ELECTRIC, WITH AN EDGE
Recognizing the intricacies of transformer cooling with the radiator can sometimes seem like disentangling a big technical problem. However, there is no demand to fret, as this guide provides understanding into the necessary function of radiators in transformer systems. Discover the science behind radiator fins, the value of top-notch rests, and uncover the innovative remedies offered by Daelim. Join us on a deep dive into the globe of transformer cooling expertise to enhance your understanding and ensure peak performance and longevity for your transformers.
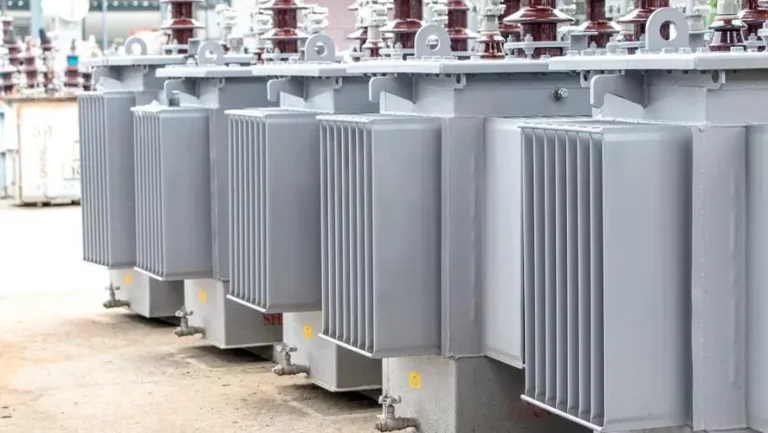
The simple transformer, an essential element in our modern globe’s framework, quietly deals with its organization of moving electric power between circuits. Thanks to these simple devices, our tools, equipment, and also our homes are able to work correctly. Inside each transformer, a synchronized dancing of components happens, with the radiator playing a crucial role in ensuring efficient power transfer.
Whenever a transformer operates, it produces heat as a result of electric losses and resistance. It is necessary to control this warmth as it can influence the effectiveness and life-span of the transformer otherwise appropriately handled.
Efficiency: Excess warm can lower the performance of a transformer, causing it to consume more power than called for.
Toughness: Prolonged direct exposure to high temperatures can cause the internal parts of the transformer to degrade more quickly, eventually shortening its life expectancy.
The radiator in a transformer serves a similar function as a cooling system. Made up of numerous slim metal fins, it offers an expanded area for warm dissipation. The device works based on convection, where the warm oil, having a reduced thickness, increases and obtains cooled in the radiator, while the colder oil comes down right into the main storage tank.
“Radiators play an important function in the functioning of transformers. They are accountable for dissipating the warmth created by the transformer’s core during operation. This assists to preserve a safe temperature variety and guarantees that the transformer operates efficiently and dependably. In addition, radiators aid to lower the threat of overheating, which can harm the transformer’s parts and decrease its life-span. By properly handling warmth distribution, radiators are crucial for the correct performance of transformers.”
Radiators are crucial for:
Warmth Dissipation: The warmth produced is distributed to stop the transformer from coming to be as well hot.
Boosting Lifespan: Radiators add to expanding the life-span of transformers by efficiently controling temperature level.
Keeping Optimal Temperatures: Proper cooling actions can avert issues such as overheating and explosions. Discover more regarding it here..

Transformers utilize different cooling strategies to control their temperature level efficiently. These techniques are made to guarantee optimum efficiency and durability of the transformer.
Importance of Regularly Checking a Transformer’s Radiator for Optimal Functionality
Ascertain that the radiator is dissipating warmth effectively.
Guarantee the ideal functioning and extended life-span of your transformers. Discover valuable insights on transformer upkeep here.
In the huge landscape of the transformer sector, particular brands rise above the remainder as a result of their commitment to high quality, technology, and customer contentment. One such star in this area is Daelim.
Daelim has actually etched its location in the annals of the transformer sector by continually supplying advanced products. Their transformers are not simply gadgets but personifications of years of study, development, and precise design.
Daelim’s radiators are developed to properly release warm, guaranteeing that transformers maintain a cool temperature also in tough scenarios.
For those excited to immerse themselves even more in the captivating globe of transformers, below are some meticulously curated short articles:
…and many more, offering insights and in-depth knowledge to satisfy your curiosity.
Eager to explore top-tier transformer solutions that align with the highest industry standards? Dive into Daelim’s extensive range of transformer products and discover innovation, quality, and reliability at its finest.
But don’t stop here. Deepen your understanding of transformers and their multifaceted world by exploring more articles and resources:
The transformer’s radiator is important for its operating, acting mechanism to keep the temperature level Heat is produced throughout the transformer’s operation, and proper dispersal is necessary to prevent performance loss and potential damage.
