
How to Choose Pad Mounted Transformer?
Table of Contents Selecting the right pad-mounted transformer requires careful consideration of several critical
ELECTRIC, WITH AN EDGE
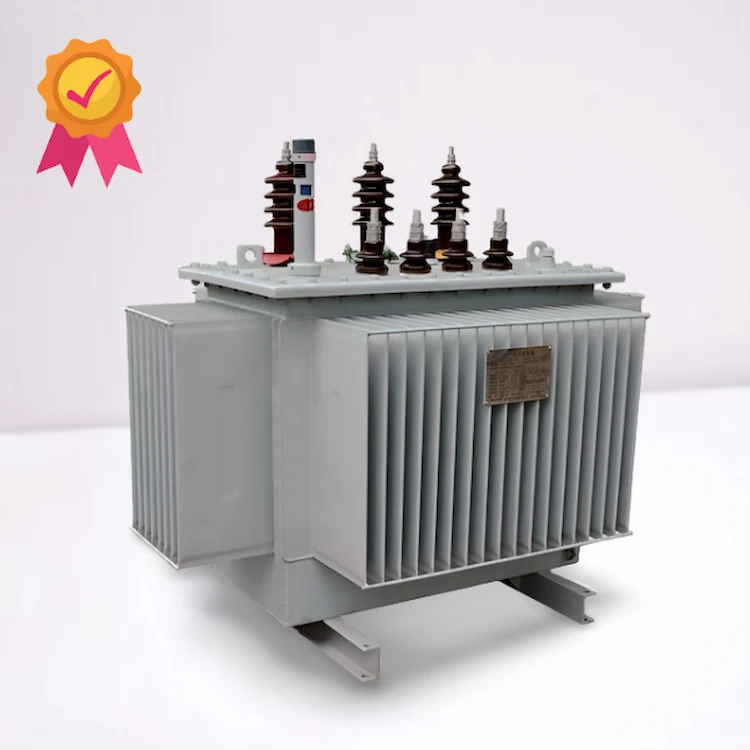

A 300 KVA transformer is a type of electrical transformer which has a rated power capacity of 300 kilowatts, with the number corresponding to the ampere-turns per volt produced in each winding. There are two primary voltage (V1, and V2) and one secondary voltage winding on this class of transformer. More than one such transformers can be interconnected with special lugs on the ends to form an H-bridge. The output voltage for each winding would then be multiples of 120 volts AC (V1 = 120 VAC, V2 = 240 VAC). There are also many other types of transformers as well, but we will focus on 300 KVA Transformer.
The primary purpose of a transformer is to change direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) electricity. The transformer’s secondary coil, which has two wires wound on it, wraps around the core which acts as the magnet in a transformer. This winding generates an induced magnetic field that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy for turning the core rotor. These generators are classified as either step-up or step-down based on their output voltage values and how they transform AC voltage levels to DC voltage levels.
Pofessional Manufacturer of Pad Mounted Transformer Substation Transformer,HV Power Transformer Single Phase Transformer IEEE/ANSI,CSA,DOE,AS/NZS,IEC and etc。standards
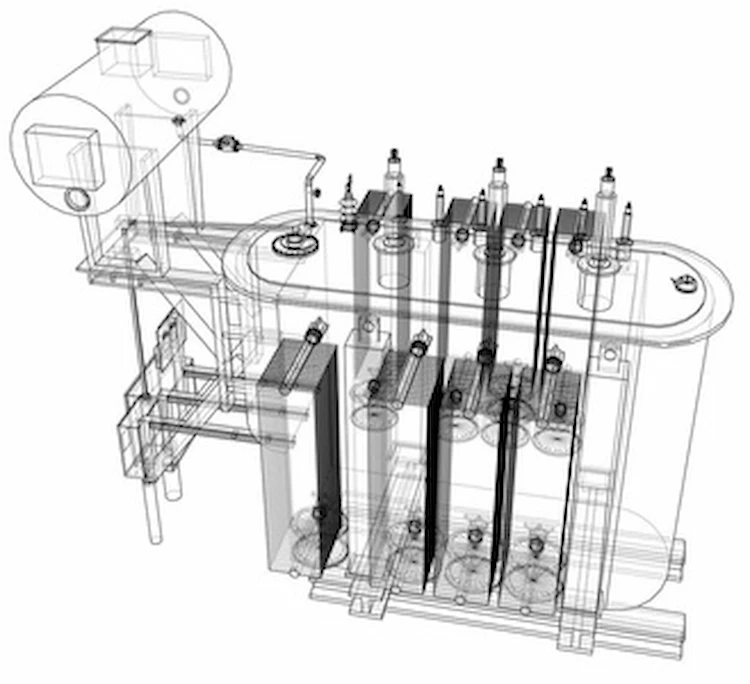
A 300KVA transformer has three coils of wire, called primary, secondary, and tertiary.
