
ELECTRIC, WITH AN EDGE

Transformers are electricity storage devices that convert electric current from one location to another. As a result of their resistance, transformers help to reduce power loss. Multiple types of transformers are available on the market and they have different specifications. Factors such as capacity, frequency range, cooling type, class, application, and many more classify transformers. If you look at it in terms of the cooling mechanism used, transformers can be separated into two kinds. Those are the Dry-type or Cast Resin transformers and Liquid Filled or Oil Filled Transformer. Oil distribution transformers are essential components for delivering energy to households. It can come in different types depending on the requirement of the application. This article will focus solely on Oil Immersed Transformer.
For information about other types of transformers and electrical equipment, please visit Daelim. Being in the industry for over 15 years, Daelim is considered one of the leading and trusted manufacturers of high-quality transformers.
Pofessional Manufacturer of Pad Mounted Transformer Substation Transformer,HV Power Transformer Single Phase Transformer IEEE/ANSI,CSA,DOE,AS/NZS,IEC and etc。standards

Distribution transformers are the end-converter of currents before they reach the households. These machines are responsible for “stepping down” high voltage current to lower usable ratings. There are a variety of cooling design transformers, and one of them is oil-cooling. In which, oil distribution transformers are among the types which use oil for cooling.
The oil-filled transformer is a voltage transformation device that uses an oil cooling technique to minimize transformer temperature. It is placed in a welded steel oil tank filled with insulating oil. When an oil-filled transformer is in operation, the coil’s heat and iron core are converted first to insulating oil. Then it is converted to the cooling medium. It may also be split into two types based on capacity: immersed natural cooling transformers and forced air cooling transformers.
Standard ratings of Oil Immersed Transformer are below 200 kVA. However, exceptions are to be made, especially in situations where higher ratings are needed.
An Oil Immersed Transformer involves the oil cooling method to reduce its temperature. Its body is connected to the welded steel oil tank, which is full of insulation oil.
These transformers work because the heat of the coil and iron core is transferred into the insulation oil. After that, it is then converted into a cooling medium. Capacity sizes allow it to be divided into immersed forced air cooling and immersed natural cooling transformers, respectively.
An oil-filled transformer utilizes dielectric oil to insulate and cool the transformer windings. It is filled with highly refined transformer oil used to isolate the transformer’s mechanical working components. Because of the effectiveness of dielectric transformer oil in cooling the transformer winding, low-temperature insulation materials may be employed.
Insulation materials commonly used include cellulose-based goods, with relative temperature indices ranging from 80 °C to 105 °C. Depending on their size and purpose, oil-filled transformers are most frequently classed as power or distribution transformers.
Gas detector relay is installed in some oil-filled transformers with a conservator or Buchholz relay. These safety devices detect gas accumulation within the transformer due to corona discharge, overheating, or an internal electric arc. These devices can trip a protective circuit breaker. It removes power from the Oil Immersed Transformer in the event of a gradual accumulation of gas or a sudden pressure rise.
Transformers without conservators are typically outfitted with sudden pressure relays, which provide the same purpose as the Buchholz relay.
The primary function of oil distribution transformers is to make high voltage electricity usable for end-users. Thus, most of these transformers are typical step-down types since they have to lessen voltages on desirable levels. Here are the main functions of an oil distribution transformer:
Aside from the conventional twin coil disc winding, Oil Immersed Transformers also have various windings developed. Optimum windings are chosen for specific purposes for maximum efficiency.
For low-voltage and large current transformers, they use cylindrical layer windings. Series capacitance disc winding is preferable for high voltage and surge protection. Finally, multi-parallel cylindrical tap windings are used for wide-range tap transformers.
The highest quality Hi-B oriented silicon steel plates make up an Oil Immersed Transformer’s core. It has enhanced components like magnetostriction, core loss, exciting current, and many others.
The core is uniformly tightened using tempered plastic bands, and it also employs core election equipment. This allows the transformer to be a little more compact, easier to move, and produce less noise.
An additional important feature to note in Oil Immersed Transformers is the oil conservator. It monitors the oil levels and provides space for thermal oil expansion. This process greatly aids in the operation of a transformer.
