
How to Choose Pad Mounted Transformer?
Table of Contents Selecting the right pad-mounted transformer requires careful consideration of several critical factors, as these ground-mounted distribution transformers play a vital role
ELECTRIC, WITH AN EDGE

Hi, this is Jens. I am an engineer with ten years of experience in transformer design. I have worked in Daelim, a manufacturer with more than 16 years of experience in the production and design of distribution transformers, for 7 years. In this article, I will introduce to you seven ways to reduce the Losses in distribution transformers.
If you think this article is beneficial to you, please share it with more people.
If you need to purchase a distribution transformer, please contact Daelim.
Daelim has a number of transformer design patents, and their products have been successfully applied in Canada, the United States, Russia, Germany, and other countries.
The basic principles of correct and reasonable selection of the capacity of distribution transformers:
The power Losses of the distribution transformer itself is minimal;
The distribution transformer has a higher utilization rate;
The capacity of the distribution transformer is adapted to the low-voltage power supply range.
Mainly consider the following points:

At present, more distribution transformers use products of the S9 series and above.
The no-load Losses of the S9 series is 8% lower than that of the S7 series, and the load Losses is reduced by 24% on average.
The no-load Losses of the S11 series is about 20% lower than that of the S9 series.
In addition, amorphous alloy iron core transformers have the effect of reducing Losses and energy saving.
The no-load Losses of amorphous alloy iron core transformers is reduced by 70% to 80% on average compared with S9 series products.
Its load Losses is equal to that of S9 series transformers.
It is the development of distribution transformers. direction.
In the distribution network, the day and night load changes greatly, and the late-night distribution transformer is basically in a light-load or no-load state.
In order to effectively compensate the reactive power of the transformer itself and avoid overcompensation at light load or no-load, resulting in reactive power reverse transmission.
Follow-up compensation is generally carried out for distribution transformers with a capacity below 100kVA at about 5% of the capacity.
For distribution transformers with a capacity above 100kVA, 7% to 10% of the capacity is used, and automatic switching is used.
In the distribution network, the day and night load changes greatly, and the late-night distribution transformer is basically in a light-load or no-load state.
In order to effectively compensate the reactive power of the transformer itself and avoid overcompensation at light load or no-load, resulting in reactive power reverse transmission.
Follow-up compensation is generally carried out for distribution transformers with a capacity below 100kVA at about 5% of the capacity.
For distribution transformers with a capacity above 100kVA, 7% to 10% of the capacity is used, and automatic switching is used.
However, special transformers for drainage and pumping wells are not allowed to be connected to other loads.
So that they can be stopped during non-use seasons to reduce the no-load Losses of distribution transformers.

The total Losses of the distribution transformer is: P∑=Pk+Po=(P2+Q2)/U2R+(U/U1 )∑P’o
Where: Pk—short-circuit Losses of the transformer, kW;
Po—transformer no-load Losses, kW;
P—The active power of the transformer, kW;
Q—Reactive power of transformer, kvar;
U—The operating voltage of the distribution network;
U1—the rated voltage of the distribution network;
P’o—Equivalent resistance of each transformer winding;
R—The equivalent resistance of the windings of the distribution transformer.
It can be seen from the above formula that the fixed Losses of the distribution transformer are proportional to the operating voltage of the distribution network, and the short-circuit Losses are inversely proportional to the square of the operating voltage of the distribution network.
Since the no-load Losses of the distribution transformer accounts for 80% of the total Losses, the operating voltage can be appropriately reduced during the low power consumption period or the low load period, and the operating voltage can be appropriately increased during the peak power consumption period and the heavy load period, but the end user’s The voltage offset is within the allowable range.
When the three-phase load current is unbalanced, it not only affects the voltage quality, but also increases the Losses of the distribution transformer.
Therefore, in the daily operation of the distribution transformer, it is necessary to frequently measure the three-phase load current and the neutral line current on the secondary side, and perform the work of balancing the three-phase load current.
The unbalance of the outlet current of the distribution transformer should not be greater than 10%.
Specially configured personnel to monitor the three-phase load of the distribution transformer, analyze the user’s current situation, and issue early warnings to the production department on a regular basis.
For example, two distribution transformers of the same capacity can be operated in parallel when the load is greater than the critical load. When the load is less than the critical load, they can be operated individually.
The actual power of the distribution transformer is:
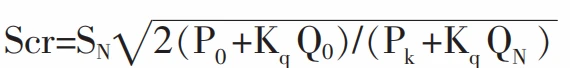
Where: SN—the rated capacity of the transformer;
Po—the no-load Losses of the transformer, kW;
Pk—short-circuit Losses of transformer, kW;
Qo—reactive power Losses when the transformer is no-load, kvar;
QN—reactive power Losses when the transformer is fully loaded, kvar;
Kq—reactive power economic equivalent (the average value is 0.1).

Table of Contents Selecting the right pad-mounted transformer requires careful consideration of several critical factors, as these ground-mounted distribution transformers play a vital role

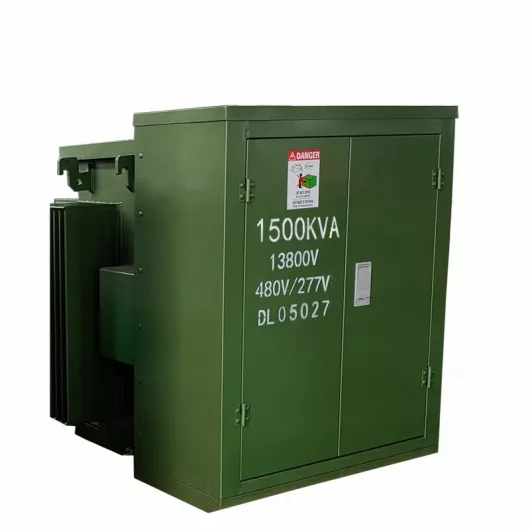
The primary function of the pad mounted transformer is to serve as a critical distribution transformer that steps down higher primary voltage from utility distribution

A pad mounted transformer operates through electromagnetic induction, serving as a crucial distribution component that converts high voltage electricity to lower, usable voltages for residential

When looking for the best pad-mounted transformer manufacturer, it’s important to find industry leaders known for reliability and innovative solutions. Pad-mounted transformers are essential in
















After filling in the contact information, you can download the PDF.