ELECTRIC, WITH AN EDGE

This article describes the types of transformer in detail, transformer working principle, parts of transformer, construction of transformer.
A transformer is a static electrical device that can increase and decrease the voltage and change the current under a certain power. Various transformers are widely used in daily production and life fields.
Transformers have a wide range of uses. With the rapid development of economic construction, various types of transformers are widely used in industrial and agricultural production and people’s daily life in factories, mines and urban construction, such as subways, sewage treatment and other major engineering projects. Entered the port, power plant, university town, commercial and residential buildings.
If you need to purchase a transformer, please contact Daelim. Daelim has been developing in the direction of transformer design and production for 16 years.
Daelim’s transformers have successfully passed IEEE, CSA, ISO9001, ANSI C57.12.00, IEC60076, and other international system certifications, focusing on the production of reliable transformers, saving you a lot of costs.
Transformers are indispensable equipment in power systems. Generally, the electrical energy used by people is mainly generated by AC motors in power plants, and the outlet voltage of large generators is generally 6.3kV.
The installed capacity of the transformer is 6 to 8 times the installed capacity of the generator. After the electric energy reaches the power consumption area, transformers of various capacities and voltages are needed for electric energy distribution.
The electric power department uses the transformer to convert the high voltage into a low voltage level suitable for the actual load on-site before it can be used.
For example, the lighting voltage is generally 36V, 48V, 110V, 220V, the power voltage is 380V, and the system voltage level is 10kV, 35kV, 60kV, 110kV. 220kV, 330kV, 500kV.
Transformers have a wide range of uses, and different uses also produce different needs. Various types of transformers are produced from this. The classification of the transformer can be divided according to its usage, structure, winding and number of phases. The classification of the transformer is shown in the table.

The distribution transformer is a commonly used ordinary power transformer, its structure is simple, the basic components have oil tank, iron core, winding and insulation, oil meter, gas relay, etc.

The S11 laminated core transformer is a new type of transformer developed on the basis of the original distribution transformer technology. It has the characteristics of low loss, low noise, strong short-circuit resistance, good impact resistance and economic operation. It is especially suitable for places with low load rates such as rural power grids.
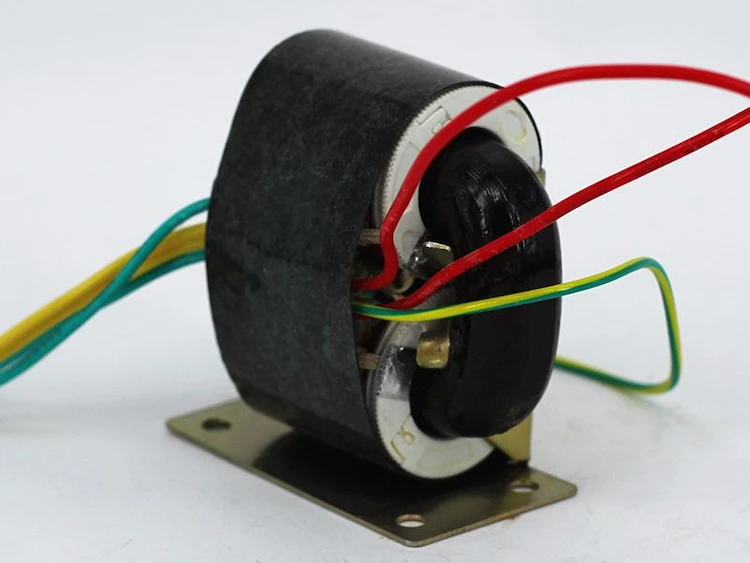
The coiled core transformer is made of thin, high-permeability cold-rolled silicon steel sheet, giving full play to the advantages of low sheet eddy current loss, so that no-load loss can be reduced.
Therefore, it has the characteristics of small size, low loss and low noise, and is a new generation of environmentally friendly, high-efficiency and energy-saving products.
It is suitable for power grid transformation of urban and rural, industrial and mining enterprises, and more suitable for combined transformers and pre-installed substations.
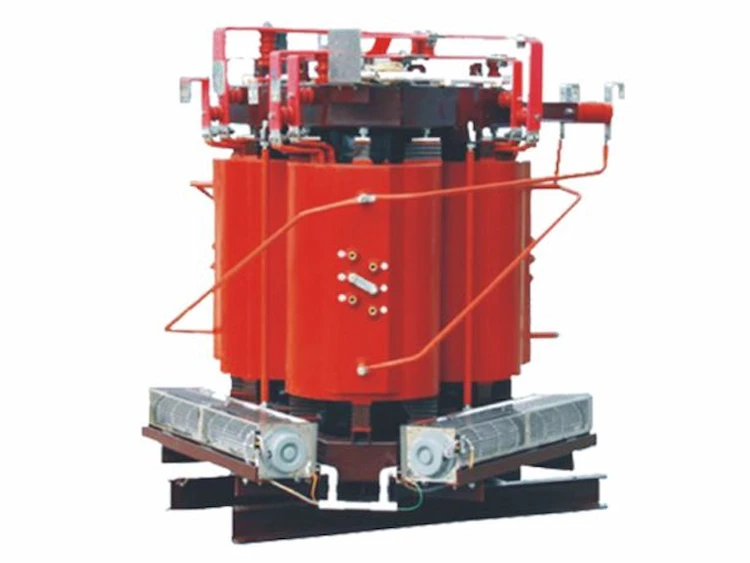

The high-voltage winding of the three-dimensional wound core transformer is layered, the low-voltage winding is layered for the capacity of 500kV•A and below, and the foil winding is used for the capacity of 630kV «A and above.
