
How to Choose Pad Mounted Transformer?
Table of Contents Selecting the right pad-mounted transformer requires careful consideration of several critical
ELECTRIC, WITH AN EDGE
In the complex world of power distribution, loop feed transformers play a crucial role in maintaining the continuity and reliability of power supply. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of loop feed transformers, from their basic operational principles to more advanced concepts and applications. By tackling commonly asked questions and examining aspects like programmable computing possibilities, dead front versus live front transformers, various transformer diagrams and schematics, and specific transformer types such as the 24kV transformer and pad mount transformer, this article provides a broad understanding of the versatile utility of loop feed transformers.


Loop feed transformers are a crucial component in many electrical systems, playing a pivotal role in power distribution and voltage regulation. If you’re considering investing in a loop feed transformer, it’s important to understand the different types available and their associated costs. In this article, we will provide a detailed breakdown of loop feed transformer prices, ensuring you have all the information you need.
The ZGS 13.8kv 750KVA Low Loss Underground Step Up Down Transformers is specifically designed for loop feed pad-mounted applications. With a price tag of $9,926.00 (minimum order of 1 set), this transformer ensures efficient energy transfer and exceptional performance.
If you’re looking for a versatile option, the Loop Feed Electric Pad Mounted Transformer is worth considering. With a price range of $5,000.00 to $80,000.00 (minimum order of 1 piece), this transformer offers flexibility in terms of voltage and power capacity. Whatever your specific requirements may be, this transformer has the capacity to meet them.
For loop feed pad-mounted applications, the 150kVA 13.8kV 60Hz Pad Mounted Transformer with loop feed is an excellent choice. Priced at $5,200.00 (minimum order of 4 units), this transformer guarantees reliability and is built to withstand rigorous usage.
| Transformer Type | Cost |
|---|---|
| ZGS 13.8kv 750KVA | $9,926.00 |
| Loop Feed Electric Pad Mounted | $5,000.00 to $80,000.00 |
| 150kVA 13.8kV 60Hz Pad Mounted Transformer | $5,200.00 |
| Factory price 200kva 11kv loop feed pad mounted transformers | Not readily available |
Note: The price for this transformer is not readily available. To explore more about this transformer and its pricing, it is recommended to visit Alibaba or consult manufacturers or distributors directly.
“The cost of a loop feed transformer can vary greatly depending on its specifications and the manufacturer. It’s always a good idea to do thorough research before making a purchase.” – Anonymous
Please bear in mind that the prices mentioned above are for reference purposes only and may vary based on factors such as specific models, brands, and additional features. It is essential to check with the manufacturer or distributor for the most up-to-date pricing information.
In conclusion, understanding the cost breakdown of loop feed transformers is vital when considering an investment in electrical systems. By exploring the different types available and their associated prices, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your budget and requirements.
A loop feed transformer is a crucial component in the realm of electrical engineering. It’s typically used in power distribution networks, especially where there are multiple power sources or potential pathways for current. In a loop feed transformer, the power source is connected in a loop arrangement.
Loop feed transformers are distinguished by their operational design that permits continuous power supply even if one section of the distribution network encounters an issue. This design enhances reliability and reduces potential downtime.
Different from a radial feed transformer, a loop feed transformer offers more redundancy, which can be essential in critical power supply systems where interruptions cannot be tolerated. The two transformer types are similar in function but diverge in configuration and application, making them suitable for varying requirements.
Loop feed transformers can be found in various settings such as industrial complexes, commercial buildings, and residential areas, owing to their versatile functionality. The choice between loop and radial feed largely depends on the specific power needs, cost implications, and the desired level of reliability.
An intriguing development in the world of loop feed transformers is their utilization as programmable computers. Recent studies and advancements indicate that loop feed transformers could potentially be used to perform computational tasks.
In this context, the concept is still in its infancy but holds significant promise. Just as traditional computers utilize a series of ones and zeros to represent information, a transformer-based computational model could use variances in electrical currents or voltages to represent the same data.
Utilizing transformers as computers might significantly alter the landscape of computing, particularly in terms of energy efficiency. The idea capitalizes on the inherent characteristics of loop feed transformers to provide a new method of performing computations.
While the technology is far from mainstream adoption, the initial research presents an exciting prospect for the future of computing. This use case also underscores the versatility and potential of loop feed transformers beyond their conventional role in power distribution.