A transformer’s performance and life-span are directly linked to its temperature. By maintaining an optimal temperature level, the radiator makes certain that the transformer runs efficiently and lasts longer. If the transformer gets too hot, it can result in minimized efficiency or perhaps failing.
The dimension of the radiator in a transformer straight influences its cooling efficiency. A bigger radiator gives a greater surface for heat diffusion, resulting in much more efficient cooling. On the other hand, a smaller radiator may not be as efficient, specifically for bigger transformers.
Transformer radiators are generally constructed from metals like steel or light weight aluminum. These products are chosen for their heat-conductive homes, making sure that warmth is effectively drawn away from the transformer core.
Transformers can be cooled down making use of either air or liquid techniques. Air-cooled transformers make use of a mix of a radiator and occasionally followers to dissipate warm, while liquid-cooled transformers utilize a liquid coolant that moves through both the transformer and the radiator.
Daelim is a leading name in the world of transformers. With over 20 years of experience, they specialize in producing high-quality transformers and their components, ensuring that their products are compliant with various international standards like ANSI, IEC, IEEE, and CSA.
Regular maintenance of the radiator is essential for the transformer’s long-term performance. This includes cleaning the radiator fins, checking for leaks, and ensuring that there’s no blockage that could affect airflow or coolant flow.
Safety is paramount when dealing with electrical equipment. Ensure that the radiator is free from leaks and damage. If there’s a coolant leak, it’s vital to address it immediately to prevent any potential hazards.
In essence, the radiator in a transformer is its lifeline. It ensures that the transformer remains cool, operates efficiently, and has a prolonged lifespan. By understanding its function and ensuring its maintenance, one can guarantee the transformer’s optimal performance.
The size of the radiator in a transformer is of utmost importance. It directly affects the cooling efficiency, which in turn impacts the transformer’s overall performance.
The primary purpose of a radiator in a transformer is to dissipate heat generated during its operation. A larger radiator offers a greater surface area for heat dispersion. This ensures that the transformer’s internal temperature remains within safe operational limits.
All transformers produce heat when they’re in operation. This heat generation is due to the resistance in the transformer windings and core. If this heat isn’t dispersed adequately, it can result in overheating, causing potential damage or reduced efficiency.
Efficiency is a critical aspect of a transformer’s operation. If a transformer becomes too hot, its efficiency drops. This can lead to increased operational costs and reduced lifespan of the transformer. An appropriately sized radiator ensures that heat is effectively dispersed, maintaining the transformer’s operational efficiency.
Several factors determine the appropriate size of a radiator for a transformer:
Leading manufacturers like Daelim recognize the importance of tailoring radiator size to individual transformer needs. They offer customized solutions to ensure optimal performance across diverse operational scenarios.
For those seeking in-depth knowledge, there are several PDF resources and manuals available. These documents provide detailed insights into the science of radiator sizing, its impact on transformer performance, and best practices for selection.
A transformer’s lifespan is significantly influenced by its operating temperature. The radiator, responsible for cooling the transformer, ensures that it operates within a safe temperature range, thereby prolonging its life.
Every piece of electrical equipment, including transformers, has an optimal operating temperature. Exceeding this can cause accelerated wear and tear. The radiator in a transformer ensures that the temperature remains within this optimal range.
Overheating in transformers can lead to:
Radiator fins play a pivotal role in enhancing the cooling efficiency of a transformer radiator. These fins increase the surface area available for heat dispersion, allowing for more effective cooling.
To ensure the radiator performs optimally, regular maintenance is essential. This includes cleaning the fins, checking for blockages, and ensuring the coolant, if used, is in good condition.
With an effective radiator and regular maintenance, transformers can often exceed their expected lifespans. This not only reduces costs for businesses and utilities but also promotes energy efficiency and sustainability.
Daelim’s commitment to excellence is evident in their high-quality transformer products. Recognizing the integral role of the radiator in transformer longevity, they’ve continuously innovated their designs and materials. This dedication ensures that their transformers not only meet but often exceed expected lifespans.
Daelim offers advanced cooling solutions tailored to each transformer’s specific needs. Whether it’s a pad-mounted transformer for a commercial building or a high-voltage power transformer for a utility company, Daelim ensures optimal cooling performance.
As technology continues to evolve, so does the science of transformer cooling. Modern advancements include smart sensors that monitor the transformer’s temperature in real-time and adjust the cooling mechanism accordingly. Such innovations are set to revolutionize the industry, and companies like Daelim are at the forefront of this transformation.
It’s essential for industries and consumers to understand the significance of radiators in transformers. Daelim, alongside other industry leaders, is active in promoting education and awareness. They provide resources, workshops, and training sessions to ensure that everyone involved in the transformer lifecycle understands the importance of effective cooling.