The first coil of wire is wrapped around the iron core (also called a magnetic core or laminated ferrite). This coil can be referred to as the primary winding. The second coil of wire wraps tightly around the first, and this can be referred to as the secondary winding. Finally, a third coil wraps around the previous two. All three coils are attached to the iron core and are called tertiary winding or sometimes outer coils.
As current flows through the secondary winding (the part of the transformer that deals with AC) there is an alternating magnetic field caused by the rotation of the primary winding. This alternating magnetic field forces electrons to move from side to side of their normal path in the coil. The electrons are pushed out of their normal path and travel in a circle along this path. As they move along this path, an equal number of the return, at perfect 90º angles, and thus create a complete circuit.
The primary function of a transformer is to allow for the change of voltage level with no heavily changing mechanical loads on either side (such as moving machinery). There are many types of transformers that have been developed over time due to improvements in materials, magnetism, or insulation technology.
Most modern-day power transformers are built in a modular fashion where several identical modules are connected together side-by-side. This way, the manufacturer can easily produce tens of thousands of units at a time. The result is that more and more power transformers will use such connections for their construction. In order for any transformer to work well, it must have the maximum possible current carrying ability without disturbance or weakening in voltage regulation by the conversion ratio of its windings.
Once a 300KVA transformer is connected to the main circuit, it puts out a certain amount of voltage which is equal to the voltage times the number of turns or flux of each winding on the core. Then it returns back to its original output voltage when there’s no current going through it. The values of the voltage and current that flow through the transformer are known as induced voltage and induced current.
If you’re wondering what the 300 KVA rating means, it refers to the ability of the transformer to handle up to 300,000 volts and 1,000 Amps at its terminals. This type of large transformer is often used on high-voltage transmission lines where there are hundreds or even thousands of homes served by a specific transformer station. A smaller KVA rating indicates that a transformer can only supply electricity for a small number of homes or businesses based on the voltage and amperage requirements for those facilities.
The power that is being fed into the transformer can come from a variety of sources. A home with a solar photovoltaic power system might feed the line via DC bus lines with up to 20 KW at a time. At the service panel, your utility company provides you with 30 VAC and 30 amps at which point you can use whatever voltage and amps you wish.
From your home service panel, the utility company transmits up to 15 KVAC and 50 amps (in some areas) so that it can connect to a substation and transmit over several hundred miles of 100 VK transmission lines before reaching its destination in another substation down the line.

What does an isolation transformer do? These power supplies convert input voltage from high currents (such as those coming from generators) into low currents that are usable by consumer appliances.
This tends to be used as a backup plan when there is a power outage or when you need protection against fluctuations in current.
What does it do?
An isolation transformer is a type of power supply that is used for various applications including backup and protection. It uses an input voltage from the main power source to produce a low-voltage level needed by consumer appliances, such as TVs and computers. If a power failure or fluctuation occurs at the input voltage, the isolation transformer can prevent any damages or accidents associated with it. Isolation transformers also act as a safeguard against radio frequency interference and stray currents.
300 KVA Isolation transformers are commonly used in industrial, commercial buildings, and government properties. In these areas, there are high risks of a power failure and fluctuations due to storms or human error. It is also commonly used in places where there are machines that run on alternative sources of power.
300 KVA Isolation transformers consist of a primary, or input section, and a secondary circuit or output section. The primary side includes the windings, which are comprised of insulated wire wrapped around an iron core. The 300 KVA iron core serves as the magnetic part of the transformer and magnetizes the wires to complete the transfer of energy from one line to another. They also include other parts that can be used for rectification and smoothing, such as diodes, resistors, and capacitors.