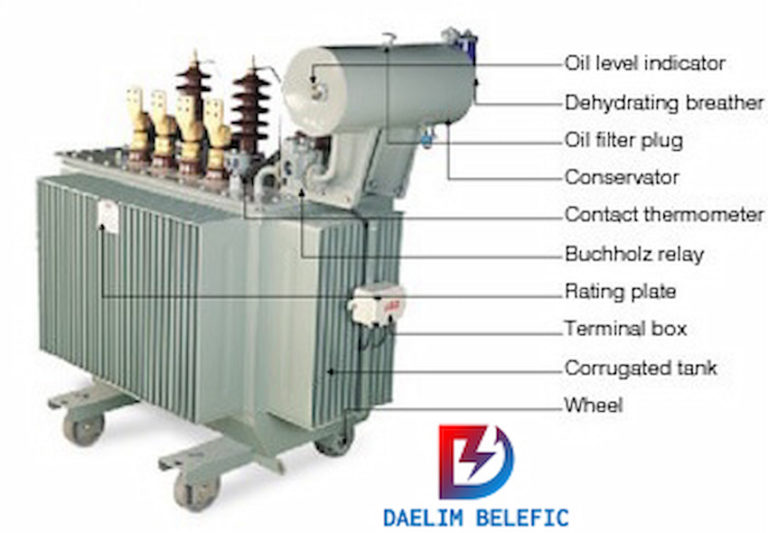
It is possible to produce a comprehensive selection of oil-filled transformers intended to satisfy specifications and provide dependable service. Oil-filled transformers provide dependability in harsh environments, with power ratings of up to 10 MVA. At the same time, the voltage ratings are up to 36 kV. It also comprises distribution, medium, power, and generator transformers with 40 MVA to 132 kV.
There is a broad range of ratings and capacities available for Oil Immersed Transformer. These transformers can have a rating of 50 kVA all the way to over 2500 kVA (that is 2.5 MVA). The On-load Loss ranges from 170w to over 3300w, and the load loss ranges from 870w to 23000w.
Oil distribution transformers come in different ratings, which cover different thresholds of power loads. Below are the standard ratings of oil distribution transformers depending on phase-type:
The three-phase oil distribution transformer uses a concept of delta or wye connection in converting voltages.
Do note that standard rating may vary depending on your location or specification of the manufacturer. It is always imperative to collaborate with your local professionals who know local standards.
Oil-filled power transformers can handle larger loads, and they are used in applications requiring higher voltages. Also, these Oil Immersed Transformer is utilized for outdoor installations since oil spills represent a fire threat. But they are also more environmentally sustainable. As a result, they are often used in separate rooms or outside.
If the installation region’s environment is relatively hot and humid, an oil-filled transformer is also a suitable option.
The common applications of oil distribution transformers are on a service drop point. Service drop points are locations wherein high power voltages undergo “transforming” before entering consumer lines. These transformers are also used for remote areas outside the city center. Farmhouses, remote settlements, and pumping stations all benefit from the use of oil distribution transformers. Further applications can also include railway supply for AC. In these scenarios, professionals typically use a single-phase version.
The amount of consumers that can benefit from an oil distribution transformer varies. For urban areas, multiple households can benefit from a single unit. Meanwhile, a single Oil Filled Transformer per household may be necessary for rural or remote areas depending on the voltage requirement.
Since Oil Immersed Transformer can work more efficiently and bear a bigger load, it is mainly used for large-scale operations. Dry-type transformers will often be seen in residential and even commercial settings because it is safer. Factories with huge spaces use the Oil Filled Transformer to handle the amount of work and power they need.
On the other hand, an industrial complex typically has several distribution points to power multiple sections of its operation. They may also have different ratings depending upon the need of the machinery they operate. While a large building may have its own distribution transformer tapped directly from the main distribution line.
Lastly, Oil Immersed Transformer is also necessary for renewable energy sources like windmills or dams. In these cases, a step-up version allows long-distance transfer to faraway substations.
The thing about Oil Immersed Transformers is that it is environment friendly but not necessarily hazard-free. Since there is always a chance of oil spilling or leaking, it poses a fire hazard. It is essential to place these kinds of transformers away from residential or commercial areas with a lot of foot traffic. It should also be placed far off from buildings to prevent fire from spreading in the event of an accident.
Oil-filled transformers are economical to operate and maintain, but they are combustible and highly dangerous. Because it is immersed in the oil tank, there is a risk of fire if the oil sprays or leaks. It is necessary to inspect for leaks and other probable sources of fire daily.
The insulating and cooling qualities of your transformer will be affected by the quality of your transformer oil. Oil quality will deteriorate little under typical operating circumstances due to oxidization and pollution. It will then increase the possibility of problems and costly repairs. You may minimize expensive downtime and repairs by implementing a thorough preventative maintenance program.
Testing the oil in your transformer should be part of your annual preventative maintenance routine. Testing the oil will assist in determining when remedial action is necessary. Initial testing will create a baseline for comparison, and yearly testing will show any changes in your transformer’s internals.
