
How to Choose Pad Mounted Transformer?
Table of Contents Selecting the right pad-mounted transformer requires careful consideration of several critical
ELECTRIC, WITH AN EDGE
A High Voltage distribution transformer is an electrical unit that distributes the conversion of voltage. Which should be transmitted in a power matrix. It converts the electromotive force that’s distributed to a version that is usable in all kinds of your properties, usually to a minimum of 240 volts.
Daelim Belefic has been creating classy power-based items and tools for over 15 years. Daelim’s project retail slogan is DAELIM EDGE + ADVANTAGE. This slogan has been the key to allowing Daelim to provide various qualities and excellence. Speedy customer care delivered customized according to client needs.
The brand has expert engineers who can find solutions to every crisis involving electric items. Daelim has more than one standard in upholding the quality of its products. Thus, Daelim offers varying high-quality electric items.

To begin with, you should know what a transformer is before we go through the details of high voltage transformers.
Chances are, you have passed by a transformer without noticing it, that is because they come in all shapes and sizes. There are transformers that are as small as a barrel, and there are transformers that are as big as a car as well.
Regardless, all of these transformers have one thing in common, and that is to regulate currents, voltages, or electricity in general.
When it comes to changing voltage levels, transformers are also capable of transferring electricity from one circuit to another. During this process, the frequency will not be disrupted. Most transformers only function with the use of an AC supply.
Fluctuation in supply voltage will be affected by the changing currents.
This means that if there is an increase in the current, there will be an increase in voltage as well, and vice versa.
In addition, transformers promote safe electrical transmissions since their function is to regulate voltage levels by either increasing or decreasing the voltage levels. This is also called step up and step down. This can be done at long distances as well.
To put it in simpler terms, a high voltage transformer is a type of transformer that effectively operates at high voltage levels. They are commonly used in high voltage laboratories for experimental purposes.
High voltage transformers are designed to work with transient voltages and surges at normal operations when the insulation under test wears down.
Since they are built to withstand impulse voltages, the insulation of high voltage transformers are precisely designed and formed. Common examples of these are single-phase core-type transformers and Oil-Immersed Distribution Transformer.

This transformer is fairly common since you can see them on utility poles, both concrete or wooden ones. They can also be mounted as a cluster.
They have the shape of a cylinder with a sealing structure. Each of which is connected with grounding devices, hooks, supporting lugs, one or two high voltage bushings on the cover, eyebolt, and connecting terminals.
Single-phase distribution transformers can be used alone for the supply of a single phase load. It can also be used for the supply as one of three units in a bank for the supply of a three phase load.
They are specifically designed for servicing residential overhead distribution loads. They are also compatible with specific commercial loads, industrial lighting, and diversified power applications.
The core of high voltage Distribution transformers works directly to the path of its magnetic field, which is between the primary and secondary coils to prevent wasting energy. Once the magnetic field reaches the second or secondary coil, this forces electrons to move, which then creates an electric current through electromotive force.
High voltage transformers are usually oil-immersed,which means that its insulator is mineral oil. Bakelite sheets are what keeps the high tension windings and low tension windings separated. High voltage transformers that are used for HV cable testing are also required to supply sufficient electric currents.
In return, this can generate a lot of heat, and this is where its cooling system comes in. However, its cooling system does need the right maintenance in order for it to survive in the long run.
When it comes to insulator testing purposes, the required current is low but while the insulator breaks down during the process of testing, you can expect a huge flow of current through the High Voltage Transformers.
For this current to be controlled, there should be a high resistance connected in series with the transformer since insulation testing does not require high currents. High voltage transformers are used for this application, and they do not need to have a high kVA rating.
Any number beyond 500 kV is no longer considered economical to use for a single transformer. This is because the size is simply too much. For situations like these where more than 500 kV is needed, there should be at least two units conjured in series to produce the required voltage.
Low voltage is supplied to the low voltage winding of a step up High Voltage Transformers. The tank of this transformer will be earther. For the secondary, it is connected to the tank of the transformer that is earthed.