The radiator in a transformer is more than just a cooling component; it’s a guardian of the transformer’s health and longevity. Through proactive maintenance, advanced cooling solutions, and continued education, the industry aims to ensure that transformers remain efficient, safe, and durable for years to come.
Daelim has actually established itself as a leading brand in the transformer industry, flaunting over twenty years of competence. The company focuses on making superior transformers and their elements, adhering to rigorous worldwide criteria such as ANSI, IEC, IEEE, and CSA.
It is vital to execute routine maintenance on the radiator to make certain the transformer runs efficiently over time. This entails tasks such as clearing the radiator fins, examining for any kind of leakages, and ensuring there are no obstructions that might impede air movement or the blood circulation of coolant.
Security is critical when managing electric tools. Ensure that the radiator is without leaks and damages. If there’s a coolant leak, it’s important to resolve it instantly to stop any potential hazards.
Basically, the radiator in a transformer is its lifeline. It guarantees that the transformer continues to be awesome, runs successfully, and has a prolonged lifespan. By understanding its feature and guaranteeing its upkeep, one can guarantee the transformer’s optimal performance.
The size of the radiator in a transformer is of utmost relevance. It straight impacts the cooling effectiveness, which subsequently effects the transformer’s overall efficiency.
The major feature of a radiator in a transformer is to take care of the warm created throughout its usage. A larger radiator supplies a higher location for the dispersal of warmth, thus guaranteeing that the transformer’s interior temperature level stays within advised restrictions for proper functioning.
When transformers are functioning, they create warmth due to the resistance in their windings and core. If this warmth is not correctly dissipated, it can lead to overheating, which may trigger injury or lower efficiency.
Effectiveness is an essential element of a transformer’s procedure. If a transformer comes to be too hot, its effectiveness drops. This can cause increased operational prices and reduced lifespan of the transformer. An appropriately sized radiator ensures that warm is successfully distributed, preserving the transformer’s operational performance.
Several factors establish the suitable size of a radiator for a transformer:
Heat Management in Transformers:
The capacity of a transformer has a straight impact on its heat generation, with larger transformers generating even more warmth. Therefore, bigger radiators are needed to efficiently cool down these transformers. In warm and moist environments, an even bigger radiator might be needed to make certain optimal cooling.
In addition, transformers running at or near their maximum capacity create more heat than those going for reduced loads. This highlights the value of cautious warm monitoring in transformer style and operation.
To deal with these warm administration difficulties, transformer suppliers use customized remedies customized to certain application demands. These solutions might include bigger radiators, specialized cooling down systems, or various other alterations designed to make sure efficient warmth dissipation and optimum transformer performance.
Leading producers like Daelim acknowledge the relevance of tailoring radiator dimension to individual transformer needs. They supply personalized services to ensure optimal efficiency across varied operational scenarios.
For those looking for extensive understanding, there are a number of PDF resources and handbooks available. These papers offer thorough understandings right into the scientific research of radiator sizing, its impact on transformer efficiency, and best methods for option.
The longevity of a transformer is significantly impacted by how warm it obtains while running. The radiator, which cools down the transformer, plays a crucial function in maintaining a risk-free operating temperature and prolonging its life expectancy.
All electrical devices, such as transformers, have a certain temperature range at which they function best. Going beyond this array can bring about enhanced damage gradually. The transformer’s radiator is responsible for maintaining the temperature level within this excellent variety.
Overheating in transformers can lead to:
Insulation Breakdown: High temperature levels can degrade the shielding products inside a transformer, enhancing the danger of shorts or failings.
Reduced Efficiency: Elevated temperature levels can lower a transformer’s efficiency, causing raised power consumption.
Physical Damage: In extreme cases, overheating can cause physical damages or even fires.
The efficiency of a transformer radiator is dramatically enhanced by the addition of radiator fins, which augment the surface area offered for warmth dissipation, therefore facilitating far better cooling.
To make certain the radiator carries out optimally, routine upkeep is important. This consists of cleaning the fins, checking for obstructions, and ensuring the coolant, if utilized, is in good condition.
Transformers can last longer than anticipated with an excellent radiator and correct maintenance. This can conserve cash for firms and utility suppliers while additionally sustaining power performance and sustainability.
Daelim’s commitment to exceptional high quality is plainly mirrored in their transformer items, which are made to last longer and do better than anticipated. The firm comprehends the essential duty of the radiator in expanding the life-span of transformers, and has actually continually boosted its layouts and materials to accomplish unequaled quality. This undeviating commitment to innovation makes certain that Daelim’s transformers exceed sector requirements, providing customers satisfaction and reputable performance.