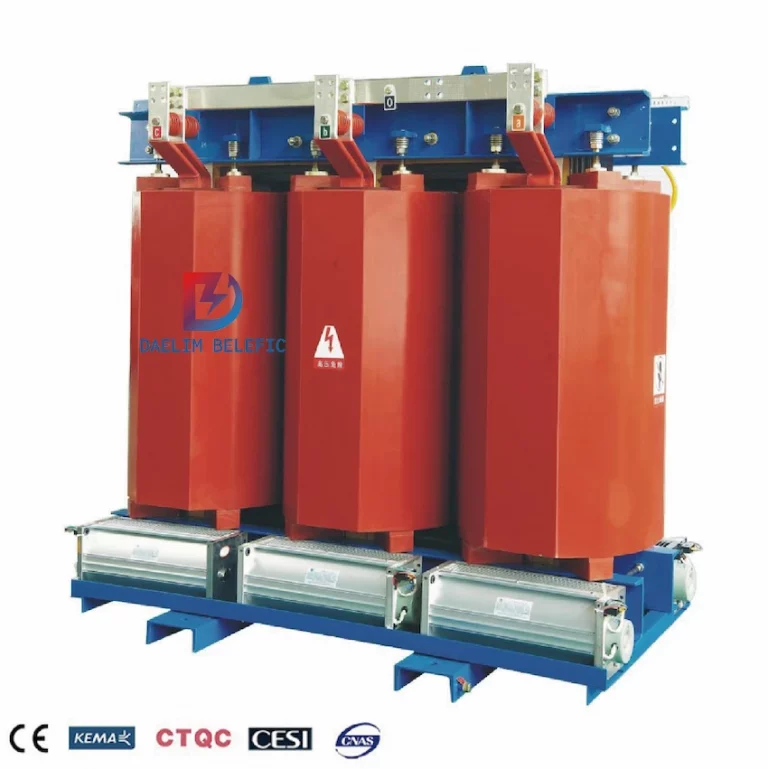

The epoxy resin cast dry-type transformer is a dry-type transformer product with less filler and thin insulation. It has the advantages of small partial discharge, low noise, low loss, good heat dissipation performance, strong moisture resistance, strong resistance to sudden short circuits, and large overload capacity. .
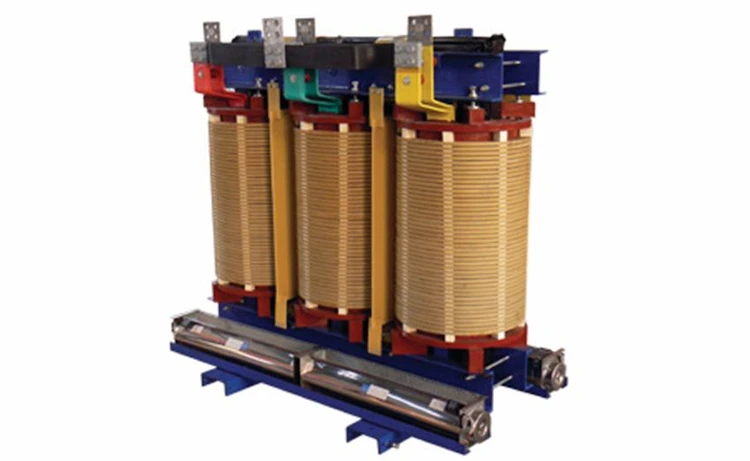

The Open dry-type transformer adopts DuPont Nomec paper-based insulation system, H-class heat-resistant insulation grade, does not require fan cooling, and allows long-term overload operation of 20%. Low loss, small local discharge, low noise, no harmful gas, insensitive to humidity and dust. It is suitable for high fire protection requirements, large load fluctuations and dirty and humid environments.
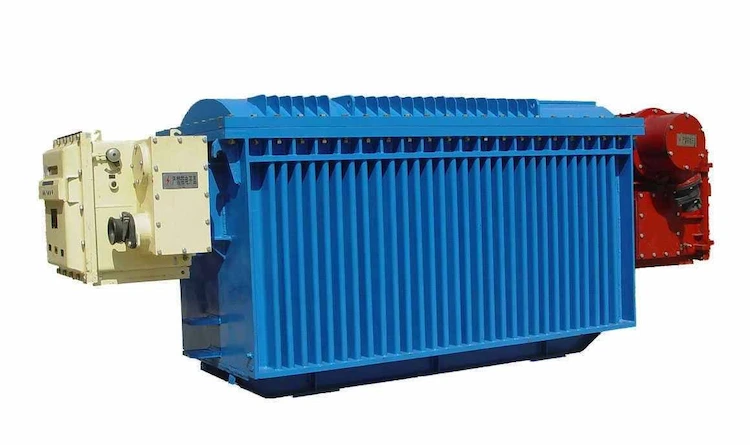

Mine transformers are suitable for explosive and hazardous locations containing methane gas and coal dust in coal mines. The mine transformers are designed, manufactured and tested in accordance with relevant national explosion-proof standards.
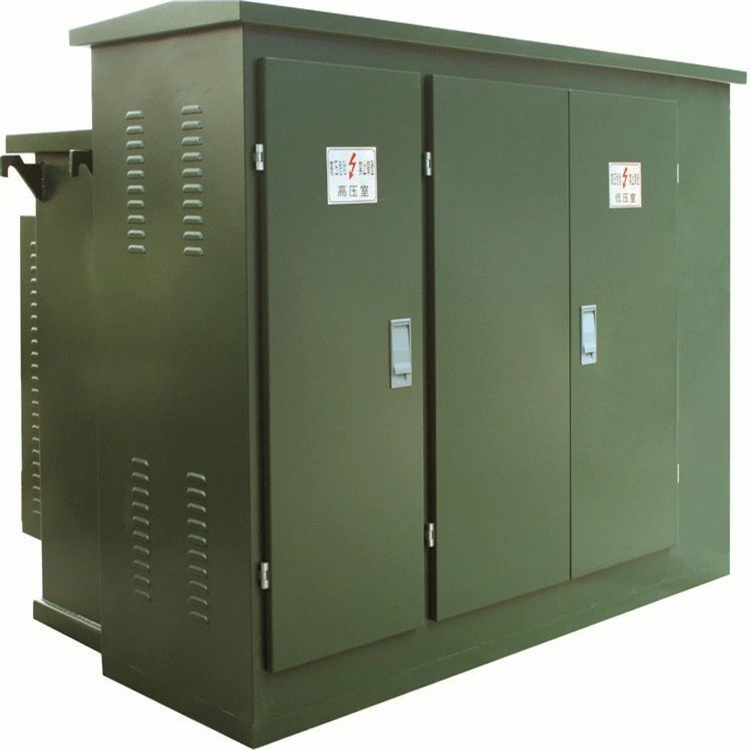

Pad mounted transformer uses medium and high voltage cables to be connected to the transformer through cable connectors in the high voltage warehouse, and low voltage cables are connected to the low voltage terminals by bolts and low voltage terminals in the low voltage warehouse. The oil tank of the Pad mounted transformer is equipped with high-voltage fuses and load switches, so that the transformer can be used for terminal operation or ring network operation, and protect and control the power supply status of the high-voltage side of the transformer.