Through the high voltage bushing is where another end comes. The bushing is specifically designed and manufactured to withstand full secondary high voltage to meet ends with the earthed potential of the transformer tank.
There will be another tapping terminal that will through the high voltage bushing. The high voltage end and the tapping terminal ends are all connected across the primary of the second High Voltage Transformer.
One of the ends of the secondary winding of the second transformer is connected to its tank. However, the tank of the second High Voltage Transformer is not earthed compared to the first transformer. The second transformer is isolated and insulated from the earth for the full secondary voltage of the transformer.
There is one element you should avoid from high voltage Distribution Transformers, and this is the surges from the high voltage side of the transformer. In terms of accuracy for voltage measurement, the voltage regulation of the transformer should be sufficiently smooth.
Sudden variation of voltages during the test should also be avoided. Voltage regulators should not disrupt the voltage waveform once the test is ongoing,
The output voltage of high voltage transformers are regulated by changing the input voltage on the primary side of the transformer.
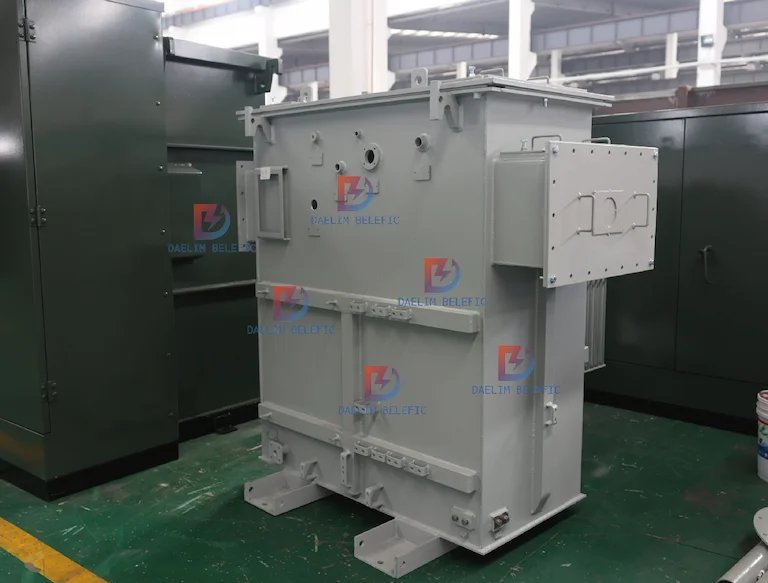
The construction features that make up a distribution transformer bear striking resemblances to tiny transformer units. There are primary parts that cover a distribution transformer. They are an oil tank, a conservator. Buchholz relay, a breather unit, an oil indicator, a temperature detector unit, a pressure relief tool, a thermal relay, a radiator, and a bushing.
The oil tank in a High Voltage distribution transformer functions in a distribution transformer. The unit absorbs the air by taking it all in. This part moderately balances the amount of air a distribution transformer has. Balanced air amount in a distribution transformer enables the electrical unit to power transmission evenly to multiple outlets.
The conservator is at the top of the High Voltage transformer’s oil tank in the external area of the electrical unit. You can see it’s attached to the primary tank via a metallic tube. The tank’s oil moves when it’s loaded, so the oil’s temperature goes up and down.
Buchholz relay simultaneously functions with the conservator. Buchholz Relay does show when there are problems with a High Voltage distribution transformer, such as insufficient oil. Because of this, there exists an inappropriate oil flow that takes place between a tank and the transformer itself.
The breather unit has a silica gel that takes in the moisture oil produces. It transforms the oil from blue to pink and cannot take in moisture in the oil.
It shows the oil level in the conservatory unit.
A temperature detector is a device used to track the oil’s temperature. If the oil’s temperature goes up at some point, then the distribution transformer shall stop operating.
This device minimizes the High Voltage distribution transformer’s pressure to prevent it from exploding.
The thermal relay indicates the winding’s current temperature.