Daelim offers innovative cooling remedies tailored to each transformer’s certain demands. Whether it’s a pad-mounted transformer for a commercial building or a high-voltage power transformer for an energy firm, Daelim ensures optimal cooling efficiency.
Advancements in transformer cooling are progressing together with technological developments. New attributes such as smart sensors are now able to constantly monitor the temperature of transformers and make necessary changes to the cooling process. These ingenious growths are positioned to bring substantial changes to the market, with business like Daelim blazing a trail in this evolution.
It’s crucial for sectors and consumers to understand the relevance of radiators in transformers. Daelim, alongside other industry leaders, is energetic in promoting education and recognition. They provide sources, workshops, and training sessions to make sure that every person associated with the transformer lifecycle recognizes the significance of reliable air conditioning.
The function of the radiator in a transformer surpasses simply providing air conditioning; it functions as a guard of the transformer’s health and life-span. By executing preventative maintenance, making use of ingenious cooling approaches, and advertising recurring knowing, the sector is devoted to maintaining the performance, security, and longevity of transformers well right into the future.
By integrating the use of radiators and followers in transformers, cooling down efficiency is substantially enhanced. This calculated strategy ensures that the warm produced throughout the transformer’s operation is appropriately dissipated, resulting in boosted efficiency and durability.
“Comparing the Benefits of Natural and Forced Cooling Methods”
While a radiator can naturally cool down a transformer via convection, including fans can cause forced air cooling. This energetic method accelerates the cooling procedure, particularly in bigger transformers or during height loads.
The radiator’s main feature is to enhance the surface area for efficient warmth dissipation. The layout, typically comprising several fins, ensures that even more warmth is moved from the transformer oil to the surrounding air.
Fans offer extra air movement across the radiator’s surface. By boosting the air circulation, the warmth elimination rate from the transformer oil boosts, guaranteeing the temperature level remains in a secure operational range.
Several contemporary transformers come furnished with temperature sensors. When the transformer’s temperature climbs past a certain threshold, these sensing units turn on the fans immediately. This vibrant technique makes sure energy-efficient air conditioning.
Boosted Cooling Performance: The synchronized activity of the radiator and follower enables the dissipation of warm to be considerably boosted, resulting in ideal cooling.
Adaptability: The followers can be activated during durations of high demand or hot weather to provide an additional cooling boost.
Energy Conservation: By just operating the followers when called for, transformers can minimize energy usage, making them eco-friendly.
Well-known suppliers such as Daelim …
Daelim, with its vast experience in transformer production, offers options where radiators and fans are sympathetically incorporated. Their layouts prioritize both effectiveness and the long life of the transformer.
The transformer industry sees a number of firms that focus on crafting excellent radiators, acknowledging the value of appropriate cooling in enhancing transformer efficiency and longevity.
Daelim sticks out as a leading name in the transformer market. Their dedication to quality and adherence to global criteria, like ANSI and IEEE, has positioned them as a leading selection for numerous markets.
Popular suppliers stick out for their advancement in presenting innovative layouts and products to improve the efficiency of cooling systems. They additionally offer tailored radiator options to meet the unique requirements of transformers. With a strong international existence, such as that of Daelim, top producers can serve a large range of markets and adhere to global standards. The partnership in between radiators and followers in transformers plays a vital duty in their operation.
Firms that integrate radiators and followers in their styles use one of the most efficient cooling systems, as they can suit various operational requirements of transformers throughout various industries and regions.
First-class quality is a leading priority for components such as radiators. Leading manufacturers guarantee adherence to global criteria and job carefully with independent screening facilities to ensure excellent quality.
Choosing a trustworthy radiator supplier is critical for enhancing the performance and long life of a transformer. Industry frontrunners like Daelim supply assurance for organizations in the quality of their transformer’s air conditioning systems.
Radiator in a transformer plays an important function in handling and dissipating the warmth produced throughout the transformer’s procedure. Its primary purpose is to make sure the transformer continues to be at an optimal temperature, safeguarding its long life and efficiency.
Every transformer, regardless of its size or application, produces warmth when it operates. This warmth arises as a result of both core losses and copper losses in the transformer.
Radiators are created with numerous upright tubes or panels. These tubes consist of transformer oil, which circulates and records the warm produced inside the transformer. As the oil travels with the radiator tubes, the surrounding air cools it down.
Cooling options for ideal performance.
Durability: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can weaken the insulation and various other parts of the transformer.
Efficiency: Maintaining an optimum temperature level ensures the transformer runs at its highest possible efficiency.
Safety and security: Overheating can bring about failures and even fire risks.
Daelim, comprehending the value of efficient air conditioning, has actually integrated top-notch radiator styles in their transformers. Their solutions align with international criteria, making sure dependability and performance.