A transformer oil test called the breakdown voltage (BDV) test shall be conducted. It is used to assess the quality of transformer oil. The oil will be refined or purified again, depending on the results of the BDV test. The breakdown voltage test is critical for the transformer or transformer oil.
It aids in the detection of a problem in transformer oil. By measuring the breakdown voltage value, we may determine whether or not the oil is suitable for the transformer. When the transformer fails to work correctly, you can use the BDV test to check the transformer oil. This test will be performed again in 6 months.
The thing about Oil Filled Transformer is that it is environment friendly but not necessarily hazard-free. Since there is always a chance of oil spilling or leaking, it poses a fire hazard. It is essential to place these kinds of transformers away from residential or commercial areas with a lot of foot traffic. It should also be placed far off from buildings to prevent fire from spreading in the event of an accident.The parts of an Oil Immersed Transformer only need to be changed once every 10-15 years.
Regular maintenance checks are necessary to prolong the lifespan of your oil distribution transformers. Additionally, regular maintenance or check-up can help prevent unpredictable downtime. Oil distribution transformers checks can be daily, monthly, semi-annually, or annually.
For daily maintenance rounds, here are a few vital things to check.
1. Check the levels of your magnetic oil gauge or MoG. Ensure that the oil level is at the desired amount.
2. Check the silica gel. Silica gels that turn pink need replacing.
3. Be vigilant of leakages. Leakages should be dealt with accordingly as they can be flammable and damaging to the cooling system
1. Ensure that oil levels are in appropriate amounts. Excessive continents can cause leaking. Meanwhile under level amounts can cause inefficient cooling, which can result in heat damage.
2. Ensure the cleanliness of silica gel breathers for efficient cooling flow.Breathing holes should be kept clean in the silica gel breather to allow for proper breathing action all the time.
3. For filling bushing, appropriate oil levels should be observed. Ensure the oil is on the appropriate level to prevent component damage or cooling inefficiency.
The main point of semi-annual checks is for gauging the flashpoint, sludge, acid level, dielectric strength, and water ratio. Other checks include IFD and DDA gauging.
Finally, for the annual check, component maintenance and clean-ups are the focus.
1. Cleanse the bushing of your transformers using soft cotton only.
2. AAnnual examination of the OLTC is also vital. Ensuring the moisture content and dielectric levels are at the right amount allows for an efficient operation.(Oil conditions should be observed and sampled for moisture content (PPM) and dielectric strength (BDV). Low BDV and high PPM value mean oil replacement is needed. )
3. Tighten all the wirings of your control and relay lines at least once a year. Additionally, check that the illumination heaters have the standard spacing and performance. You should also clean marshaling boxes at least once a year.(Marshalling boxes should be cleaned. Illumination heaters should also be checked alongside the space functions. )
4. Use the prescribed cleaning agent for cleaning your control switches, alarms, and relays along with their circuits.
5. Check if your Press Release Device and Buchholz are functioning.
6. Check the oil level on indicators and ensure they contain the necessary amount to function.
7. Measure the resistive rating of your earth connection and riser. Do this by gauging the earth resistance meter clamp.
Depending on your transformer brand additional check might be prescribed. Consult your manufacturer for possible additional maintenance checks.
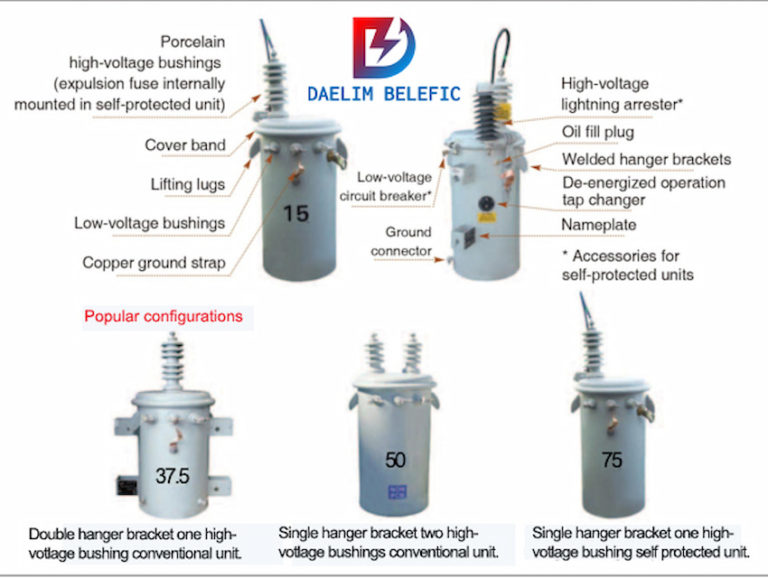

The main types of oil Oil Filled Transformers include mineral oil-based, silicone-based, and bio-based. Among these three, mineral oil-based is the most favored because of its performance and cost-efficiency.
