
How to Choose Pad Mounted Transformer?
Table of Contents Selecting the right pad-mounted transformer requires careful consideration of several critical
ELECTRIC, WITH AN EDGE
Transformer substation is complex machines that convert electric energy into another form of energy. They come in many different types, and in this article, we’ll discuss some types of transformer substations. The most common types include single-phase, three-phase, and four-phase transformers, and the type you’ll need depends on your project, location, and power requirements.
One of the best producers of electrical equipment and professional transformers is DAELIM. Serving the electric business with reasonably priced, high-quality equipment for 15 years. DAELIM has been abiding by global standards set by organizations like ANSI, IEEE, IEC, CSA, AS/NZ, etc.
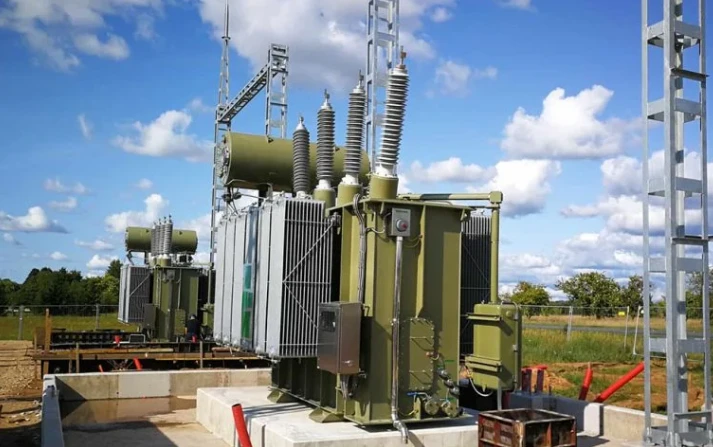


Did you ever come across those giant metal boxes near power lines? Chances are, you’ve passed by a transformer substation without even realizing it. But what exactly is it, and what does it do?
In this post, you can look at the role of substation transformers in your electrical grid and explore some of the unique features of these vital facilities.
DAELIM offers various high-quality electric products and equipment. They’ve been in the business industry for over 15 years. They have already built a concept called Daelim Edge+ that allows them to deliver multiple standards, cutting-edge service/speed, and expert-level customization skills.
A transformer substation converts electric energy from one type of circuit to another. This can be done by changing the voltage, frequency, or phase angle of the signals traveling through each circuit. It is also a facility that works with transformers to regulate power flow.
In most cases, transformer substations are located on high voltage transmission lines and serve to change the higher voltages into lower ones. The main purpose is to allow for easier transmission over long distances without using more expensive equipment such as step-up transformers or substations.
Additionally, they are used in situations where power lines must travel over long distances without having their voltages changed as they pass through different regions or areas.
Substation transformers are an electrical system component comprising transmission or distribution lines and switchgear. These dark gray stations are located at the crossroads of many electrical cables that run above and below ground.
In most cases, they include several pieces of electrical equipment, closed-off systems, and transformers that serve as their core components. Additionally, everything needed to regulate and protect power is often found in the substation.
The flow of electric power may go through numerous substations operating at varying voltages before it is utilized. Changing the voltage levels between higher transmission and lower distribution voltages, or at the interface of two separate transmission voltages, is the job of the substation.
This piece of equipment serves as a conduit for converting electricity from a larger source to a smaller one and vice versa. It makes it possible for the electricity to enter the local grid, which the customers will receive.
The substation will then send bulk electricity back into the system once it is used to convert power for local usage. Because it is practically difficult to store electricity of this sort, the transformer removes surplus power from the local system and transforms it back to bulk power. This allows the extra power to be used elsewhere.