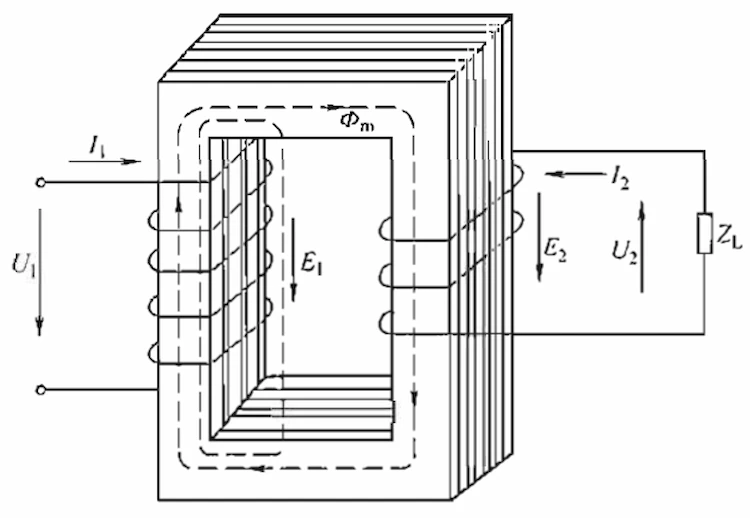
Transformers are static electrical equipment made by the principle of electromagnetic induction, which can convert alternating current with a certain voltage value. The working principle of the transformer is shown in the figure.
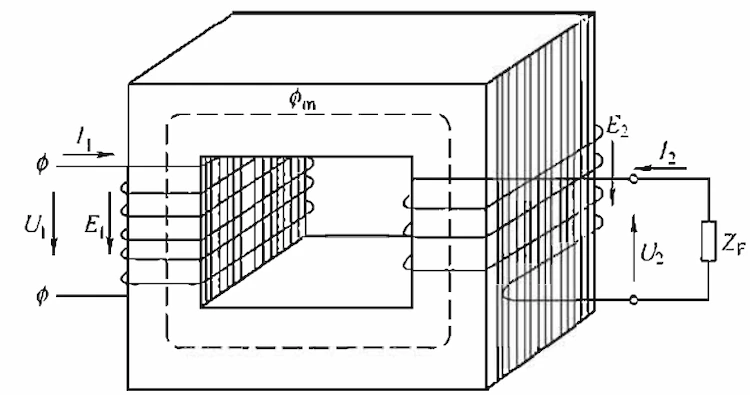
The winding connected to the power supply is the primary side, and the winding connected to the load is the secondary side. Under the action of the applied voltage, an alternating current flows through the primary side, and an alternating magnetic field is established in the winding.
Since the permeability of the iron core is much greater than that of air and transformer oil, most of the magnetic flux passes through the iron core, and at the same time interlinks the primary and secondary windings, and the electromotive force is induced in the primary and secondary windings.
According to the law of electromagnetic induction, the induced electromotive force of the primary and secondary windings is proportional to the number of turns. By reasonably arranging the number of turns of the primary and secondary windings, the required voltage can be obtained on the secondary side to achieve the purpose of changing the voltage.
Generally, the current and voltage generated by large and medium-capacity generators are not only unsuitable for general electricity consumption, but also a large amount of electric energy needs to be transmitted to a distant place, and it is impossible to use lower voltage transmission.
Due to the low voltage, the current delivered by it is very large, and the large current will cause a lot of power loss and voltage drop on the transmission line, and it cannot be economically transported to far-reaching places.
The use of higher power transmission voltage enables us to appropriately and conveniently deliver the power to the appropriate places.
It usually takes a long transmission line to transmit the power of AC power from the power plant to the user.
When the transmission power P and the power factor cos are fixed values, the higher the voltage U, the smaller the current I in the line, and the smaller the cross-section of the transmission line can be obtained, which can save a lot of material.
Conversely, most or all of the electrical energy may be consumed on the transmission line.
In order to reduce energy loss on transmission lines and improve transmission efficiency, transformers are often used to increase the voltage to the required value before power transmission.
AC power is connected to the primary winding of the transformer, the secondary winding is not connected to the load, and the secondary current is zero. This state is called the no-load operation of the transformer.
The current of the primary winding is represented by I0. The number of turns of the primary winding is N1, then ION1 is the magnetomotive force of the primary winding when there is no load.
Under the action of this magnetomotive force, the main magnetic commuter closed by the iron core is produced.
Because the primary and secondary windings are on the same iron core, the main magnetic flux in the iron core passes through the primary and secondary windings at the same time, generating self-induced electromotive force E1 in the primary winding and mutual induction electromotive force E2 in the secondary winding.
According to the basic law of electromagnetic induction, the magnitude of this electromotive force is proportional to the number of winding turns linked by the magnetic flux and the maximum value of the magnetic flux.