This device is used to augment the efficiency of the cooling operation of the High Voltage distribution transformer.
Single Phase Transformer: What is it?
A bushing is used to connect the High Voltage distribution transformer’s windings connected within it with the aid of an external electric network.
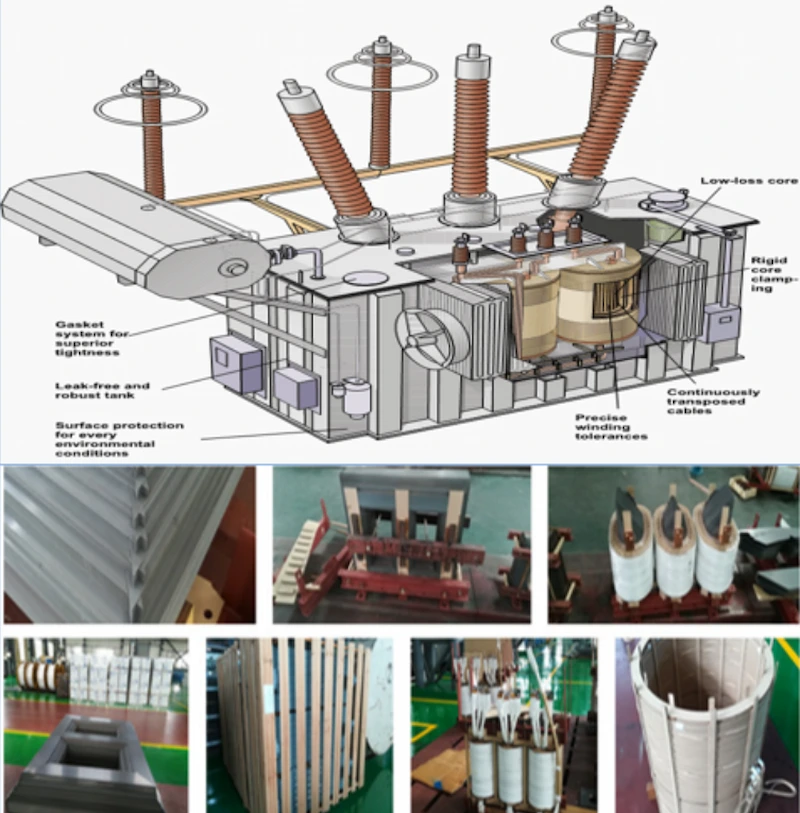
Unlike distribution transformers, HV Power Transformers execute the distribution and absorbing means of electricity. The voltage level of power transformers fluctuates between 756kV and 11kV. You see, power transformers have more MVA ratings as compared to distribution transformers.
HV Power Transformers generally have a greater voltage level than distribution transformers.
The average market ratings of power transformers include 400kV, 200kV, 66kV, and 33kV. Meanwhile, distribution transformers’ ratings average within 6.6kV, 3.3kV, 440v, and 230 volts.
HV Power Transformers are at total capacity for entire load operations, with few glitches. Distribution transformers operate in substantially lower levels of load operations.
Dry-type Transformer Model List
HV Power Transformers operate at 100 percent efficiency with a proportionate ratio of output/input. Besides, distribution transformers’ efficiency level is 50 to 70 percent, based on the All Day Efficiency calculation.
Transformer three-phase dual power supply automatic switching
HV Power Transformers work in stations where power is generated, and substations produce power distribution. Distribution transformers produce energy within their own premises.
HV Power Transformers are significantly bigger than distribution transformers.
One thing that the distribution transformers and HV Power Transformers have in common is their critter vulnerability. Such a similarity that both transformers have produces power knockouts. Animals chew on and, in turn, destroy the parts of both distribution and power transformers
A single-phase distribution transformer is usually suitable for use for an outlet where it’s not needed to have a supply in a three-phase fold.
Your single-phase transformer is used most of the time to repair overhead distribution loads. In-home and industrial properties and other light commercially-based electric purposes.