Transformers are very important in the power system. They convert alternating current (AC) from one voltage level to another or from one frequency to another. Transformers come in different forms, depending on the voltage required, frequency, and amount of power delivered.
The substations transform mechanical energy into electrical energy and carry this through a network of lines to distribution substations and finally transform it into alternating current (AC).
Transformer substations are the largest and most complex transformer stations. They consist of two or more high voltage transformers, a network of transformers, and control systems to manage these facilities. Generally, transformer substations are divided into four distinct types:
These are used in the primary circuit of the system, which means they connect directly with the source of electricity or generators. They serve as the first connection point between the utility and a transformer and have a rating between 400 kV and 3000 kV.
Primary grid substations are located in the distribution systems and supply power to consumers. They are used for supplying power to consumers, who may be residential or commercial. These substations can either be single or multiple transformer stations connected.
They’re designed to provide power to the transformer, switchgear, and other equipment that serves the customer’s needs. The primary grid substation may be located at the end of a transmission line, or it may be located at a substation closer to where it feeds power into distribution systems.
Among the types of transformer substations, this one has no direct connection between one part and another because its secondary circuits connect directly with other transformers to transfer electricity. In addition, secondary transformers also have a rating between 400 kV and 3000 kV.
Secondary substations are located at the interface of the primary grid and distribution system (usually on an equal-distribution transformer or step-up transformer). Here they supply power to consumers through transmission lines or transformer stations. Using multiple feeders, these substations may feed two or more consumers from one transformer station.
Distribution substations are responsible for supplying electricity to consumers within their service area. They provide power to customers in areas served by more than one feeder line (feeder).
This includes areas with multiple service zones within a single area and where there is no immediate connection between feeders because of factors that make direct connection difficult.
They serve as an interface between the primary grid and distribution system by supplying them with electricity through transmission lines or transformer stations. Distribution substations can be categorized into DSs that serve multiple consumers within their service area, and DSs that serve only one consumer within their service area, called islanded DSs (ISDs).
ISDs have higher costs due to additional equipment required to protect against faults in these systems. Distribution transformers at these locations typically have higher capacity ratings than those found in normal service areas since they must handle higher voltages over longer distances (e.g., 500 kV).
These substations can be found in power plants, which primarily enhance the operating point. In order to balance the transmission system, the energy production voltage, which is now 11 kV, is increased to 220 kV or 132 kV.
Step-up substations are typical of the outdoor variety and are situated inside or close to the grounds of the generating facility. Step up refers to an increase, so the voltage is raised in this sort of transformer in order to lower the losses at lengthy transmission lines. Generally, most step-up transformers are situated close to power plants, which helps with supply and transmission.
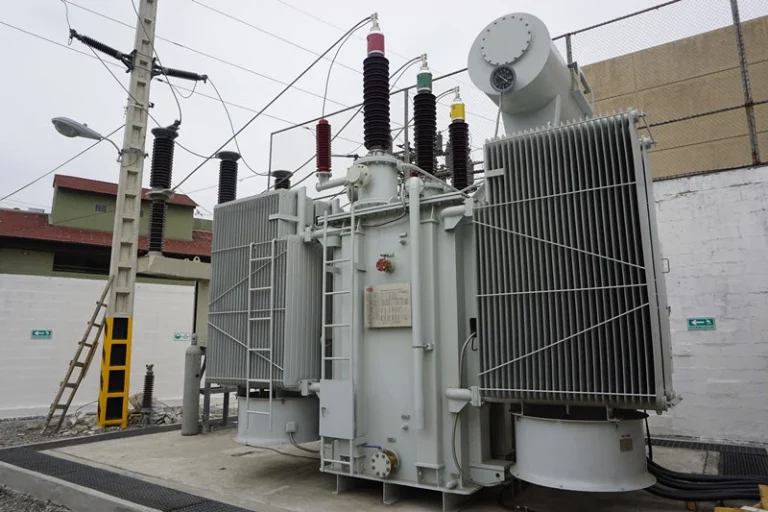