Just how can a person obtain specs and designs for transformer radiators
You can find details about the capabilities and effectiveness of transformer radiators by taking a look at their technological specifications and designs in various means.
Many producers, consisting of well-established brand names such as Daelim, use detailed PDF records that provide a riches of info on their items. These records consist of in-depth layout layouts, technical specs, and various other relevant details that aid customers comprehend the item’s features and capacities.
Many producers have actually dedicated areas on their websites where they list item details. These usually include datasheets, design principles, and sometimes also study.
Specialized magazines concentrated on transformers regularly consist of material like write-ups, examinations, and promos that highlight the most recent in radiator styles.
These celebrations act as main points for sharing details. Business their most recent products and improvements providing participants direct accessibility to info and sources.
Speaking to suppliers such as Daelim directly can supply customized services and comprehensive info that is personalized to meet private demands. Their technological personnel is capable of replying to concerns and providing suitable paperwork.
Having accurate and in-depth details concerning radiator specifications is vital for:
When it comes to choosing a radiator, it’s important to think about the transformer size and load demands to make sure the appropriate fit. Comprehending the design of the radiator can also aid with anticipating and precautionary upkeep, guaranteeing that it runs efficiently and efficiently. In addition, safety and security is a top priority, and the radiator has to adhere to stringent safety and security and operational requirements to prevent any type of potential dangers. By taking these aspects right into account, you can make an informed decision when picking a radiator for your needs.
It is essential for people engaged in the acquisition, administration, or maintenance of transformers to possess an extensive understanding of radiator requirements and have simple access to such information. Thanks to a wide range of resources, including PDF records and individualized aid from producers, individuals in the industry are equipped to make well-informed choices concerning their transformer-related requirements.
The function of radiator fins is vital in spreading the warm generated by transformers. Their unique structure and careful positioning enhance the effectiveness of the entire cooling system.
The radiator fins are slim, extended metal pieces, normally made from light weight aluminum, that are linked to the radiator’s outside. They are made to boost the radiator’s warmth exchange capability by broadening the surface area, thereby improving the cooling process successfully and swiftly.
Effective Heat Transfer: By expanding the surface, fins facilitate much faster warm dissipation from the transformer oil to the ambient air.
Compact Design: Fins permit radiators to maintain a portable form aspect while still using optimal air conditioning.
Economical: Incorporating fins is an inexpensive technique to improve radiator efficiency without significant modifications.
Daelim’s transformers feature cutting-edge radiator fin modern technology, carefully crafted by specialists to make best use of cooling efficiency. The tactical positioning and sizing of these fins allow the transformers to operate at peak efficiency, ensuring ideal heat dissipation and minimal energy loss.
Transformers count on breathers to avoid dampness from entering the system and to enable the transformer oil to breathe. Numerous business concentrate on producing superior rests made for different kinds of transformers.
The primary function of rests is to stop wetness from entering the transformer. When the transformer oil temperature level boosts, it expands and forces air out, while contraction takes place when it cools down, attracting air in. By ensuring the inbound air is free of wetness, breathers play an important duty in preserving the transformer’s effectiveness and longevity.
Daelim: With their considerable transformer experience, Daelim likewise offers rests customized for their series of transformers.
ABB: A prominent name in the power and automation modern technology sector, ABB provides a range of transformer devices, including rests.
Siemens: Another titan in the electric industry, Siemens creates high-grade rests ideal for numerous applications.
Silica Gel Indicator: Many rests incorporate a silica gel, which alters color when filled, showing a replacement requirement.
Durable Construction: A rest has to hold up against numerous ecological conditions, guaranteeing long life.
Compatibility: It’s necessary to pick a rest compatible with the particular transformer design.
Choosing a top-notch breather is vital for making sure the transformer’s resilience. Breathes are crucial in upholding the internal problems of the transformer and securing it versus possible problems caused by wetness.
The efficiency and lifespan of transformers rely greatly on the quality of their elements, such as radiator fins and breathers. Suppliers like Daelim go to the forefront of producing premium parts that markets can trust for their transformer needs.
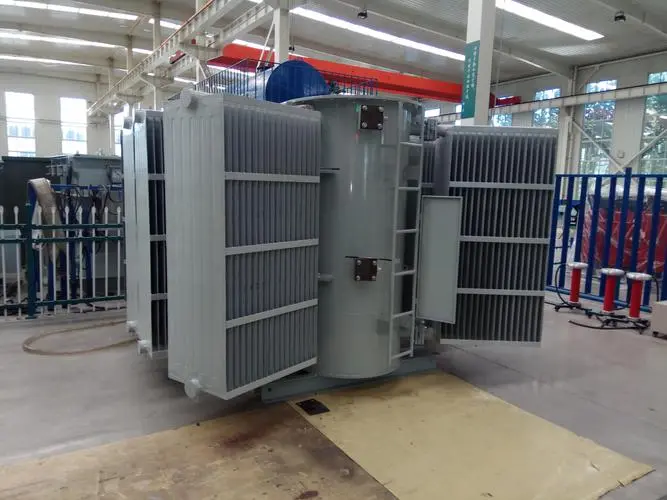

The radiators in transformers, generally misinterpreted for conventional cooling tubes, are in fact a crucial element in controling the temperature level of the transformer. Allow’s take a more detailed look at just how they function and why they’re so essential to the proper performance of the system.