If the internal voltage drop of the transformer is ignored, that is, U1≈E1, U2≈E2, the following formula can be approximately written:
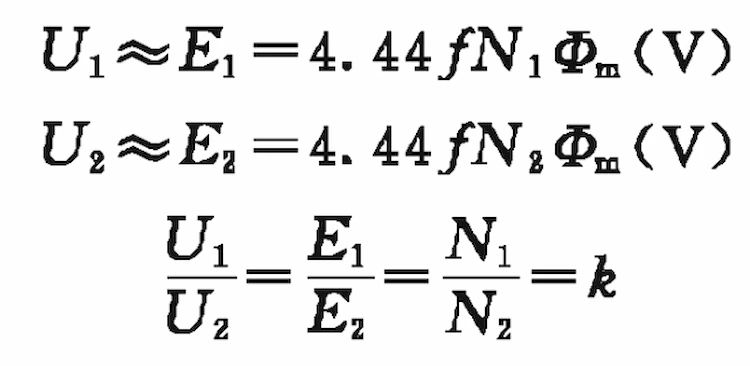
This formula is one of the basic formulas of the transformer. It means that when the transformer is no-load, the ratio of the voltage of the primary and secondary windings is approximately equal to the ratio of the number of turns, and the ratio k is called the transformation ratio of the transformer.
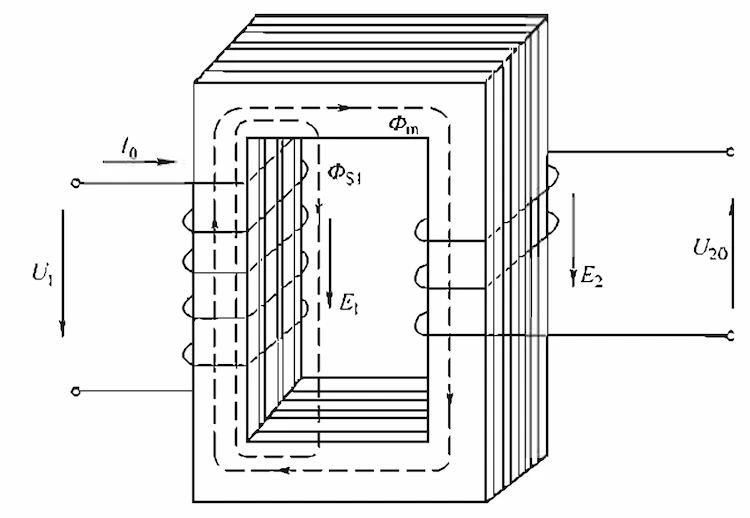
AC power is connected to the primary winding of the transformer, and the load is connected to both ends of the secondary winding. This state is called transformer load operation.
The secondary side of the transformer is connected to the load under the action of the secondary winding U2, and the current I2 passing through the load is the load current of the transformer. The size of I2 depends on the load impedance.
The relationship between the primary and secondary winding currents of the transformer can be analyzed by the magnetomotive force balance relationship.
If the number of turns of the secondary winding is N2 and the passing current is I2, the magnetomotive force is m. The main magnetic flux in the iron core when the transformer is operating with a load. It is produced by the two magnetomotive forces I2N1 and I2N2 of the primary and secondary windings.
When the power supply voltage does not change, the main magnetic flux is basically unchanged.
The magnetic flux produced by the magnetomotive force of the primary and secondary windings is approximately equal to the magnetic flux produced by the no-load magnetomotive force. This is the flux balance relationship of the transformer load operation.
Since the no-load current is very small, the no-load magnetomotive force, Ni, is also very small and can be omitted. Therefore:
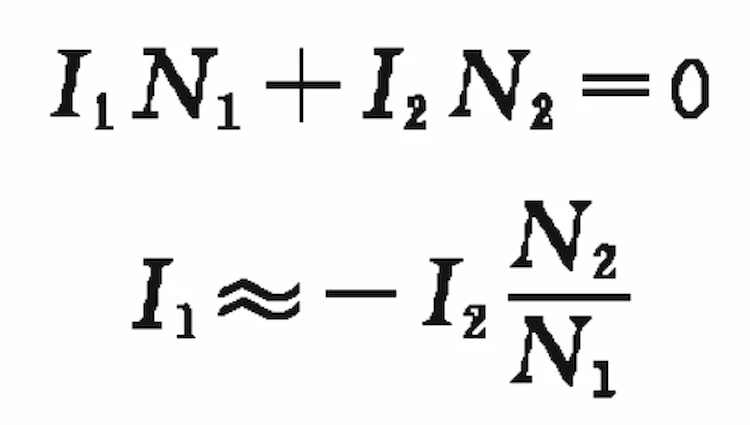
This shows that when the secondary winding passes current, the corresponding current will also pass through the primary winding, and the ratio of the current in the primary and secondary windings is approximately equal to the inverse ratio of the number of turns of the primary and secondary windings.
This shows that the transformer not only changes the voltage, but also changes the current.
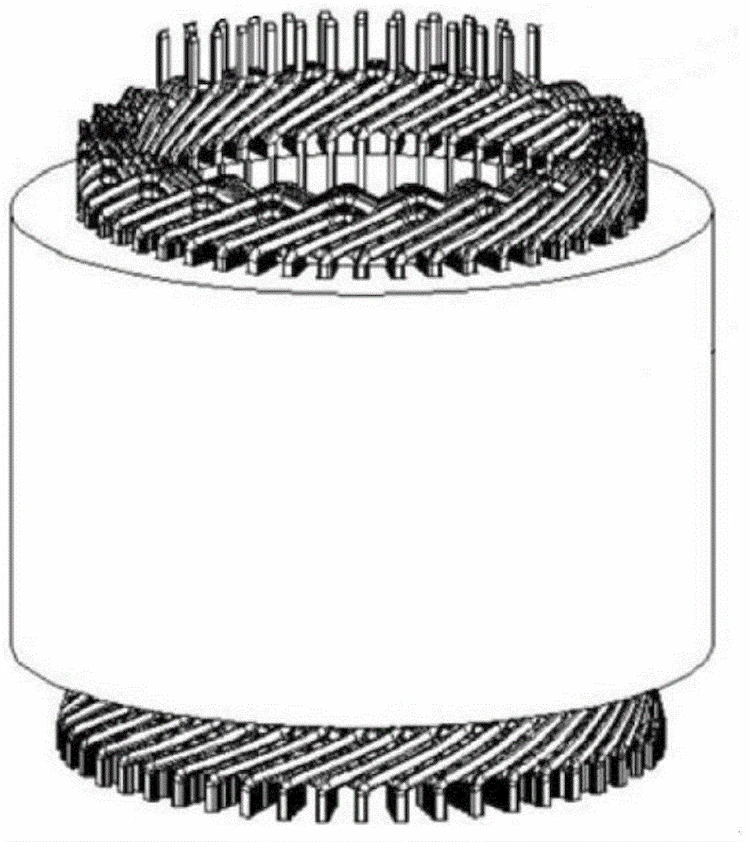
The construction of transformer is roughly the same.