When examining the different types of transformers, you may come across terms like ‘dead front’ and ‘live front’. These terminologies mainly refer to the design and safety features of a transformer, particularly in terms of accessibility to live parts.
A dead front transformer is designed such that all energized components are not accessible when the equipment is in operation. This design considerably minimizes the risk of accidental contact with live electrical parts, enhancing safety. A dead front loop feed transformer thus combines this safety feature with the operational advantages of loop feed transformers.
In contrast, a live front transformer has components that are accessible and can potentially be live when the transformer is in operation. This design demands a higher level of caution during operation and maintenance due to the increased risk of accidental contact.
The choice between a dead front and live front transformer depends on factors such as safety requirements, operational demands, and regulatory stipulations. In many modern applications, dead front transformers are preferred due to their enhanced safety features.
Loop transformer Arxiv refers to academic and research papers related to loop feed transformers that are housed on Arxiv.org, an open-access archive for scholarly articles. These articles provide valuable insights into the function, design, and advances in loop feed transformer technology.
This research provides a wealth of knowledge, offering deeper insights into the nuances of loop feed transformer operation and design. These papers cover a wide array of topics, ranging from the basic principles of operation to cutting-edge advancements and potential future developments.
Whether you are an engineer looking to gain a better understanding of loop feed transformers, a researcher exploring the latest developments, or a decision-maker attempting to make informed choices about power distribution systems, the resources available on Arxiv can be an invaluable tool.
The term ‘service transformer’ is often used to describe transformers that supply power to end users from the main distribution grid. In a loop feed configuration, a service transformer would be one of the components of the distribution network that provides power to individual consumers.
Service transformers play a crucial role in power distribution, stepping down the high voltage from the distribution lines to lower voltage levels suitable for use in homes, businesses, and other facilities. In the loop feed system, service transformers are connected in such a way that power can be supplied from multiple directions, adding redundancy and improving reliability.
While service transformers are common in both loop feed and radial feed systems, their connection and configuration can vary significantly. Understanding the role of service transformers and their function in the overall distribution system can greatly aid in system planning and design.
A 24 kV transformer refers to a transformer that is designed to handle voltages up to 24 kilovolts. This voltage rating is common in distribution systems, where transformers are used to step down voltages from high levels on transmission lines to more manageable levels for distribution.
In a loop feed configuration, a 24 kV transformer would be part of the overall system, providing power to various parts of the distribution network. The transformer’s rating would dictate the maximum voltage that it can safely handle.