Transformers produce warmth as they run. Like any equipment, when it gets too hot, it risks malfunctioning. Below exists the importance of the air conditioning tube and transformer radiator. With each other, they function to dissipate the gathered heat and make sure the transformer runs efficiently.
Benefits of Efficient Cooling:
Extends transformer life-span.
Decreases risk of breakdowns and breakdowns.
Improves general efficiency and performance.
The transformer’s air conditioning system is comprised of two important components: the cooling tube and transformer radiator. These parts collaborate to maintain the transformer’s optimal temperature level, consequently prolonging its lifespan and guaranteeing reliable efficiency.
The air conditioning tube plays an essential role in controling the temperature level of the transformer by facilitating the blood circulation of a coolant, usually an oil-based compound, around the tool. When the coolant takes in warmth from the transformer, it expands and moves towards the radiator, which possesses a bigger area because of the visibility of fins. This makes it possible for the radiator to successfully dissipate the heat right into the surrounding setting. As the coolant cools, it contracts and returns to the transformer, ready to duplicate the process and proceed preserving a secure temperature level.
Production of Goods:
Transformers radiators are generally made from pressed steel. Their design integrates huge surface areas to guarantee reliable warmth dissipation. The introduction of cooling fans has actually even more improved their efficiency, especially in high-capacity transformers where the heat created is substantially a lot more.
Distinctions in between Cooling Tube and Radiator:
While both satisfy of air conditioning, their procedures vary:
Cooling Tube: Facilitates the flow of coolant throughout the system.
Transformer Radiator: Principally in charge of eliminating warm collected by the cooling tool.
Maintenance and Upkeep:
To guarantee ideal cooling efficiency, it’s crucial to frequently examine and preserve the radiator and cooling down tubes. This includes monitoring for any kind of clogs, cleansing the fins, and monitoring the coolant level. By doing these routine jobs, you can help stop getting too hot and prolong the life of your cooling system.
Taking into consideration the value of the radiator in transformer operations, several producers concentrate on producing top notch radiators tailored to details transformer needs. One such instance is the <lsi keyword=””> pressed steel radiators for transformers, which are known for their resilience and performance.
Selecting the Right Radiator:
The selection of radiator largely depends on the transformer’s capacity. As an example, huge transformers require radiators with a greater area and usually come with cooling down followers. The <lsi keyword=””> air conditioning follower for transformer radiators is a popular addition for improved air conditioning.
To summarize, the cooling tube and transformer radiator work in tandem to make sure the transformer’s ideal procedure. Their function in handling and managing the transformer’s temperature level is essential, and understanding their function can considerably aid in transformer maintenance and durability.
Electric radiators play a vital duty that establishes them apart from radiators in various other sectors. Their main responsibility is to control and distribute the warmth created by electrical devices like transformers. Allow’s take a closer look at the distinctive characteristics and functions of these devices.
In an electric atmosphere, the objective of the radiator is not primarily to heat up a space yet rather to avoid particular parts, such as transformers, from overheating. Radiators act as heat exchangers that assist in the transfer of thermal energy between different tools in order to manage temperature levels.
Overheating can be a transformer’s worst opponent. Without reliable air conditioning:
Electrical components deteriorate quicker.
There’s a heightened risk of system failings.
Power usage might climb, as hotter systems often tend to be less efficient.
Radiators play a crucial role in managing the temperature of the transformer to maintain it safe and operating successfully.
Parts and Aesthetics
Easy Designs for Electrical Radiators
Fins: Increase the surface area to enhance warmth dissipation.
Tubes: Allow coolant, such as transformer oil, to move through and move heat.
While the basic principles continue to be the same, styles can differ based on the details needs of the electric equipment they sustain.
Electric radiators are simply one technique of air conditioning. There are other techniques like water air conditioning, yet radiators use particular benefits:
Uncomplicated Installation and Upkeep: Radiators are a wind to establish and maintain, making them a useful choice for heating solutions.
Cost-friendly: By having less components, radiators lessen the probability of breakdowns, consequently reducing costs.
Nonetheless, for incredibly high-power systems, water air conditioning could be thought about due to its greater heat-dissipation abilities.