Power transformers are the most commonly used transformers.
Take it as an example to illustrate the construction of transformer.
The main construction of transformer includes the body, the oil tank, the voltage regulating device, the cooling device, the protection device, and the outlet device.
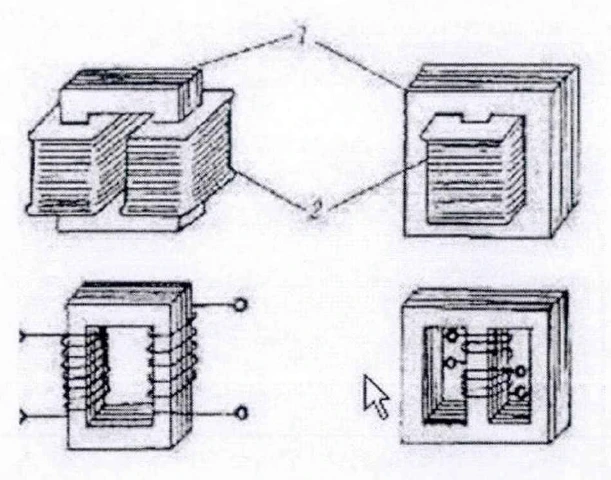
The iron core is the magnetic circuit part of the transformer. It is manufactured according to the principle of electromagnetic induction. There is no direct electrical connection between the primary coil and the secondary coil of the transformer, only the magnetic connection is formed through the iron core. The iron core of the transformer can be used to obtain a strong magnetic field, enhance the electromagnetic connection between the primary and secondary coils, and generate electromagnetic induction. Phenomenon.
There are core type and shell type, single-phase and three-phase, plane and three-dimensional type, laminated core and wound core. The two basic structural forms of iron core are shell type and core type.
The coil is the circuit part of the transformer, which is wound with insulated flat wire or round wire.
From the perspective of the relative position between the high and low voltage windings, the windings of the transformer can be divided into two types: concentric and overlapping.
The coil is the circuit part of the transformer, which is wound with insulated flat wire or round wire. From the perspective of the relative position between the high and low voltage windings, the windings of the transformer can be divided into two types: concentric type and overlapping type. The high and low voltage windings of the concentric winding are sleeved on the iron core column concentrically. In order to facilitate insulation, the low voltage winding is generally close to the iron core, and the high voltage winding is sleeved outside the low voltage winding. The concentric winding structure is simple and easy to manufacture. Overlapping windings have low leakage reactance and are easy to form multiple parallel branches. They are mainly used in low-voltage and high-current electric welding, electric furnace transformers and shell-type transformers.
Since the transformer is subjected to various working voltages for a long time in operation, in order to ensure that there is no flashover or breakdown between the live parts, and between the live parts and the iron core and the fuel tank, a good insulation structure must be provided.
The lead wire of the transformer refers to the connecting wire between the coils, between the coil and the outlet bushing, and between the coil and the tap switch.
The lead insulation of the transformer is an important part of the internal insulation. Some leads pass between the coils or between the coil and the iron pivot clamp and the wall of the fuel tank.
Therefore, it is necessary to ensure that these leads have sufficient insulation strength, that is, the insulation distance.
The transformer tap switch should also have strong insulation.
The 10kv no-load tap changer is generally insulated with a rolled insulating paper tube as the ground insulation.
The contact part of the no-load tap-changer with a voltage level of 35kV and above is installed in a phenolic insulating paper tube, and the insulating paper tube is then installed on a wooden frame, and the operating handle is connected to the moving contact of the tap-changer through a wooden insulating rod.
The insulation of the on-load tap-changer to the ground is composed of the insulating paper tube and the insulating connecting plate of the switch itself.
The transformer oil tank mainly circulates insulating oil for cooling and heat dissipation of the transformer.
Transformer oil is a refined insulating mineral oil. Its main function is to insulate, cool and extinguish the arc of the transformer.
Because the electric strength of transformer oil is much higher than that of air, and the transformer core and coil are put into the oil tank to avoid the influence of moisture in the air on the coil.
Through the oil temperature difference, the heated oil rises to the upper part of the oil tank.
It flows to the oil pipe through the upper port of the oil pipe, dissipates heat in the oil pipe, and flows back to the bottom of the oil tank after cooling. The transformer achieves the purpose of cooling through oil circulation.
When an electric arc occurs in the oil, the transformer oil can extinguish the electric arc within a certain range.
Transformer cooling devices can be roughly divided into the following types.
The bushing of the transformer is an insulating device that leads the leads of the transformer coil to the top of the oil tank respectively.
It is the insulation of the lead wire to the ground (fuel tank) and the fixing device of the lead wire. Therefore, the casing must have insulation strength, mechanical strength, and thermal stability.
In addition, moisture absorbers, oil purifiers, oil conservators, thermometers, gas relays, etc. are indispensable parts of transformers.
The winding is the circuit part of the transformer, and generally transformers have primary and secondary windings.
The winding connected to the power supply, that is, the coil that receives external AC power, is called the primary winding.
The winding connected to the load, that is, the coil that outputs electrical energy to the outside, is called the secondary winding.
According to different winding methods, transformer windings can be divided into layer windings, continuous windings, spiral windings and foil windings.
Mainly used for the voltage regulating winding of small and medium transformers and large transformers.
It can be wound with a single wire or with multiple flat wires in parallel.
Can be made into single-layer, double-layer or multi-layer barrel type.
The insulation paper or oil passage between the layers depends on the voltage between the layers and the heat dissipation of the windings.
It is composed of several wire cakes wound by paper-wrapped flat wire, and each wire cake is continuously wound by several turns in sequence.