This High Voltage Transformer distributes electricity from the primary outlet to a secondary power unit. A three-phase distribution transformer minimizes the voltage level of the primary power outlet. This transformer lessens the amount of voltage availability of the primary power outlet per the needs of users.
To add to it, the functions of a three-phase High Voltage Transformer constantly change. This transformer operates in compliance with the individual requirements of each country. A three-phase transformer with a pad is primarily good for use in primary underground outlets.
Three-Winding Transformer | Three-Phase Transformer | Daelim
These connections vary based on the structural modifications of the distribution transformer enforced. A single-phase distribution transformer has one or two units of bushings in wye-shaped forms. The primary parts of these connections consume three, or four-wire wye connections gathered.
As your High Voltage distribution transformer shifts its power from a high voltage power to a low voltage one. It’s used primarily on residential and commercial properties. This transformer separates primary and secondary windings. A distribution transformer spreads the electricity supply where access to power is difficult. Such a supply comes from the power plants.
What’s more, a distribution transformer provides power to home and commercial properties, with voltage below 33KV and 440 volts to 220 volts.
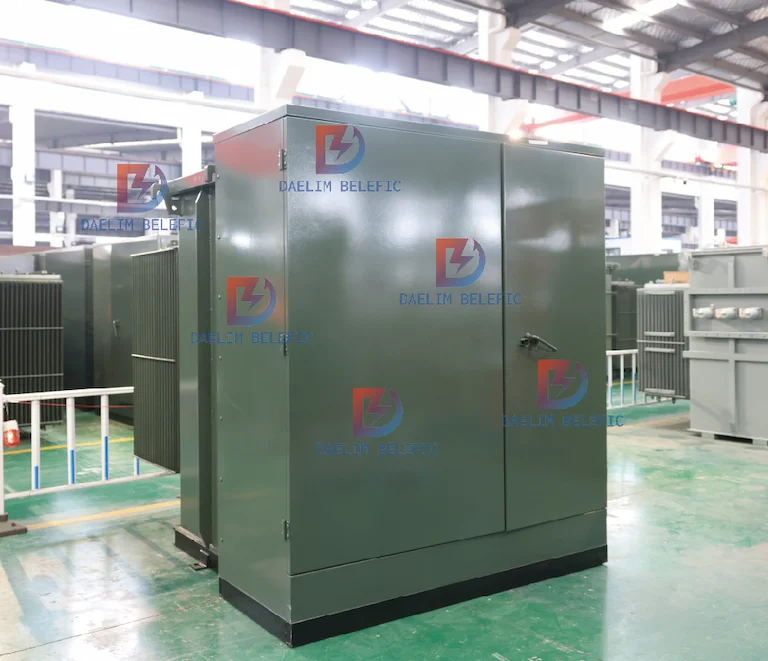
A High Voltage pad-mounted distribution transformer has a locked steel cupboard that forms on a concrete pad. This pad-mounted transformer is seen in locations where there is no fenced protection. It’s also used in power distribution outlets within a primary electrical unit. To minimize the provision of primary voltage to users.
One unit of a pad-mounted distribution transformer can serve users in many properties. The power level of this transformer is within 75 KvA and 5000 KvA and features outlets that have definite uses.
A High Voltage pole-mounted distribution transformer is located atop an electric service pole above the primary head cables.
This transformer modifies high-level voltage to a low-level one. Approximately measuring 120/240 electrical volt levels. A pole-mounted transformer is usually used in rural neighborhoods, having voltage power ranging from 16 KVA to 100 KVA.
More so, this small-sized transformer can easily fit a structure that’s of a single pole. This transformer is resistant to bad weather conditions in neighborhoods that are not easily accessible.
This transformer’s tanks are resistant against eroding elements and accumulation of liquid. When located in offshore premises, a pole-mounted distribution transformer is zinc spray resistant. While a pole-mounted transformer located in substantially eroded areas uses a stainless tank.
There are no studies or evidence that prove that exposing oneself near or fram from magnetic fields from transformers, power lines and other electrical sources cause any health effects.