Improvements in modern technology have brought about various renovations in radiator, the assimilation of cooling down significant technology, assisting in the effective dissipation of warm. The <lsi keyword=””> air conditioning follower made for transformer radiators exhibits this progress by significantly boosting cooling down performance.
Coolants play an important role in transformers, which is often neglected. They flow within the transformer, capturing warm and relocate to the radiator. Without these coolants, transformers would certainly go to danger of severe overheating.
The key coolant in transformers is oil. This oil isn’t just any type of oil; it’s particularly created to have exceptional electrical insulating properties while additionally being a good thermal conductor.
Oil is picked as a coolant for a number of factors:
Various sorts of oils are made use of in transformers for their capability to act as excellent insulators, protecting against electric arcs from happening within the transformer. These oils possess the ability to absorb a significant amount of heat and circulation easily with the transformer and its radiator.
Mineral oil, which is removed from crude oil, is one of the most widely utilized range. Silicone-based oil, on the other hand, is utilized in high-temperature contexts. For those seeking an environmentally friendly alternative, bio-based oil is derived from renewable energies and supplies a greener service.
The choice is frequently based upon the unique requirements of the transformer and the problems in which it will certainly be used.
While the transformer remains in usage, it creates warm that is soaked up by the oil. The oil broadens as it absorbs the warm and the warm broadened oil moves upward and gets in the radiator for air conditioning.
Inside transformers, there’s a globe of parts working in consistency. One important element that ensures smooth operation is the cooling liquid. However, what exactly is this fluid? Allow’s dive in!
Transformers are not just a collection of coils and electromagnetic fields. They have an essential component that keeps them running smoothly – a fluid coolant that circulates with their core. This liquid heart, specifically designed for power transformers, plays a crucial duty in guaranteeing their longevity and ideal efficiency.
The cooling fluid mostly offers 2 features:
The transformer’s liquid part serves a dual purpose: it takes in and dissipates warmth produced within the transformer, preventing getting too hot and damage to the tools. Furthermore, the fluid function as an insulator, stopping electrical arcs and shorts that might compromise the transformer’s effectiveness and life-span. It’s not just oil, it’s an essential part in making sure the transformer’s secure and dependable procedure.
While oil is the most commonly known air conditioning liquid, transformers can consist of other fluids. Some alternatives consist of:
High-temperature security: Silicone fluids master this location. Eco-friendly: Bio-degradable fluids are a far better selection. From eco-friendly sources: Bio-degradable fluids are typically originated from these sources. Precaution: Important factors to consider for the safe use fluids.
Given the important function of the air conditioning liquid, transformers are created with security systems. These guarantee that in case of a leakage or decrease in fluid levels, the transformer can either self-repair or close down to avoid damages.
For a transformer to work successfully, its fluid heart requires normal check-ups. Routine screening makes certain the fluid hasn’t degraded or been infected, making sure a long, efficient lifespan for the transformer.
The lifeblood of a transformer, its cooling fluid, has actually been the subject of much research study and advancement. Knowing which liquid fills up a transformer is critical for upkeep, safety and security, and efficiency.
Mineral oil, derived from crude oil, is one of the most common air conditioning liquid. It’s preferred because:
This item supplies outstanding air conditioning abilities, works as a remarkable protecting product, is easily obtainable, and comes at a sensible cost. New Options
With innovation progressing and ecological issues increasing, choices to mineral oil are getting grip. Some of these include:
Synthetic fluids: They offer improved defense versus fires. Organic esters: Commonly extracted from plant oils, they are environmentally friendly and have a better flash point. The Importance of Choosing Wisely
Effectiveness in air conditioning: Certain fluids may be more efficient at cooling down than others.
Influence on the atmosphere: Bio-based fluids have a smaller sized ecological influence in case of spills or leaks.
Security from fires: Fluids with higher flash points assist reduce the risk of fires.
Making use of the pressed steel radiators for transformers can even more enhance the effectiveness of these cooling fluids, ensuring ideal temperature level control.
With time, the cooling fluid can degrade. Regular tests aid in establishing its health and wellness. If needed, changing the liquid can rejuvenate an aging transformer and improve its operational performance.
Modern transformers and the markets that rely on them are coming to be progressively eco-conscious. Therefore, there’s a growing focus on utilizing bio-based and environmentally-friendly cooling liquids. These not only reduce the ecological impact however additionally line up with worldwide green efforts.
Quality assurance is critical when selecting an air conditioning fluid. To this end, worldwide standards like ANSI, IEC, and IEEE established standards on the residential or commercial properties and efficiency of these fluids. Adhering to these requirements ensures that the transformer runs securely and at its peak efficiency.
The transformer’s cooling oil is usually referred to as transformer oil or insulating oil.