If mishandled and under-maintained, Oil Distribution Transformer can be harmful. First, their oil constituents have polychlorinated biphenyl or PCB. Long-term exposure to this substance is toxic to humans.
Second, transformers induce electromagnetic frequencies. Low frequencies are the least of your worries since, theoretically, it exists in every electronic device. However, high-level frequencies commonly observed in substations can be harmful in the long run as it is associated with childhood leukemia.
Lastly, fire hazards for leaking transformers can be risky. These considerations emphasize the need for responsible maintenance.
These hazards can be alarming but are highly unlikely as long as proper maintenance, preventive measures, and standards are observed.
The cooling medium in this transformer is air. Vacuum pressure impregnation in polyester or silicone varnish is used to make it. For harsher environmental conditions, some of them are also manufactured using VPI epoxy and cast resin. Because they are limited in terms of cooling, the maximum voltage is limited to 35kV.
Dry-type transformers are also high fire-resistive, may be put in the load center to decrease voltage and power loss. On the other hand, dry-type transformers are costly, extensive, moisture-proof, and dust-proof and produce a lot of noise.
Oil-type transformer employs transformer oil as a cooling and insulating medium. The body of an oil-filled transformer is to be placed in a fuel tank filled with transformer oil. Oil-filled transformers are inexpensive to operate and maintain, but they are explosive and dangerous.
There are many differences between Oil Immersed Transformers and Dry-type transformers. Oil Immersed Transformers require more maintenance precautions compared to Dry-type transformers. The oil needs to be sampled often to check for possible contamination. At the same time, Dry-type transformers are highly resistant to contaminants.
Most Oil Immersed transformers generally last longer than Dry-type transformers. This is due to the higher operating loss in Dry-type transformers. It is also due to the higher standard energy efficiency in Oil Immersed Transformers.
Oil Immersed Transformers tend to have a more accessible coil and core reclamation compared to Dry-type transformers. These Oil Filled Transformers produce less waste and require fewer parts replacement. They also make less noise compared to Dry-type.
Compared to Oil Immersed Transformers, Dry-type transformers are bigger units. They are also limited in voltage and size, so they are prone to overheating when overloaded. This results in higher electrical losses, which make it more expensive to maintain long-term. Oil Immersed Transformers have a smaller environmental footprint, saves space better, and are more efficient.
Dry-type transformers are used for smaller scaled functions compared to the Oil Immersed transformers. Heavier loads and higher volt capability jobs are more suited for Oil Immersed transformers.
The most significant consideration on the type of transformer to use will depend on the area or location it will be placed. Dry-type transformers are a better choice for areas inside or in the vicinity of buildings or residential zones. This is because Dry-type transformers are safer around people. They are less combustible and less of a fire hazard.
Oil Immersed Transformers are more suited for outdoor placement and distant commercial and residential areas. This is because of the possibility of oil-related accidents and spills, which pose a fire hazard.
An excellent way to differentiate these two is Dry-type transformers are environmentally safer, but Oil Immersed Transformers are more environment-friendly.
Transformer oil, also known as insulating oil, is a kind of oil with good electrical insulating characteristics and temperature stability. It is used in oil-filled electrical power transformers to insulate, prevent arcing and corona discharge, and dissipate transformer heat.
Transformer oil is a mineral oil widely used in transformers because of its chemical characteristics and dielectric strength. This oil works as an insulator and a cooling agent in your transformer.
Transformer oil is also used to protect the transformer’s core and windings, wholly immersed in the oil. Another essential characteristic of the insulating oil is its capacity to keep cellulose-made paper insulation from oxidizing. The Oil Distribution Transformer oil acts as a barrier between the oxygen in the atmosphere and the cellulose. It prevents direct contact and reducing oxidation.
Two types of transformer oil are often used.
Naphtha oil oxidizes more easily than paraffin oil. However, the oxidation product in naphtha oil is more soluble than sludge in paraffin oil. As a result, no naphtha-based oil sludge accumulates at the transformer’s bottom. Thus, it does not hinder oil convection circulation, which means it does not interfere with the transformer cooling system.
Paraffin oil oxidizes at a slower pace than Naphtha oil. The oxidation product, which is a sludge, is insoluble and precipitates at the tank’s bottom. This muck impedes the transformer cooling system. Another issue with paraffin-based oil is that the dissolved waxes within it might cause a high pour point.