The continuous winding has high mechanical strength, good heat dissipation, and can adapt to the capacity and voltage requirements, but the winding process is more complicated and there are more connections from the outside.
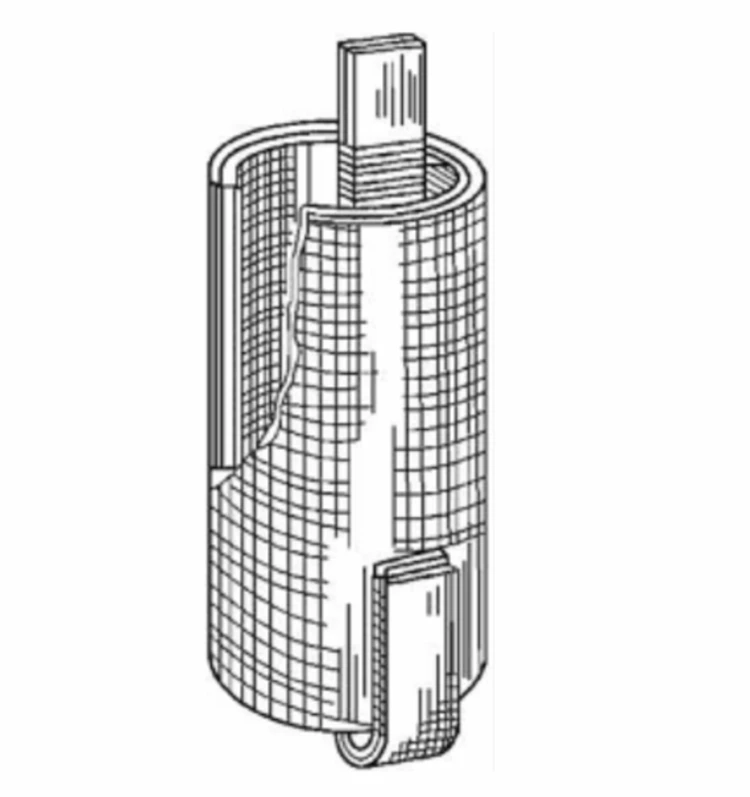
Single or multiple wires can be wound in parallel, leaving gaps between the turns, and padding between the gaps to form the radial oil passage of the winding.
The spiral winding is simple to wind and has good cooling conditions.
It is not applicable if the winding has a large number of turns.
Generally used for three-phase capacity of 630kV•A or higher, voltage of 35kV and below high current windings and voltage regulating windings of on-load voltage-regulating transformers.
It is a winding that uses aluminum foil or copper clamps as a conductor.
The clamp structure is made up of a layer of conductor clamps and a layer of thin insulation intertwined uniformly and tightly.
The contact surface of the conductors between layers is large and the spacing is small, and the ability to withstand short circuits is strong.
Power transformer is the principle is: when the primary winding through the alternating current (U1), will produce alternating flux, alternating flux along the core to form a closed-loop circuit, in the secondary winding to induce the alternating current electromotive force U2. power transformer is to achieve the same frequency voltage conversion of each other electrical equipment, the main role is to transmit electrical energy. It is through the primary and secondary coils with different wang numbers (n is the number of faces), the primary side voltage is converted into the secondary side voltage.
According to the type of transformers, different uses, can be divided into step-up transformers, step-down transformers, distribution transformers, contact transformers, plant transformers, etc..
According to the structure, there are three-winding transformers, double-winding transformers, self-reliance transformers, etc.; according to the cooling method is divided into oil-immersed transformers, dry-type transformers.
Also in order to distinguish certain technical characteristics, transformers have some main technical parameters: such as voltage ratio, apparent power, temperature rise, copper and iron loss, efficiency, etc.
The so-called voltage ratio is the ratio of the secondary voltage to the primary voltage, which is usually equal to the ratio of the facets of the secondary to the primary.
When the secondary voltage V2 is greater than VI, known as step-up transformer, when the secondary voltage V2 is less than VI, known as step-down transformer, the original side, secondary voltage and the number of coils between the West has the following relationship.
N = V2 / V1 = N2 / N1
Where N is called the voltage ratio (circle ratio).
At rated power, the ratio of transformer output power to input power is called the efficiency of the transformer, and
n = (P2/P1)*100%
where n is the efficiency of the transformer; P1 is the input power, P2 is the output power. Theoretically, the transformer can W achieve 100% efficiency conversion, but the actual is impossible to achieve. Transformer transmission of electrical energy will always produce losses, such losses mainly include copper and iron losses.
Copper loss is the loss caused when current flows through the transformer coil resistance. It is generally expressed in the form of W thermal energy. As the coil is generally wound by steel wire with insulation, it is called copper loss.
The iron loss of a transformer consists of two parts: hysteresis loss and symmetrical current loss. When the AC current passes through the transformer, the alternating magnetic field is generated, and the direction and size of the magnetic lines of force also change, and the magnetic lines of force pass through the inside of the steel sheet to generate heat, thus losing some of the electrical energy, which is the hysteresis loss. When the transformer core has magnetic lines of force through, the surface of the iron coincidence will produce induction current, which is known as the bogey current. This loss is called hysteresis loss.
The iron loss of a transformer consists of two parts: hysteresis loss and symmetrical current loss. When the AC current passes through the transformer, the alternating magnetic field is generated, and the direction and size of the magnetic lines of force also change, and the magnetic lines of force pass through the inside of the steel sheet to generate heat, thus losing some of the electrical energy, which is the hysteresis loss. When the transformer core has magnetic lines of force through, the surface of the iron coincidence will produce induction current, which is known as the bogey current. This loss is called hysteresis loss.
The core of a transformer is made of laminated sheets of Guinness steel and is divided into two parts: the core column of the transformer and the iron vehicle. The core column of the transformer is wound and the iron yoke connects the core column of the transformer to form a closed magnetic circuit. The total structure of the core of the transformer is generally core type and shell type, of which the core type is widely used in large transformers, such as power plant oil-immersed transformers, because of its simple structure and simple process. Shell type transformers are mostly used in small capacity transformers and electric furnace transformers.