Oil in a transformer isn’t just a filler; it’s a lifeline. Its duties are complex, from cooling down to insulating, making it a crucial element for transformer wellness and performance.
Transformer oil’s primary features at its significance:
The transformer’s thermal conductor plays a vital duty in preserving ideal operating temperatures by effectively dissipating warm produced within the device. Furthermore, the electric insulator prevents inner electric discharges that could trigger harm or damages to the transformer. Ultimately, there are various types of transformer oils offered, each with their own one-of-a-kind residential properties and advantages.
Oils can be extensively identified right into a number of types, consisting of:
Mineral oils: The traditional option, recognized for their dependability.
Silicone oils: Often selected for extreme temperature applications.
Bio-based oils: Gaining appeal because of their environment-friendly nature.
Every category comes with its benefits and drawbacks, and the decision is normally based on the particular operational demands and ecological elements.
The utmost top priority is making certain safety and security at transformers, especially in largely booming areas or proximate to important framework. This demands the usage of oil with an exceptionally high flash point to significantly minimize the possibility of fires. In addition, routine assessments for contaminations are performed to ensure that the oil preserves its performance as a dependable insulator.
Today’s transformer oils are not simply basic fluids; they are often fortified with additives that increase their performance. These improvements can expand the oil’s life-span, increase its cooling capacities, and even reduce the risk of oxidation.
The handling and disposal of used transformer oils need cautious consideration to avoid harmful ecological influences. Standard mineral oils, if thrown away poorly, can cause significant ecological damages. In contrast, bio-based oils use a more sustainable choice as they are biodegradable and can be taken care of in an environmentally friendly way, supporting the global initiative towards sustainability.
The unification of Lsi key phrase pushed steel radiators for transformers can significantly affect the effectiveness of these oils, consequently maintaining the air conditioning system and maximizing the performance of transformers throughout their service life.
In the context of transformer systems, the radiator is a vital component that warrants mindful consideration past plain expense. While budget is definitely an element, it’s essential to additionally think about the lasting efficiency and integrity of the system. By prioritizing quality and performance, you can make sure that your transformer system runs smoothly and successfully, ultimately saving you time and resources over time.
Elements influencing costs of transformers’ radiators differ.
Product Used: Whether it’s stainless steel, aluminum, or an additional material, the kind can significantly influence the expense.
Size and Capacity: Larger transformers need a lot more extensive radiator systems, which can be more expensive.
Ingenious Features: Advanced functions, such as automated air conditioning or enhanced fins style, can include in the expense.
While the preliminary price may appear high, purchasing a high quality transformer radiator guarantees decreased upkeep prices and a longer transformer life. It’s a proactive action to prevent possible functional hiccups later on.
The choice of a supplier can impact the overall expense. Well-known suppliers such as Daelim offer reputable and efficient options that are personalized to satisfy your specific demands, ensuring you get excellent value for your money. It is very important to also think about the schedule of after-sales help and guarantee protection when examining the prices.
Focusing on cost-cutting actions at the expenditure of top quality can have a causal sequence that leads to more substantial expenses down the line, whether it’s via repeated maintenance, decreased transformer life expectancy, or, in worst-case situations, ruining system malfunctions. It’s important to take a go back and consider the long-lasting consequences.
As the emphasis on sustainable energy alternatives and efficient energy use remains to expand, the marketplace for transformer radiators is experiencing changes in prices patterns. Maintaining up-to-date with these advancements can aid you make a well-informed purchase choice.
The function of a transformer radiator includes more than providing cooling. It is important for protecting the effectiveness, safety, and resilience of a system.
The radiator plays an important duty in preserving the optimal temperature of a transformer by distributing the warm it produces. This preventive measure safeguards the transformer versus prospective malfunction or failure brought on by excessive warmth buildup.
Contemporary radiator styles have actually undergone a substantial change, including ingenious functions such as cooling fans for transformer radiators. These sophisticated layouts enhance airflow and substantially increase the radiator’s capacity to dissipate warmth, leading to unrivaled effectiveness.
“Prioritizing Protection”
The radiator is important for making sure security along with its cooling functions. By regulating the transformer’s temperature level, it minimizes the probability of oil failure, interior malfunctions, and fires, thereby guarding the system’s safe and secure procedure.
“Maximizing Life’s Potential: Strategies for Enduring Success”
A well-functioning radiator ensures that the transformer oil maintains its protecting properties and does not deteriorate quickly. This, consequently, increases the transformer’s life expectancy and operational efficiency.
The transformer market is experiencing a makeover of its very own, with the surge of advanced innovations that deal with the transforming needs of the energy market. Innovations such as automated cooling mechanisms and enhanced fin designs are ending up being significantly crucial for transformer radiators to supply optimal efficiency in modern-day power grids.