The choice of transformer voltage rating is typically determined by the power requirements of the distribution system. It must align with the voltages present on the distribution lines to ensure effective and safe power transmission.
A loop feed transformer diagram provides a visual representation of the configuration of a loop feed system. The diagram usually includes the transformer, the distribution lines, and the loads (such as households or businesses) that the transformer supplies power to.
Understanding a loop feed transformer diagram can greatly aid in comprehending how these systems function. It shows how power is distributed in a loop, allowing for redundancy and greater reliability.
In addition, these diagrams can be instrumental in planning and designing power distribution systems. They provide a visual tool to help engineers and designers visualize how the system will function and identify potential problems or improvements.
A loop feed transformer one-line diagram is a simplified representation of a loop feed system. This diagram condenses the system into a single line, showing the flow of power from the source, through the transformer, and to the loads.
While not as detailed as a full schematic, a one-line diagram can provide a quick, easy-to-understand overview of the system. This makes it a useful tool for anyone trying to understand the basics of loop feed transformers and their operation.
One-line diagrams are often used in planning and designing power distribution systems. They allow engineers and designers to easily see the major components and how they are interconnected.
A loop feed transformer schematic provides a more detailed diagram of a loop feed system. It generally includes not just the transformer and the loads, but also other components such as circuit breakers, protective devices, and conductors.
A schematic diagram provides a comprehensive view of the system, detailing the various components and how they connect. This can be crucial in understanding the finer points of how the system operates, as well as in diagnosing issues or planning enhancements.
Understanding a loop feed transformer schematic requires a degree of knowledge about electrical systems and symbols. However, for those with the requisite knowledge, a schematic can provide a wealth of information about the system’s operation and design.
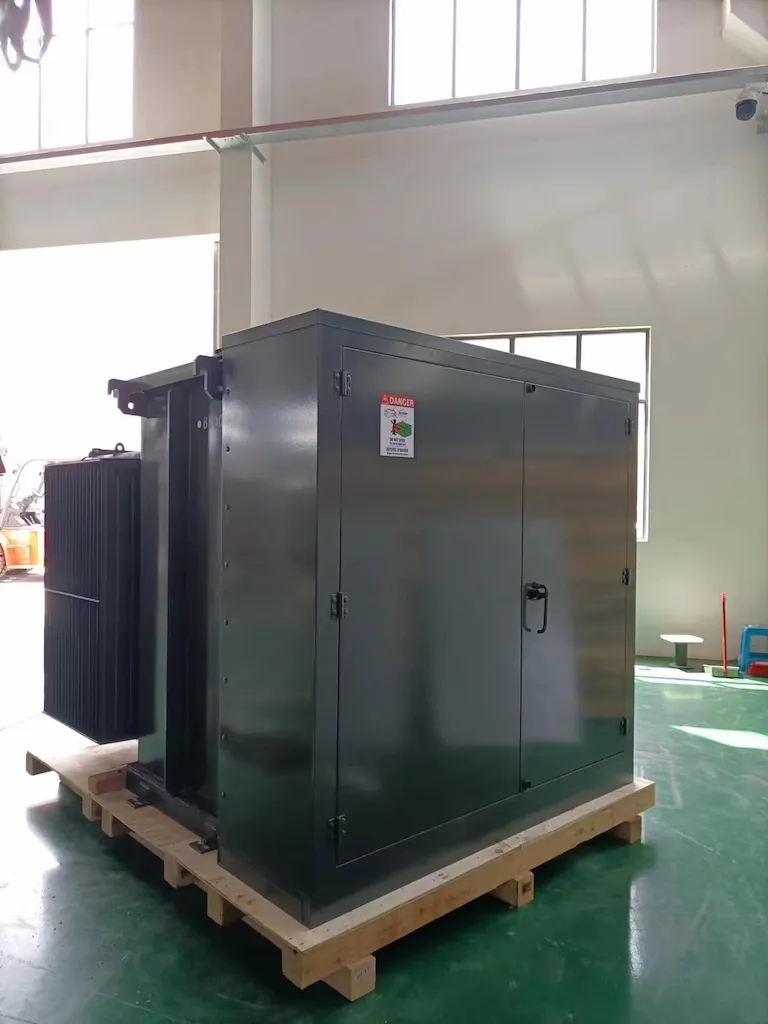
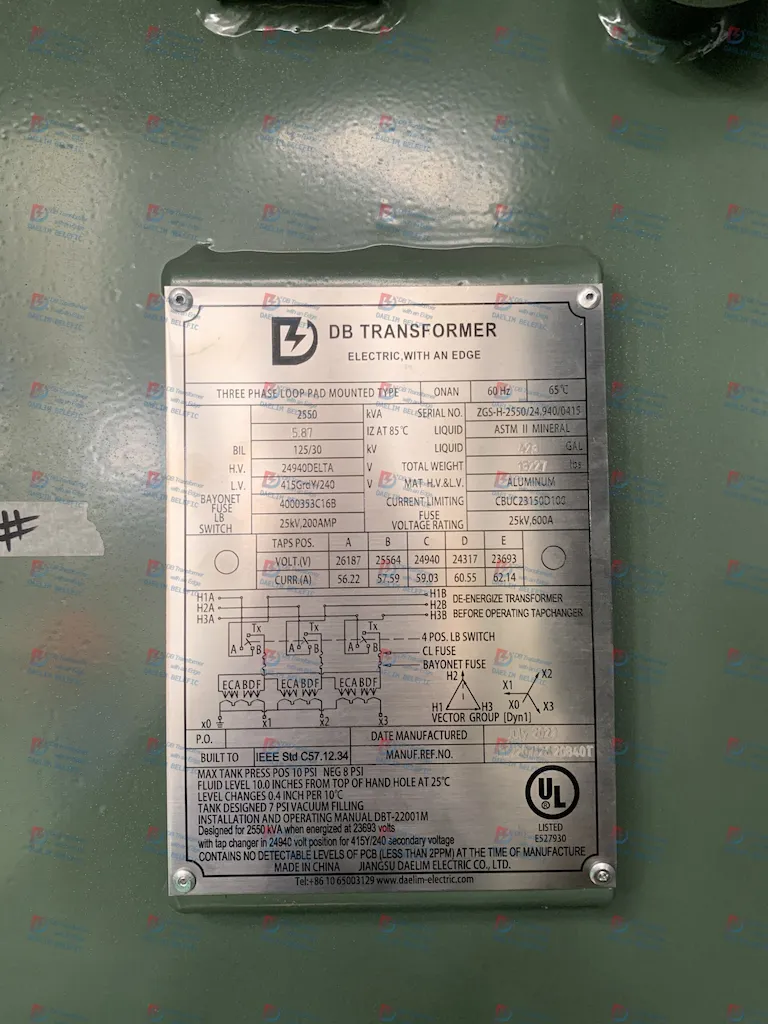
A loop feed pad mount transformer is a type of transformer that is mounted on a concrete pad and used in a loop feed system. These transformers are often used in urban areas where overhead lines are not
practical, and are designed to be robust and low-profile.
Pad mount transformers have the advantage of being relatively compact and unobtrusive, making them a good choice for areas where aesthetics or space is a concern. The loop feed design provides redundancy, which can be particularly useful in areas with high power demands or reliability requirements.
Understanding the function and benefits of a loop feed pad mount transformer can aid in making informed decisions about power distribution system design and equipment selection.
Download Resource

Table of Contents Selecting the right pad-mounted transformer requires careful consideration of several critical

The primary function of the pad mounted transformer is to serve as a critical distribution

A pad mounted transformer operates through electromagnetic induction, serving as a crucial distribution component that
After filling in the contact information, you can download the PDF.