When looking for mining power supply for various industries, transformer substations play a big role in providing the energy needed. These transformers are a type of substation that is used to transmit and distribute electrical power. They are used in the mining industry and are a vital part of the mining process.
Transformer substations also provide power to other industries, such as oil and gas exploration, bitcoin mining power systems, and a reliable source of crypto power/crypto farm power. Different types of transformer substations are used in power supply systems and are usually located in remote areas, away from populated areas and other buildings.
Bitcoin mining power systems rely on power transformers to convert AC to DC and to maintain a constant voltage. They protect the miners from electrical sparks generated by moisture or humidity. It is also their job to prevent system failures caused by abrupt voltage changes.
A low-frequency current is employed in most cases, but high-frequency transformers can also be used. Using transformers, you may split a single supply of direct current (DC) electricity into two or three streams of alternating current (AC).
This equipment is normally made up of a metal casing and internal structures used to perform their tasks. Protective measures, like insulation and a cooling system, are also included in transformers.
You can classify transformer substations according to three different categories. Looking at them concerning the voltages associated with them, you can classify them into four groups:
However, when considered in terms of their position on the grid, then they could fall into two main types of transformers:
The third type of substation classification would be according to the purpose of usage, which would consist of the following subcategories:
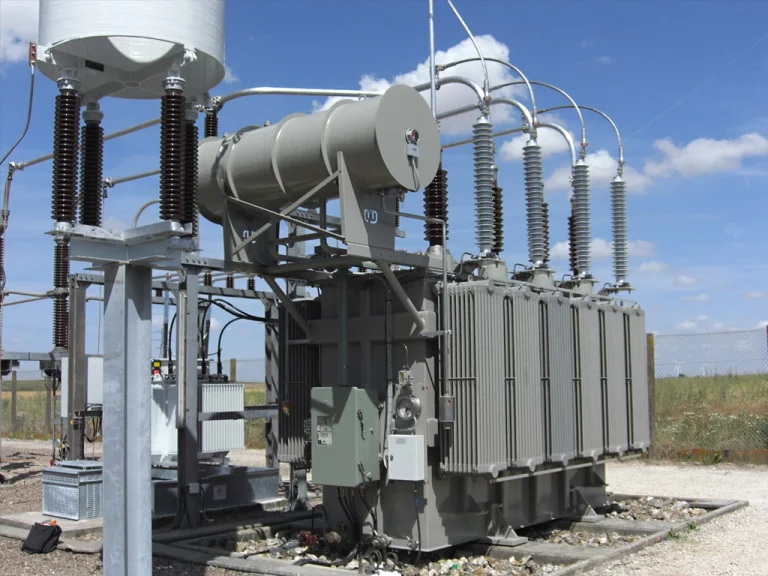

An outdoor transformer substation is a power distribution center that serves a wide area. It supplies electricity to homes and businesses through the main transmission line. Generally, the electrical substation has several transformers and other equipment that allows it to convert power from one voltage to another.
It usually consists of several transformers and other equipment to generate and distribute electricity over large areas.
They’re often located in remote locations, far from any other electric power plants or substations. Generally, an OTST provides electricity for large areas such as cities and townships, where there are no other sources such as coal or nuclear power plants. An OTST can also be used for emergencies if there is a blackout or outage at another facility.
An intermediate transformer substation is an electrical substation that connects to the distribution transformer. It transfers power from the distribution transformer to the transmission line.
The intermediate transformer substation contains one or more transformers, rectifiers, and switches that connect it to other substations. Generally, the advantage of using intermediate transformer substations is that they allow more efficient use of space.
For example, less space will be required if an intermediate transformer substation is built with only one type of equipment instead of having multiple types in one location.
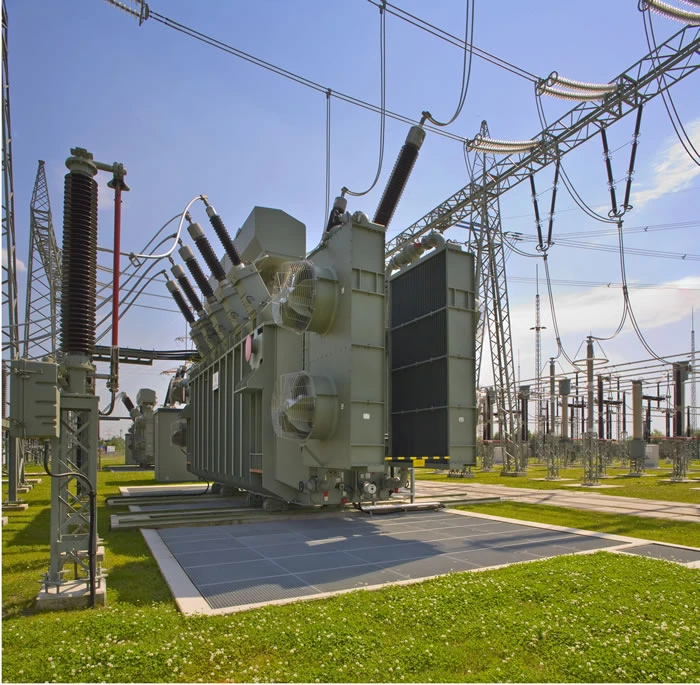

