
ELECTRIC, WITH AN EDGE
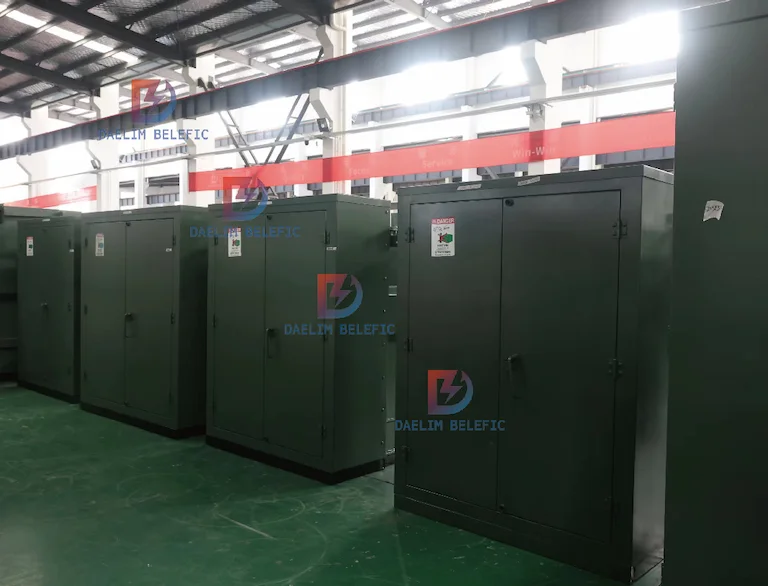

A pad mounted transformer, i.e. ground mounted transformer, is a ground mounted power distribution transformer enclosed in a metal box, usually mounted on a concrete base. Its main function is to convert high-voltage electricity into low-voltage electricity to be supplied to customers in residential or industrial areas. Since all electrically charged connections are securely enclosed in a grounded metal enclosure, the pad mounted transformer can be installed in areas that do not need to be protected by fencing, such as along streets or near buildings. This design not only improves safety, but also makes it possible to install them in areas where space is limited, making them ideally suited to the power distribution needs of modern cities and residential areas. When choosing the right pad mounted transformer, it is important to assess the specific power requirements and installation environment to ensure that its power rating and structural design meet the requirements of the actual application.
The main operating principle of a pad mounted transformer is to convert electricity from high voltage lines to low voltage power suitable for domestic or industrial use. It is usually connected to an underground power distribution line, which converts the high voltage (usually below 35 kV) to a lower secondary voltage (e.g. 240V or 120V) by means of a “service drop”, which is then distributed to the consumers. For specific implementation, the steps for connecting underground power distribution lines are as follows:
Preparation: Ensure that all necessary tools and equipment (e.g., cables, connectors, and protective gear) are in place and verify that the work area is safely isolated.
Installation of base: Install the concrete base at the selected location. The base should be flat and stable to ensure that the transformer will not tilt or move after installation.
Connecting High Voltage Cables: Use special elbow connectors to connect the high voltage cables to the high voltage terminals of the transformer. These connectors can be operated under power and are connected using a “hot stick”, which contributes to flexibility in maintenance and repair.
Connecting the low voltage cables: Connect the low voltage cables to the transformer’s low voltage terminals. Make sure all connections are tight and secure to avoid loose or poor contact.
INSPECTION AND TESTING: After completing all connections, perform a thorough inspection and testing of the transformer and cables to ensure that all connections are made correctly and that the equipment is functioning properly.
By following these steps, you can ensure that the pad mounted transformer is correctly installed and connected to provide users with a stable and reliable power supply. In practice, strict adherence to these steps not only improves installation efficiency, but also ensures safety and long-lasting reliability of the equipment.
To learn more about the specific application of pad mounted transformer, please check this page for more professional guidance.
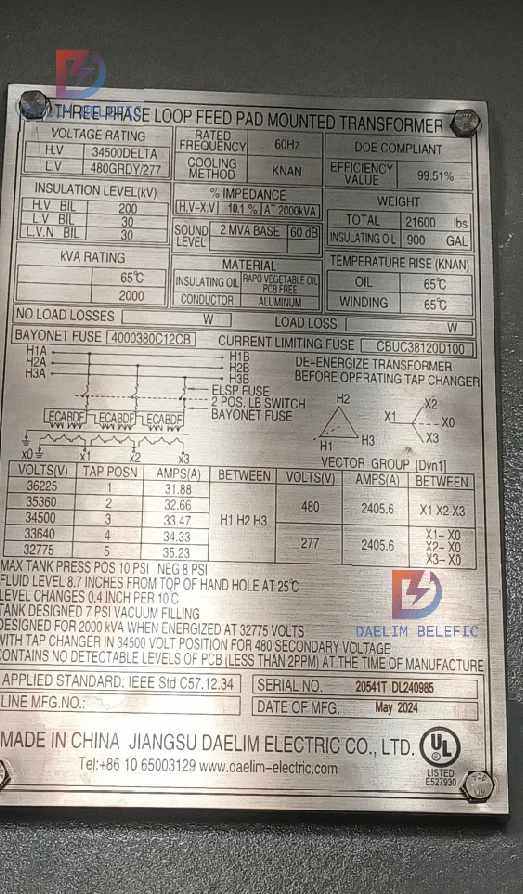
Pad mounted transformers have a number of key features in their design and functionality, an understanding of which can help in selecting the right transformer and applying it correctly. Below are some of the key features and their selection guides:
Power ratings for Pad mounted transformers typically range from 15 kVA to 5000 kVA. The selection of the right power rating should be based on the actual power demand and application scenario. For example:
In order to select the correct power rating, consult an electrical engineer or use a professional calculation tool to assess the specific needs.
A typical structural design of a Pad mounted transformer consists of an oil tank and wiring cabinet:
When selecting a pad mounted transformer, the following points should be noted:
By understanding and evaluating these features, you can more accurately select and apply a pad mounted transformer that suits your needs, ensuring the safety and efficiency of your power distribution system.
For a detailed look at the technical parameters of the pad mounted transformer, please visit this article by Daelim for more expert guidance.
Maintaining the pad mounted transformer is essential to ensure its long and reliable operation. Regular inspections and proper maintenance can prevent malfunctions and extend the life of the equipment. The following are specific maintenance and troubleshooting guidelines to help you better understand and apply them in practice.
Visual Inspection:
Cleaning:
Electrical Inspection:
Oil level and oil quality check:
Transformer overheating:
Oil leakage:
Abnormal noise:
Voltage instability:
For a detailed understanding of the types of faults and solutions for pad mounted transformers, please visit this article by Daelim for more professional guidance.
Through regular maintenance and timely handling of common problems, you can effectively prevent pad mounted transformer failures and ensure its safe and stable operation. In practice, strict adherence to maintenance guidelines and safety practices can maximise the service life of the equipment and enhance the reliability of the power distribution system.
After filling in the contact information, you can download the PDF.