This is accomplished by using a step-up transformer, which increases the voltage level to reduce the transmission losses over long distances. The output voltage of a step-up transformer is higher than the input voltage, hence the name “step-up”.
On the other hand, a step-down substation does the opposite; it receives high-voltage electricity from a transmission line and reduces the voltage to a level suitable for distribution to consumers. This is achieved through the use of step-down transformers, which reduce the voltage to safe levels.
The main difference between the two types of substations is the direction of voltage flow. While step-up substations increase voltage levels, step-down substations decrease voltage levels. Additionally, step-up substations are typically located near power generation stations, while step-down substations are usually closer to population centers and distribution lines.
An underground distribution substation is a type of electrical substation that is located underground. It is designed to transform the voltage of electricity from high voltage to low voltage, which is then distributed to homes, businesses, and other facilities. Underground distribution substations are commonly used in urban areas where space is limited and aesthetic considerations are important.
One of the main advantages of an underground distribution substation is that it is not visible above ground. This makes it a popular option in urban areas where the appearance of the landscape is important. Additionally, underground distribution substations can be designed to be more compact than above-ground substations, which can be important in areas where space is limited.
Another advantage of underground distribution substations is that they are less likely to be affected by extreme weather conditions such as high winds, lightning strikes, or flooding. This is because they are located underground and are not exposed to the elements in the same way as above-ground substations.
However, underground distribution substations can be more expensive to build than above-ground substations due to the additional costs associated with excavation and the installation of underground equipment. They also require specialized equipment and procedures to ensure safe and efficient operation, which can increase maintenance costs.
A step-up substation typically consists of various components that play a crucial role in transforming the voltage level of electricity. Some of the key components of a step-up substation include:
Transformers: These are one of the most essential components of a step-up substation. The transformers are used to increase the voltage level of the incoming power supply so that it can be transmitted over long distances with minimal power loss.
Circuit breakers: Circuit breakers are used to interrupt the flow of current in the event of a fault or overload in the system. This helps to protect the electrical equipment from damage and ensures the safety of personnel working in the substation.
Surge arresters: These are used to protect the system from high voltage surges and lightning strikes. They absorb and dissipate the energy of the surge, thereby protecting the equipment downstream.
Busbars: These are used to conduct electricity from one component to another. They are typically made of copper or aluminum and are designed to handle high levels of current.
Isolators: Isolators are used to disconnect certain parts of the system for maintenance purposes. They are typically installed at various points in the system and are designed to handle high voltages.
Protection relays: These are used to monitor the performance of the system and to protect it from overloads and faults. They are designed to trip the circuit breakers when an abnormal condition is detected in the system.
Overall, a step-up substation is a complex system that is designed to transform and transmit electrical power efficiently and safely. Each of these components plays a critical role in ensuring the reliability and performance of the substation.
In conclusion, step up substations are a critical component of the power transmission and distribution process. They play a vital role in transforming the voltage of electrical power from a lower level to a higher level for efficient long-distance transmission. With the rise of renewable energy sources, step up substations have become increasingly important in enabling the use of clean energy and reducing the environmental impact of power generation.
When you need to find more than just existing transformers, Daelim’s Transformer Service Center can help you design and produce distribution transformers that meet your unique needs.
We have our own factory and a professional team of engineers, which can design and modify application requirements that meet all your conditions.
Download Resource
ELECTRIC, WITH AN ENGE-- DAELIM BELEFIC