In fact, many scientists believe that exposing oneself to low-level EMF’s near power lines is safe. However, the study with regards to health risks from these fields are still continuously researched. For now, there is simply no evidence for health risks being near high voltage transformers or power lines.
In short, you cannot get any diseases or health risks just by standing near or far from operating High Voltage Transformers.
The most common cause or main cause for voltage surges in power systems are because of lightning impulses, and as well as switching impulses. But this is only one of the causes. For over voltage in power systems, this might be due to insulation failures, arcing ground, resonance, etc.
The amount of current in a single circuit will depend on the voltage being supplied.
If the voltage is too high, the wire will possibly melt. Other devices might stop working or even burst into flames, causing an explosion afterward.
For high voltage transformers, they also have their limits as well. Too much voltage will cause the transformer to fail, but if the over voltage is within 1 to 10 percent past the limit, the transformer will most likely be okay and heat up a little more.
However, it is highly recommended that you do not use your transformers to operate past their limits for safety purposes. Too much voltage will destroy your transformer and endanger those who are near the transformer since it might burn up and explode.
Below are the advantages and disadvantages of high voltage Distribution Transformers. This section is specifically made for you to help you with your purchase decision.
Should you have any more questions or concerns about high voltage transformers or other transformers, do not hesitate to contact DAELIM’s team of professionals.
Here are the main advantages of using high voltage transformers.
Transformers are static devices, which means they have no moving parts in them but they do have the following:
The alternating current magnetic field created in one of the windings induces a current in the other winding that is proportional to the number of turns. High voltage transformers are used in electrical power systems to transfer power through electromagnetic induction from circuit to circuit with the same frequency level.
However, it is possible to encounter power losses, voltage drops, and waveform distortion during the process.
High voltage transformers are fairly easy to use, but for those of you who are worried that the high voltage transformer you are going to purchase will work differently, you can contact DAELIM to assist since they offer after-sale services.
Transformers will always be an important device in the power distribution system and power electronic system, which is why knowing how to properly use it is essential to utilize its benefits and for safety purposes.
High voltage transformers has the ability to step down high voltages in transmission as well.The same goes for increasing, but never go over its limit to avoid danger,
Distribution, transmission, and power generation are the three fundamentals of today’s power system. High voltage transformers play a vital role in this, especially for high voltage applications, because their capabilities made electricity economic delivery at long distances possible.
When it comes to distribution, high voltage is stepped down for industrial, residential, and commercial use with distribution transformers.
High voltage transformers can be used in various ways including stepping up and stepping down voltage levels, distributing power from one circuit to another, etc.

Below are the following drawbacks of high voltage transformers, if there is an element that you find that is not suitable, then do reconsider your thoughts and check other high-quality transformers that are compatible to what your purpose of using one is.
Transformers have different cooling mediums. Some transformers only require forced air while other types use mineral oil. Both have their pros and cons as well.
For forced air, it helps users save money since air is sufficient for cooling the transformer’s temperature. When it comes to using oil as the cooling medium, it is considered the most effective way of cooling. However, it will cost more because mineral oil itself can be expensive, as well as its maintenance.
High temperatures in a transformer will degrade the longevity of the insulating materials used in the windings and structures. But with proper regulation, our transformer’s materials will remain in pristine condition.
In fact, increasing the cooling rate of a transformer will increase the capacity. Regardless, you will need to spend for the cooling medium of your transformer, as well as do regular check ups for its maintenance.
You can also take advantage of external cooling. This include heat exchangers, fans, oil pumps, and heat exchangers, which once again, will cost you more
HV Power Transformers are known to not pass DC. This means that transformers can be used to keep DC voltages on the output of an amplifier stage. For the AC signal, it is coupled through the HV Power Transformer between amplifier stages.
Even though high voltage Distribution Transformers are widely used, there are several characteristics of it that do not meet the standards of the modern distribution grid. This is why transformers are not advisable to be placed inside establishments. Even building fire codes are not compatible with transformers.