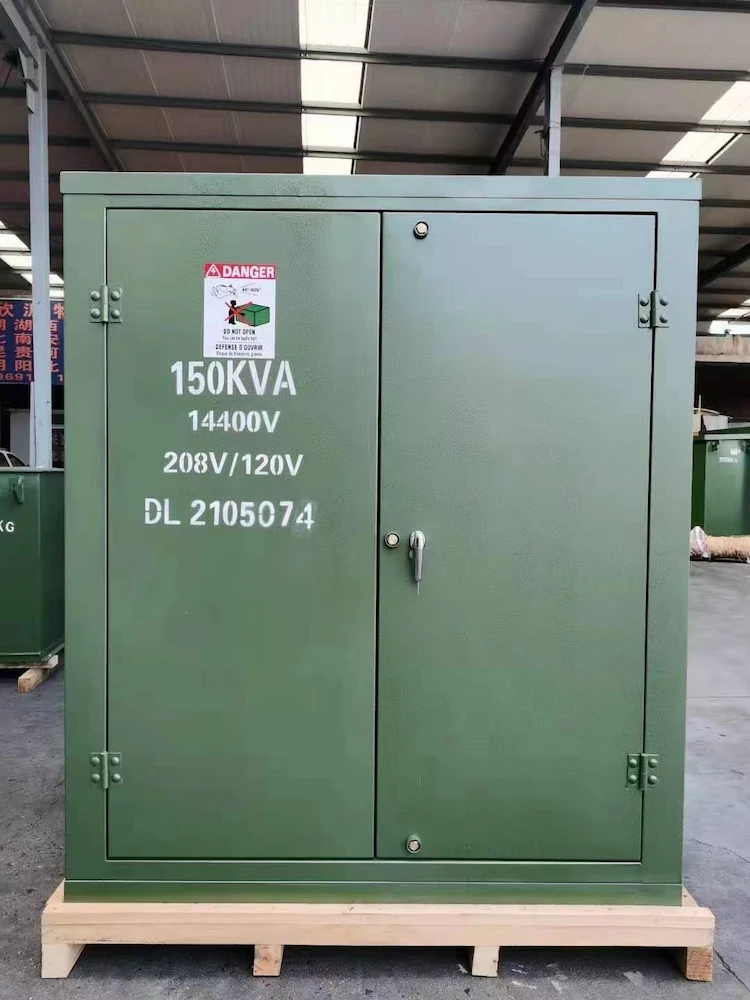

A 300 KVA Transformer is an auto-reclosing untwisted transformer. It’s also available in single-phase versions of 250 and 375 KVA. The transformer has three windings that are connected to the three phases of a 208V AC power source.
300 KVA transformers operate on a pure sine wave, so there is no need for a smoothing or filter capacitor – it produces clean power from the source. These types of transformers are used typically as standby generators, substations, and electrical substations where large amounts of power are needed to be brought at short time periods over long distances or when load requirements exceed the capabilities of other types of transformers. For both single and 3-phase transformers of the same KVA rating, it takes about 60 seconds to cycle the transformer from fully closed to fully open.
A 300 KVA Transformer converts the voltage from 208VAC to an alternate current at a variable frequency depending on load. The variable frequency (VF) is designed to provide power when the line frequency (LF) exceeds 60 cycles per second. For example, Current frequencies above 60 Hz can be used to create power during a lull inline current at 50 Hz. VF also compensates for line losses and variances in the load that reduce output voltage, such as where multiple AC loads are connected in series or parallel.
This feature of 300 KVA provides a continuous hot standby for line power that is as reliable as direct current (DC) power and significantly more efficient than battery backup. The transformers are usually installed indoors or in a dry, vented enclosure. Enclosures can be air-conditioned and have a dedicated 480VAC to 208VAC isolation transformer and electrical switchgear inside the enclosure.