However, this is not a problem in warmer climates. Despite the drawbacks noted above, paraffin-based oil is still widely utilized in many countries due to its widespread availability.
Breakdown Voltage is abbreviated as BDV. It refers to transformer oil’s dielectric strength. The primary purposes of transformer oil are to insulate and cool a transformer. As a result, it must have high dielectric strength, thermal conductivity, and chemical stability.
It must maintain these qualities even when kept at high temperatures for lengthy periods. Typical requirements include a flashpoint of 140 °C or higher and a dielectric breakdown voltage of 28 kV.
BDV might also be an indication of the presence of pollutants. If the BDV value is more significant, it suggests that the presence of contaminants is less.
However, the breakdown voltage differs depending on the transformer oil used in oil-filled transformers. The breakdown voltage can also range between 30 and 40 kV. It is determined by the amount of moisture in the transformer oil. The breakdown voltage in transformer oil will be lower if the moisture content is high. It is a critical factor for transformer oil.
The oil capacity is entirely determined by the tank volume design. To determine the volume capacity that an oil-filled transformer can hold, compute core volume first, then winding volume. Then subtract the core volume and winding volume from the tank volume. That will be the oil volume capacity of an oil-filled tank. In most cases, a 300kVA oil-filled transformer needs 300 to 400 gallons of transformer oil.
Oil Immersed Transformer can be overloaded as long as the temperature is regulated properly. Although it may compromise the longevity of the machine and its parts when done frequently. This is why it is vital to know the ratings and capacities of the different transformers. This will allow you to choose the correct one that can meet your requirements and needs.
Transformers last between 15-40 years, depending on their purpose. The ones used in residential and commercial areas can typically last from 35 to 40 years. On the other hand, the transformers used in the industrial setting can only last from 20 to 25 years. The lifespan of transformers may also depend on proper maintenance and use.
Voltage transformation stands for the process of converting voltages. This is the primary function of transformers wherein they either step up or step down a voltage depending on purpose. Voltage transformation follows the principle of induction wherein the concept of electromagnetism is applied.
On the other hand, distribution is simply the process of delivering electricity from one place to another. Oil distribution transformers are part of the distribution system. However, they can hardly be called distributors, but a point of conversion that permits distribution. After all, electricity needs to be at certain voltages for distribution, and transformers are responsible for allowing that.
Oil-cooled transformers convert voltages to specific ranges as desired. The voltage ‘transformation’ follows the principle of induction. These machines use oil as a cooling medium as high-rating conversion can cause excessive heating.
Voltage transformers can only convert voltages and not the power itself. Volts represent the potential difference and not the power, which is Watts.
Overloading increases the rate of degradation among transformers. The built-in insulation systems are only capable of withstanding specific rates of heat. Thus, frequent overheating bruises this system which can ultimately lead to system failure.
The load should not, in any case, exceed 200% of the rated kVA of the transformer. This is to prevent the life expectancy compromise.
Oil should be checked every 6 months to figure out if it needs to be replaced. If there are chemical contaminations, then the oil should be replaced immediately.
The oil is mainly responsible for the cooling and insulating of a transformer.

The main element of transformer oil is polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) which can be toxic for humans. Chronic exposure to this oil may cause hepatotoxicity and neurotoxicity in people.
An oil-filled transformer is a type of voltage transformation technology that provides oil cooling to lower transformer temperatures. Transformer oils are meant to cool, insulate, and halt corona discharges and arcing at extremely high temperatures.
Oil-filled transformers appear to be the better overall option given these considerations, with higher energy efficiency and cheaper running costs. In any event, these transformers can’t be used under any circumstances. For high-quality oil filled transformers, choose Daelim. The company has been around for 15 years and continues to produce quality electric products.
If you are looking for a transformer that is great for outdoors, then oil transformers are definitely for you! However, if you are planning on placing it indoors or inside establishments, be aware of the fire code since one of the drawbacks of this transformer is its highly flammable oil.
Oil distribution transformers are among the most widespread electrical components because of their function. Besides, they are proportional to the number of electrical consumers in a system. Thus, getting high-quality oil distribution transformers is necessary to ensure a smooth flowing power supply.
In this regard, you can never go wrong by trusting Daelim. With over 15 years of good industry reputation, Daelim rose as a globally competent brand. Daelim is your partner for every electrical product or solution you may need.
Should you have any further questions or concerns, DAELIM would be more than happy to assist.
After filling in the contact information, you can download the PDF.