To meet the requirements or standards of the modern distribution grid, a new design and build is required. This is why a lot of manufacturers are on the process of manufacturing an intelligent transformer.
A lot of high voltage transformers degrade or deteriorate in just a course of a year for various reasons, in which the majority of these reasons can be prevented with proper maintenance. With that being said, this is the reason why transformers can be a hassle, due to its regular check up routine.
There are different kinds of high voltage circulation transformers, each with its special qualities. What establishes them apart?
Transformers with core types have their windings surrounding a central core. The core is generally composed of layers of steel that have actually been pressed together, forming a rectangle-shaped shape.
Covering Type Transformers: In this type, the windings are surrounded by the core. It provides far better mechanical toughness and is generally used in high voltage applications.
High-power transmission networks rely upon power transformers, which have a capacity of 500 kVA or higher.
Distribution Transformers are utilized for distributing reduced voltage, typically under 500 kVA.
High-voltage line operators utilize Instrument Transformers to manage and run instruments from another location.
Phase Shifting Transformers: These transformers control the power flow in specific lines.
Autotransformers: Autotransformers have just one winding and are much more cost-effective.
Oil-Immersed Transformers are developed to be cooled down by oil and are excellent for exterior applications.
Dry Type Transformers: Unlike oil-immersed kinds, these transformers are air-cooled.
Specialized Transformers: This group consists of a range of transformers especially produced for specific usages, such as heater transformers.
Here is a comparison table to show the differences:
| Transformer Type | Application | Cooling Method | Voltage Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Type | General | Oil/Air | Medium/High |
| Shell Type | High Voltage | Oil | High |
| Power Transformer | Transmission | Oil | High |
| Distribution Transformer | Distribution | Oil/Air | Low/Medium |
| Dry Type | Indoor | Air | Medium |
Comprehending the different kinds of High Voltage Distribution Transformers is vital for their choice, use, and upkeep. Familiarity with transformer types permits much better decision-making in the electric and power industries, whether it’s a Core Type for widespread usage or a customized transformer customized to a specific sector.
Three-phase distribution transformers play a critical function in three-phase power circulation networks. They work based upon the basic concepts of single-phase transformers, yet they handle three alternating current inputs and outputs simultaneously.
Performance: Three-phase transformers include three collections of main and second windings, each set corresponding to one stage. These windings can be attached in various configurations, one of the most typical being the Delta (Δ) and Star (Y) links.
In a Delta (Δ) configuration, the windings are linked together in a series, producing a shut loophole. This plan is frequently employed for the high-voltage part of a transformer.
Celebrity (Y) Configuration: In the Star arrangement, one end of each winding is linked with each other to develop the neutral factor, while the various other ends are linked to the stages. It’s usually made use of on the low-voltage side.
Applications: Three-phase transformers are predominantly made use of in industrial settings where big equipments call for three-phase power. They are additionally typically discovered in power circulation networks, transforming high voltages from power plants to lower voltages ideal for business and household usage.
These transformers’ ability to handle 3 phases at the same time leads to an extra structured and cost-efficient technique than utilizing 3 individual single-phase transformers, therefore enhancing general efficiency.
Compact Design: Three-phase transformers have a compact structure that occupies less area compared to single-phase transformers with the exact same power capability.
Well Balanced Load Distribution: They make sure a well balanced circulation of electrical loads throughout the three stages, decreasing the danger of one stage becoming overwhelmed.
Security: By giving a neutral in the Star (Y) setup, they use a path for mistake currents, improving the security of the system.
Flexibility: They can likewise convert in between different voltage degrees, facilitating the connection in between different parts of the power circulation grid.
Three-phase transformers assist to minimize harmonic distortions within the system, resulting in an extra constant power circulation and lowering the danger of damage to linked equipment.
Tool voltage transformers play a vital role in reducing high voltages to safer and much more practical levels for usage in industrial and business settings. It is important to be aware of their technological specs and industry standards to guarantee secure and efficient procedure, as well as to make sure that they can be incorporated perfectly into existing systems.