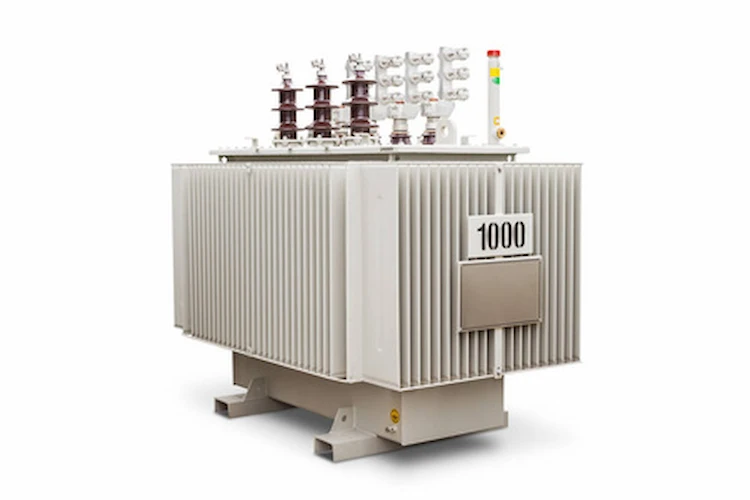

The specification of the 300 KVA transformer is based on the following assumptions: One phase three-pole (3P) line input and one phase three-pole (3P) output load line with a maximum current of 0. 75 times the line current. Single-phase systems are limited to a maximum of 400 KVA (220V).
Phase voltage rating is limited to 1500V. A double-ended single-phase system must be capable of driving two loads of equal rating. The combined line input and output ratings should not exceed the transformer rating. The transformers must be rated for continuous operation at elevated temperatures up to 105F (40C). The transformer must be compatible with the line voltage and phase voltage(s) on which it is to be used. It must also have sufficient cooling capability, including adequate ventilation, if the ambient temperature exceeds 105F (40C).
The 300 KVA transformer must be capable of short circuit, normal, and reverse polarity operation. The transformer must be able to withstand the full line voltage and phase voltage(s) during normal operation. The line input side of the transformer may be grounded but not grounded at the same time as the output side.
For two-phase systems, it should be possible to divide the load equally between two transformers connected in series, with each half-load connected to separate input and output (or ungrounded side of a single-phase transformer). Each half-load must have its own tap or taps on its ungrounded (tapped) leg(s).
The transformer must be able to meet the voltage drop and current limitations of specified over-current protection devices. The transformer must be protected by a circuit breaker (when a line switching or motor protector is specified) that has an emergency operation and automatically latches when the short circuit fault is cleared.
The line to ground and line to neutral connections of the switchgear, inverter, or motor must be made through an appropriate rated overcurrent device with no less than 500V rating; however, for 360V systems, a fused switch is normally used. The circuits may also be protected by overcurrent devices with a protective rating greater than 500V, but with built-in auxiliary breakers.
Full-Form Transformer,The Ultimate Guide
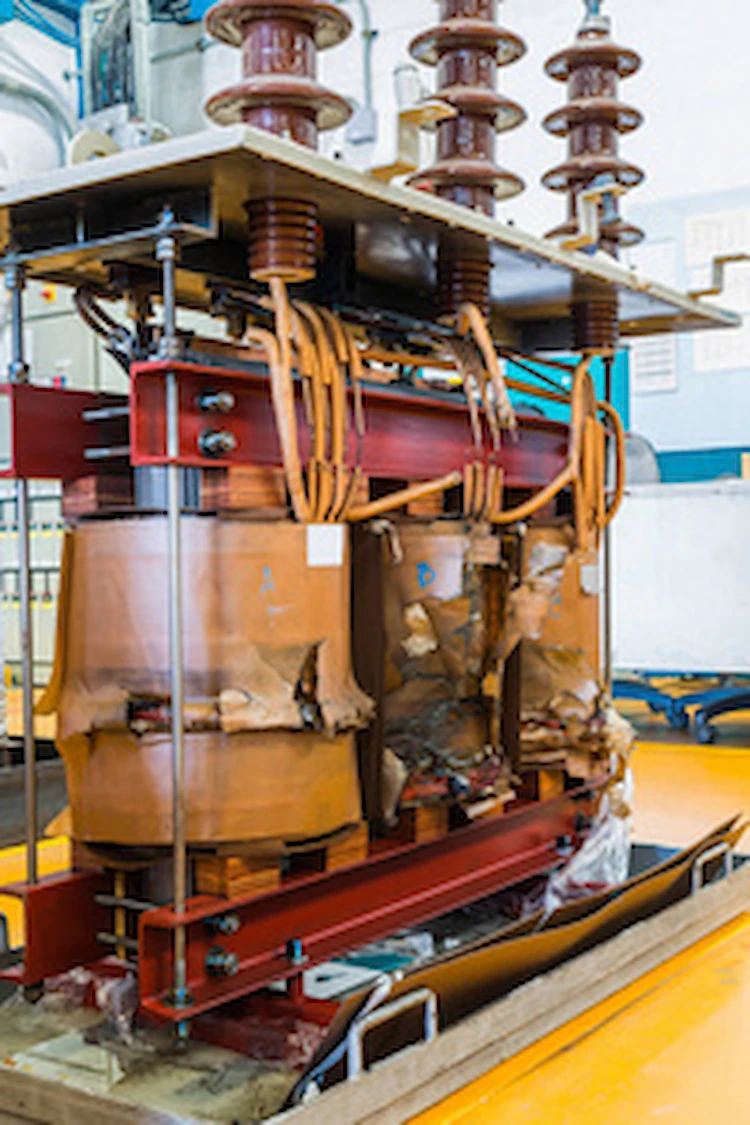
The 300 KVA transformer itself can handle up to 300,000 volts and 1,000 Amps. You would only see this kind of high power transfer if you were feeding it out of a very large inverter that was converting the DC output of your solar inverter into AC for transmission to your service panel. Examples of such devices are used by commercial solar sites that need the capability of transmitting at least 1 MW of energy using only standard commercial switching equipment from the service panel.
For residential applications, a large 300 KVA transformer is not needed. You probably should not be feeding more than about 30-50 KW at any one time depending on the number of panels you have and the voltage and amps you are transmitting. For example, a 100 KW system that has 230 VAC and 30 amps would need 35-60 KVA depending on the length of the transmission line it needs to travel over. This is not a huge amount of power and it is considered “backup power.”