Transformer winding is made of multiple strands of round copper wire or flat copper wire wound on the core, generally with the low voltage side inside and the high voltage side outside, which is the transformer current circuit. It is divided into primary winding (also called primary winding) and secondary winding (also called secondary winding) according to the position of winding on the core.
Primary winding (primary winding): input power
Secondary winding (secondary winding): output power
Because of the same transformer ratio and western number ratio, usually the number of turns of primary and secondary windings will be different, when the core through the alternating flux, the current is induced in the secondary side.
The first and second windings are set on the same core column, from the inside to the outside, in the order of low-voltage winding and high-voltage winding. The transformer winding can be divided into concentric type and overlapping type according to different positions. Concentric winding is widely used because of its simple structure and convenient manufacturing, while crossover type is mainly used in special transformers.
For insulation and heat dissipation, the transformer body is immersed in a closed oil tank, which is filled with transformer oil.
Transformer oil is usually Kramer #25, which has good insulating properties and fluidity. Transformer operation will generate a lot of heat, in order to facilitate heat dissipation, the general oil tank will be equipped with cooling devices and heat dissipation oil pipe, increasing the heat dissipation area.
Some large transformers are also equipped with submerged oil poly and cooling fan, or water cooling device.
Oil storage cabinet is located at the top of the tank, the main role is to reduce the contact between transformer oil and air, slow down the oxidation of transformer oil and moisture absorption rate, so as to ensure the quality of oil. The oil level of the oil storage cabinet fluctuates up and down according to the transformer load, which reduces the pressure in all parts of the tank.
Gas relay, also known as gas relay, is the most important protection device for transformers.
Its role when the transformer internal failure, will produce a lot of heat, heat will make the transformer oil vaporization expansion, oil flow surge will trigger the gas relay to send an alarm signal or cut off power.
If it is a serious accident, transformer oil in addition to triggering the gas relay, will be cascaded from the top of the tank pressure relief valve to avoid the tank pressure deformation.
The role of insulating bushing is to lead the transformer internal high and low voltage leads to the outside of the tank, to avoid the lead and tank shell insulation breakdown.
Insulation bushing not only plays an insulating role, but also has a fixed role. At the same time, the insulating bushing needs to withstand the rated current, and under severe circumstances also need to withstand the impact of short-circuit current. The casing is generally made of porcelain casing, oil casing and hexavalent sulphur casing, etc.
Tap changer is also known as a voltage regulator, divided into five-load regulator and on-load regulator. Its main role is to adjust the number of high-voltage side coil pitch, so as to change the transformer ratio, by changing the ratio to achieve the purpose of voltage regulation.
How to improve the quality of the supplier’s transformer?
The main factors affecting the quality of transformers include three aspects: poor manufacturing quality, improper design and selection, and aging equipment.
In the design selection, coil design structure is not reasonable, conductive rod and insulation layer bias also, casing head current carrying current selection is not appropriate have occurred, the need to take measures to avoid repeated occurrence in the design, on the one hand, the need for manufacturing plants in the design optimization design program, processing and manufacturing to ensure the quality of processing outside, equipment supervision also has a lot of work work can be carried out.
In terms of manufacturing quality, the transformer body coil manufacturing process is poor or accessory accessories (such as bushings, tap changer, oil conservator and oil tank, cooling system, gas relay, etc.) quality is not up to standard is the main reason.
This includes both manufacturing process defects, but also the quality of external spare parts is not the problem.
In addition to the manufacturing plant needs to continuously improve the process, strict control of the quality of outsourced parts, equipment supervision as an important party, but also from the perspective of equipment supervision to strengthen management, the development of specific and feasible methods to ensure that the transformer manufacturing quality is reliable, to achieve the quality of outsourced spare parts can be controlled.
The main factors affecting the quality of transformers include three aspects, poor manufacturing quality, improper design selection and equipment aging.
In the design selection, coil design structure is unreasonable, conductive rod and insulation layer bias also, casing head current carrying current selection is not appropriate have occurred, need to take measures to avoid repeated occurrence in the design, on the one hand, the need for manufacturing plants in the design to optimize the design plan, processing and manufacturing to ensure the quality of processing outside, equipment supervision also has a lot of work can be carried out.
In terms of manufacturing quality, the transformer body coil manufacturing process is poor or accessory accessories (such as bushings, tap changer, oil conservator and oil tank, cooling system, gas relay, etc.) quality is not up to standard is the main reason.
This includes both manufacturing process defects, but also the quality of external spare parts is not the problem.
In addition to the manufacturing plant needs to continuously improve the process, strict control of the quality of outsourced parts, equipment supervision as an important party, but also from the perspective of equipment supervision to strengthen management, the development of specific and feasible methods to ensure that the transformer manufacturing quality is reliable, to achieve the quality of outsourced spare parts can be controlled.
In terms of equipment selection, equipment supervision engineers should intervene in the design stage to understand the structural characteristics, technical parameters, performance indicators of the supervised products, the type specifications of the main materials and outsourcing group components, outsourcing / outsourcing manufacturers, new technologies, new materials, new group components, new processes used in the supervised products.
At the same time should have the necessary ability to verify whether the design results in a comprehensive and accurate implementation of the requirements of all terms on the procurement contract, focusing on economic and technical indicators, such as loss, noise, temperature rise, impedance and its deviation.
In particular, for years of transformer accident statistics in transformers generally weak short-circuit resistance, casing current-carrying capacity and other issues, focus on the design of the beginning of the transformer short-circuit resistance parameters, and require the manufacturer to provide short-circuit withstand capacity calibration report, in the transformer technical agreement, clearly require the manufacturer in the design, material selection and manufacturing process to protect the product’s short-circuit resistance.
And the equipment supervisor should supervise the manufacturing plant according to the design of the same type of product that has passed the short-circuit withstand capability test, to ensure the stability of the structure, raw materials and process.