Transformer substations are an integral part of the power grid that provides electricity to homes and businesses. They are crucial to the stability of the electric grid and the quality of power. Hopefully, this discussion on the different types of transformer substations and how they work was helpful to you.
When it comes to today’s looming power shortages, rising demand, and the debate over energy efficiency, how the electrical network is operated is becoming increasingly more critical. Thankfully, substations can play a significant role in ensuring that the power station fulfills the needs of today’s consumers. Here are some benefits of substation transformers:
When erecting a transformer bank consisting of three autotransformers rated at 500 kilovolts, the question of size will always arise. Generally, when the transformer in question is buried beneath the streets of a megacity, this becomes an even more pressing concern.
Each unit’s length, width, and height measure a mere 9 by 5.6 by 7.3 meters (L x W x H). Despite this, the total size of the units is rather condensed.
When a transformer generates power underground, the demand for its cooling capacities increases. The conventional air-cooling method proved insufficient for these transformers since they can sustain increasing voltage and load levels. So, an innovative water-cooling system was conceived of and constructed as a solution to the problem.
Not only did the criteria for the voltage level seem unusually strict, but the requirements for the short-circuit strengths seemed unusually stringent as well. Each transformer should be able to sustain a specified level of load when subjected to a short circuit.
On the other hand, the autotransformers used for the underground substation in Shanghai have an impedance tolerance of up to 22 percent. This indicates that the units will continue to function normally even if they are subjected to a load that is 22 percent greater than their current rating.
The high impedance posed difficulties in terms of both hot spot control and stray loss management. Generally, the design of the shielding structure, which is fully supported by a 3D magnetic model tool, contributes to an increase in total efficiency. This is notably true of the tank and the clamping frame.
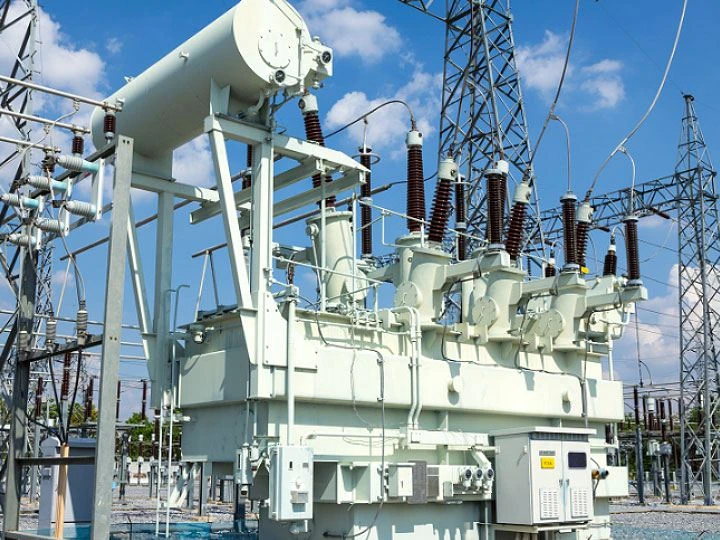