If you install several solar systems, all feeding into a single transformer (and only one inverter), then 20 or 30 KW will be “theoretically” able to be transferred at one time.
The physical dimensions of a transformer play a crucial role in its installation and overall suitability for a particular application. When it comes to a 300kVA transformer, its size can vary based on factors such as the manufacturer, design, and intended usage. Typically, a 300kVA transformer is compact and designed to be mounted on a pad or installed in a substation. The dimensions may range from approximately 5 feet in height, 4 feet in width, and 3 feet in depth, making it a reasonably manageable size for different installation scenarios.
Understanding the rating of a transformer is essential for selecting the appropriate equipment for specific power requirements. In the case of a 300kVA transformer, “kVA” stands for kilovolt-ampere, which is a unit used to measure the apparent power of the transformer. The rating signifies the maximum amount of power the transformer can handle under normal operating conditions. A 300kVA transformer can handle an apparent power of 300 kilovolt-amperes, reflecting its capacity to manage significant power loads.
While there are different types of transformers available, oil-filled transformers remain a popular choice due to their efficiency and reliability. A 300 kVA oil-filled transformer typically weighs more than dry-type transformers due to the oil insulation and additional components. On average, a 300 kVA oil-filled transformer weighs around 2500 to 3000 kilograms (5500 to 6600 pounds). The weight can vary based on factors such as the specific design, insulation materials, and cooling mechanisms employed.
The cost of transformers can vary significantly depending on their power capacity, design, specifications, and market conditions. Big transformers, such as those with higher power ratings, generally come with a higher price tag. For example, a large-scale 3000kVA transformer can cost anywhere from $20,000 to $50,000 or more. However, it’s important to note that prices can fluctuate due to factors such as demand, raw material costs, and technological advancements. Obtaining detailed quotes from reputable manufacturers like Daelim Electric is crucial to determine the specific cost based on your requirements.
In the realm of transformers, size matters when it comes to power capacity and application suitability. The biggest transformers are known as ultra-high voltage (UHV) transformers, designed to handle extremely high voltage levels for long-distance power transmission. These mammoth transformers can reach power ratings of several thousand megavolt-amperes (MVA). For example, some UHV transformers have power capacities of up to 1000 MVA or even higher. These colossal transformers are crucial for efficiently transmitting electricity across vast distances, minimizing power losses during long-distance transmission.