In the selection of transformer manufacturers (also known as suppliers), should be combined with the manufacturing capacity of the manufacturing plant, manufacturing qualifications, corporate reputation and other comprehensive considerations, for many times in the power system due to poor transformer manufacturing quality leading to failure of the enterprise, with the penalty of blacklisting, resolutely not used. In the transformer accessories (such as bushings, on-load tap-changers, cooling devices and submerged oil corn, etc.) selection, should pay special attention to the specification of bushings, on-load tap-changers, cooling devices and submerged oil springs and other group components technical requirements. In the tender documents, the equipment supervisory party should assist the owner, focusing on clarifying the main group components, raw material suppliers and origin information, casing, tap changer should specify the model.
At the same time, strict audit of raw materials, group parts suppliers and their products, for the key production links prone to quality problems, equipment supervision engineers should be stationed at the plant to supervise the manufacture.
Transformer manufacturing quality control is the top priority of transformer supervision and manufacturing work, mainly because.
(1) the high quality requirements of the equipment.
As the transformer equipment in the power system as an important component, its quality determines the stability of the operation of the entire transmission and substation system and power security, so the requirements for quality control will be relatively high.
In the process of transformer equipment supervision and manufacture, high quality requirements have undoubtedly become one of the key difficulties, supervision and manufacture work must be strictly controlled.
(2) equipment production in the special process.
In the production of transformers, will involve a lot of non-standard parts production, non-standard parts in the production of its standards are not clearly defined, usually some large use of steel plates and assembly welding process, these processes often belong to the special processing, in the whole supervision and manufacture of the work is more difficult.
3) The quality of the equipment manufacturing process mainly relies on manual control.
In the process of transformer supervision and manufacture, it is often difficult to supervise the quality of the equipment manufacturing process with manual control.
In the production process of transformers, except for a small number of equipment parts plus king will use fixed production line equipment, the vast majority of processes still need to rely on manual, adding difficulty to the whole supervision and manufacturing work.
Therefore, in the manufacturing of transformers inevitably appear quality problems, which requires equipment supervision of its strict control, especially some key and difficult issues need special attention. Deal with these problems can effectively improve the quality of transformer manufacturing.
At present, the power industry on the key processes, key processes of quality control mostly use the project management of quality acceptance methods, using documents witness point, site witness point, stop work pending inspection point.
1) Document witnessing.
According to the key difficulties in the process of transformer equipment supervision and manufacturing, document witnessing is a good solution. Document witnessing is the supervision and manufacturing unit of the equipment provided by the manufacturing unit of the process plan, material certification and inspection reports and other specific documents and information for document inspection to ensure that the equipment conforms to the contract technical agreement and relevant standard provisions.
(2) on-site witnessing.
On-site witnessing is to witness each process of transformer manufacturing to ensure that its quality meets the requirements of the technical agreement and relevant standards. It includes the inspection of coil winding, core lamination, oil tank manufacturing, body assembly, etc. of the equipment.
3)Stop work pending inspection.
The stop-work inspection is an inspection of the transformer’s overall assembly, vacuum after assembly and factory test, etc., and its work is characterized by the fact that when each process has passed the inspection, the next process can be carried out.
4) Roving inspection.
Roving inspection is mainly based on the needs of the supervisory unit, the equipment production of materials into the field and in the production of equipment in the process of forming the material, heat treatment, processing and assembly tracking inspection, roving inspection is both a process of supervision of the equipment is also the quality assurance of the manufacturer.
In order to realize the quality control methods in equipment supervision work to be well implemented, to achieve standardization of equipment supervision work, table, combined with the analysis of the transformer in Chapter H of the lack of accompanying and hidden problems, the author according to the relevant provisions and requirements, the preparation of raw materials control methods, while for the transformer tank, coil, core manufacturing, coil assembly, drying and transformer assembly put forward the main points of supervision and Table, improve the equipment supervision of quality control operability.
Transformer common failure types can be seen, transformer accessories (such as bushings, tap changers, gas relays, etc.) prone to problems, and the transformer’s long period of stable operation caused by a greater impact, need to keep good quality from the manufacturing link, but with the advent of the era of industrialized mass production, most of these accessories are provided by transformer supporting manufacturers, which needs to find ways in the control of raw materials, to eliminate unqualified Products appear.
Material selection as the first process of transformer manufacturing, must be strictly good quality. Equipment supervisor after entering the manufacturing plant, should be from the source of procurement to strengthen the key raw materials, group components into the factory inspection. Including.
(1) strengthening the sampling inspection of electromagnetic wire, inspection items including enameled wire withstand voltage, yield strength, etc., to ensure the electrical and mechanical properties of electromagnetic wire.
(2) strengthen the 500kV and above transformers important parts of the use of insulation molding parts, cardboard X-ray inspection spot checks, sampling ratio of not less than 20%.
(3) take measures to ensure the quality of the casing, the casing that is not tested with the product should create conditions for the measurement of dielectric loss and local discharge test at high voltage, or go to the casing plant for on-site test witnessing. Random inspection should be strengthened for casing purchased in large quantities.
(4) should be carried out gui steel flatness, unit iron loss measurement.
5) strengthen the on-load tap-changer together with the winding action characteristic test.
6) Strict inspection of the group components that provide non-electricity protection signals (such as pressure release valves, gas relays, pressure mutation relays) to avoid misoperation and rejection of non-electricity protection due to group component problems, especially the vacuum tolerance of gas relays to match the vacuum oiling process.
(7) In the raw materials, group parts after the completion of the inspection, will not be used temporarily, to be in storage, transit and other links from time to time random inspection, long time storage of raw materials, group parts before use should be tested again. Important parts should avoid the mixing of insulation parts.
At the same time, the quality of raw materials and group parts with problems should be informed to the owner in time, and family defects should be warned in advance to stop them from entering the manufacturing workshop.
Line solid is an important part of the transformer, is the key component to achieve power conversion, but also accident-prone parts, equipment supervisor in the quality control of the coil, is the entire supervision work in the focus, for better quality control of the transformer coil.
Transformer total assembly is the last process to test the integrity of the transformer, directly test the transformer components between the assembly can meet the requirements, need to focus on.
After filling in the contact information, you can download the PDF.