The following items are the components of the substation’s hardware and perform the majority of its duties:
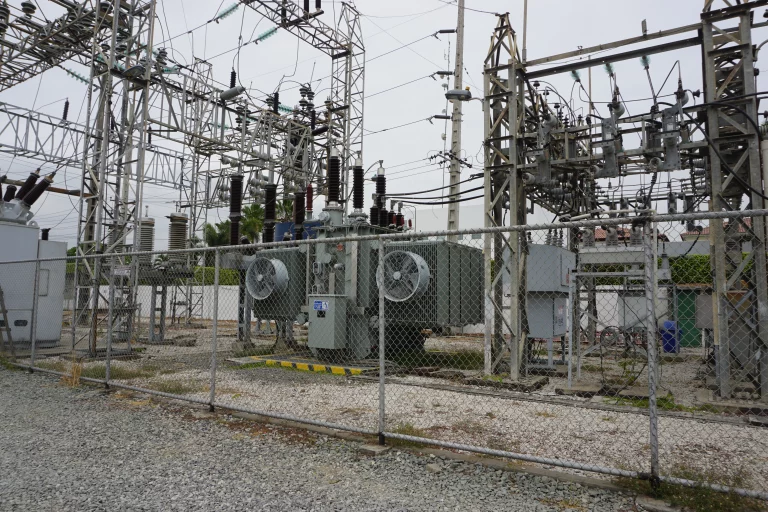

When designing a transformer station, it must meet the following criteria:
Requirements for a Main 11 kV Substation
Here are the following requirements for an 11 kV substation:
DAELIM provides various substation solutions, from transformers to electrical cabinets, and is trusted by clients to satisfy their demands and construct all sorts of substation transformers. With an ultra-short delivery time of ten to thirty weeks, outstanding transformer quality, and 24/7 online support, DAELIM proves they are among the good substation transformer manufacturers.
Transformers are electrical devices that either increase or decrease voltage. A substation is a location where switching and transformation occur. A substation can be a transformer installed on a pole or pad along with its corresponding safety equipment in its most basic form (HV and lV fuses).
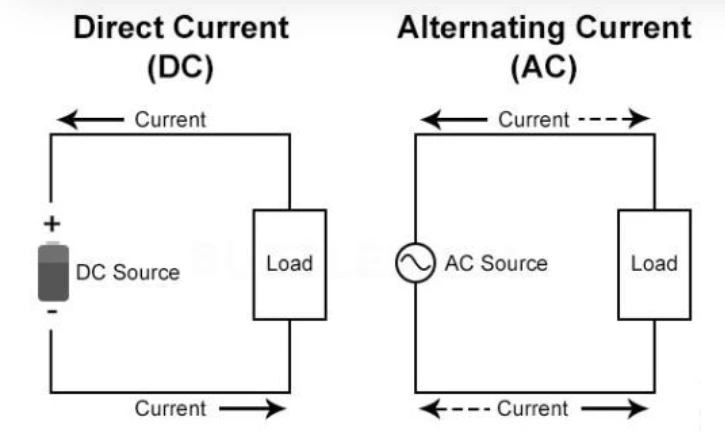
DC power supply is a requirement for substations. Every type of control necessary in substations uses a DC supply, from charging the battery banks to providing a steady supply to every powered system in your company.
There are many different substations, and while each type has a unique structural design, all substations contain the following components: transformer, isolation knife, and busbar system.
There are a variety of transformer substation classifications available on the market, including those based on voltage, location on the grid, and function.
Finding the electrical needs that are suited to your substation transformers might prove to be a challenging endeavor. Be confident that the information presented here can be useful to you while you search DAELIM for the things you demand.
Download Resource

Table of Contents Selecting the right pad-mounted transformer requires careful consideration of several critical

The primary function of the pad mounted transformer is to serve as a critical distribution

A pad mounted transformer operates through electromagnetic induction, serving as a crucial distribution component that
After filling in the contact information, you can download the PDF.