Over time, transformers may become obsolete or reach the end of their operational lifespan. In such cases, the question arises: Is scrapping transformers worth it? The answer depends on various factors, including the condition of the transformer, its recyclability, and the value of the materials it contains. Transformers often contain valuable metals like copper and steel, which can be reclaimed through recycling. Additionally, recycling transformers promotes environmental sustainability by reducing the demand for new raw materials. However, it’s important to follow proper recycling protocols and consult local regulations to ensure compliance and safety.
When it comes to transformers, the largest size can be found in the realm of power generation and transmission. Extra-high voltage (EHV) and ultra-high voltage (UHV) transformers are typically the largest in terms of physical size and power capacity. These massive transformers are utilized in power generation plants and high-voltage substations to step up or step down voltage levels for efficient transmission and distribution. The largest transformers can reach power ratings of several thousand MVA and can weigh hundreds of tons.
Voltage transformers, also known as potential transformers (PTs) or voltage potential transformers (VPTs), are instrumental in measuring voltage levels accurately. The biggest voltage transformers are typically found in high-voltage applications such as electrical utilities and industrial power systems. These voltage transformers are designed to handle extremely high voltage levels, often exceeding several hundred kilovolts (kV) or even reaching into the megavolt (MV) range.
Determining the average price of a transformer requires considering several factors, including power capacity, voltage rating, construction type, and market conditions. Transformer prices can vary significantly based on these variables. On average, for a 300KVA transformer, the price range falls between $5,000 and $15,000. However, it’s important to note that prices may differ based on specific requirements, customization, and brand reputation. Consulting with reputable manufacturers like Daelim Electric can provide accurate pricing information tailored to your needs.
Transformers are not limited to the realm of science fiction; they have real-life counterparts used in various industries. The cost of a real-life transformer depends on the specific application, power capacity, voltage rating, and additional features required. For instance, large-scale transformers used in utility power grids can cost millions of dollars. However, smaller transformers for residential or commercial applications may range from a few hundred to a few thousand dollars. To get an accurate cost estimate, it’s best to consult with manufacturers and suppliers based on your unique requirements.
When discussing the “biggest and strongest” transformer, it’s important to clarify whether we mean physical size or power capacity. In terms of physical size, the largest transformers can be found in ultra-high voltage (UHV) transmission systems, where they are responsible for long-distance power transmission. These transformers can have massive dimensions and weigh several hundred tons. In terms of power capacity, the “strongest” transformers would be those designed for extremely high voltage levels, such as UHV transformers with ratings in the range of thousands of megavolt-amperes (MVA). These transformers enable efficient transmission of large-scale electrical power.
Transformers can vary in size depending on their intended application and power capacity. The size of a transformer is primarily influenced by factors such as voltage rating, power capacity, cooling method, and insulation requirements. While smaller transformers can be as compact as a refrigerator, larger transformers used in power generation and transmission can be massive structures with dimensions measured in meters. The largest transformers can be several stories high and weigh hundreds of tons, requiring specialized equipment and infrastructure for transportation and installation.
Transformers come in a wide range of sizes to cater to various power requirements. They can be classified into different power rating categories such as low voltage (LV), medium voltage (MV), and high voltage (HV) transformers. The sizes of transformers can vary from a few kilovolt-amperes (kVA) for residential applications to several megavolt-amperes (MVA) for large-scale industrial and utility systems. Common sizes include 50 kVA, 100 kVA, 200 kVA, 500 kVA, 1000 kVA, and beyond, each serving different power distribution needs.
In this third part of our analysis on the impact of market trends on 300KVA transformer prices, we’ve explored the average price range of transformers, the cost of real-life transformers, the largest and strongest transformers, the size variations, and the range of power capacities available. These insights provide a comprehensive understanding of transformer pricing and the diverse landscape of transformers in terms of size and capabilities. As we continue our journey through market trends, we will delve deeper into the intricate factors influencing transformer prices, equipping you with valuable insights as a professional transformer market analyst.
Download Resource

Table of Contents Selecting the right pad-mounted transformer requires careful consideration of several critical

The primary function of the pad mounted transformer is to serve as a critical distribution

A pad mounted transformer operates through electromagnetic induction, serving as a crucial distribution component that
After filling in the contact information, you can download the PDF.