Optimum Tolerable Voltage: The transformer’s designed temperature limitation is not surpassed when operating at this voltage rating.
The ranked power suggests the highest quantity of power that the transformer can providing to the load.
The frequency defined for the transformer style is usually 50Hz or 60Hz.
Cooling Down Type: Indicates if the transformer is immersed in oil, cooled down with air, or makes use of a various air conditioning system.
Resistance: An important aspect, as it influences the transformer’s efficiency, especially during abrupt surges.
Insulation Class refers to the highest possible temperature level that the insulation material can endure without obtaining damaged.
Performance: Reflects the transformer’s ability to transform input power into valuable output energy.
Audio Level: Specifies the sound degree generated by the transformer throughout operation.
Medium voltage transformers are generated and examined according to global standards like IEC, ANSI, and IEEE to ensure high quality, security, and compatibility.
Safeguards: This gadget is equipped with various safeguards, such as security versus excessive temperature level, short-circuiting, and voltage rises.
| Specification | Typical Values |
|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | 11kV, 22kV, 33kV |
| Rated Power | 100kVA – 5000kVA |
| Frequency | 50Hz, 60Hz |
| Cooling Method | Oil-immersed, Air-cooled |
| Impedance | 4% – 6% |
| Insulation Class | Class A, B, F, H |
| Efficiency | >98% |
| Sound Level | <60dB |
In radiological tools, specifically in X-ray equipments, high stress (or high voltage) transformers play a critical duty. These transformers make sure the X-ray tubes receive the high voltage essential to create X-rays.
The high stress transformer in radiology is responsible for improving voltage levels to fulfill the demands of X-ray tubes, which necessitate voltages between 10s and numerous kilovolts for optimum efficiency.
Acceleration from Cathode to Anode: The X-ray tube uses the high voltage produced to speed up electrons moving from the cathode to the anode. This quickening procedure results in the development of X-rays upon the accident of electrons with the anode.
Reputable High Voltage Output: The transformer should offer a constant and stable high voltage supply to guarantee consistent X-ray generation.
Security: Given the high voltages involved, these transformers come with enhanced safety features to protect both the tools and the operator.
Pulse Control: Advanced radiological makers have the capability to change the pulse of the X-ray light beam. The transformer contributes in regulating these pulses by altering the voltage sent out to television.
Reducing Radiation Exposure: plays a vital role in reducing the amount of revealed to by keeping the efficient procedure of the X-ray tube.
The X-ray tube’s resilience is prolonged by supplying a stable and trusted voltage supply.
In the most up to date radiological tools, transformers are set up to be little in dimension while keeping high performance and safety criteria.
These transformers regularly call for smooth assimilation with different other systems,, person positioning systems,
Cooling setups: Due to the significant quantity of energy used, cooling arrangements are often combined with these transformers to disperse the heat produced while they are in usage.
As a High Voltage distribution transformers power up residential and commercial properties. Now you need this for your electrical home and industrial needs.
Daelim came up with the term Electric, keeping in mind the Belefic Edge concept. Keeping this slogan concept in mind enables Daelim to produce only high-class electric items for its clientele. Edge is what Daelim brings to every product its competitors try to beat.
High Voltage Distribution Transformers are at the heart of modern power distribution systems. This comprehensive guide has explored various aspects of these essential devices, from understanding different types and specifications to delving into their role in radiology, energy efficiency, safety, and future trends. Whether you are an engineer, technician, student, or simply someone interested in the world of electrical technology, understanding High Voltage Transformers is essential to appreciating their significance in our daily lives and the broader context of sustainable energy. The continuous innovation and adherence to standards and best practices will ensure that these vital components continue to power our world safely and efficiently.

Table of Contents Selecting the right pad-mounted transformer requires careful consideration of several critical

The primary function of the pad mounted transformer is to serve as a critical distribution

A pad mounted transformer operates through electromagnetic induction, serving as a crucial distribution component that
ELECTRIC, WITH AN ENGE-- DAELIM BELEFIC
After filling in the contact information, you can download the PDF.